What is search engine? Learn about search engines
Search engines work by crawling data from billions of pages using web crawlers. Also known as spiders or bots, crawlers navigate the web and follow links to find new pages. These pages are then added to an index from which search engines pull results.
Understanding how search engines work is important if you are doing SEO. After all, it's hard to optimize something unless you know how it works.
Part 1: Search engine basics
Let's start by exploring what search engines are, why they exist, and how they make money.
What is a search engine?
Search engines are searchable databases of web content. They are made up of two main parts:
- Search index. A digital library of information about websites.
- Search algorithm(s). The computer program(s) responsible for matching results from the search index.
What is the purpose of search engines?
Every search engine aims to provide the best and most relevant results to users. That's partly how they gain market share.
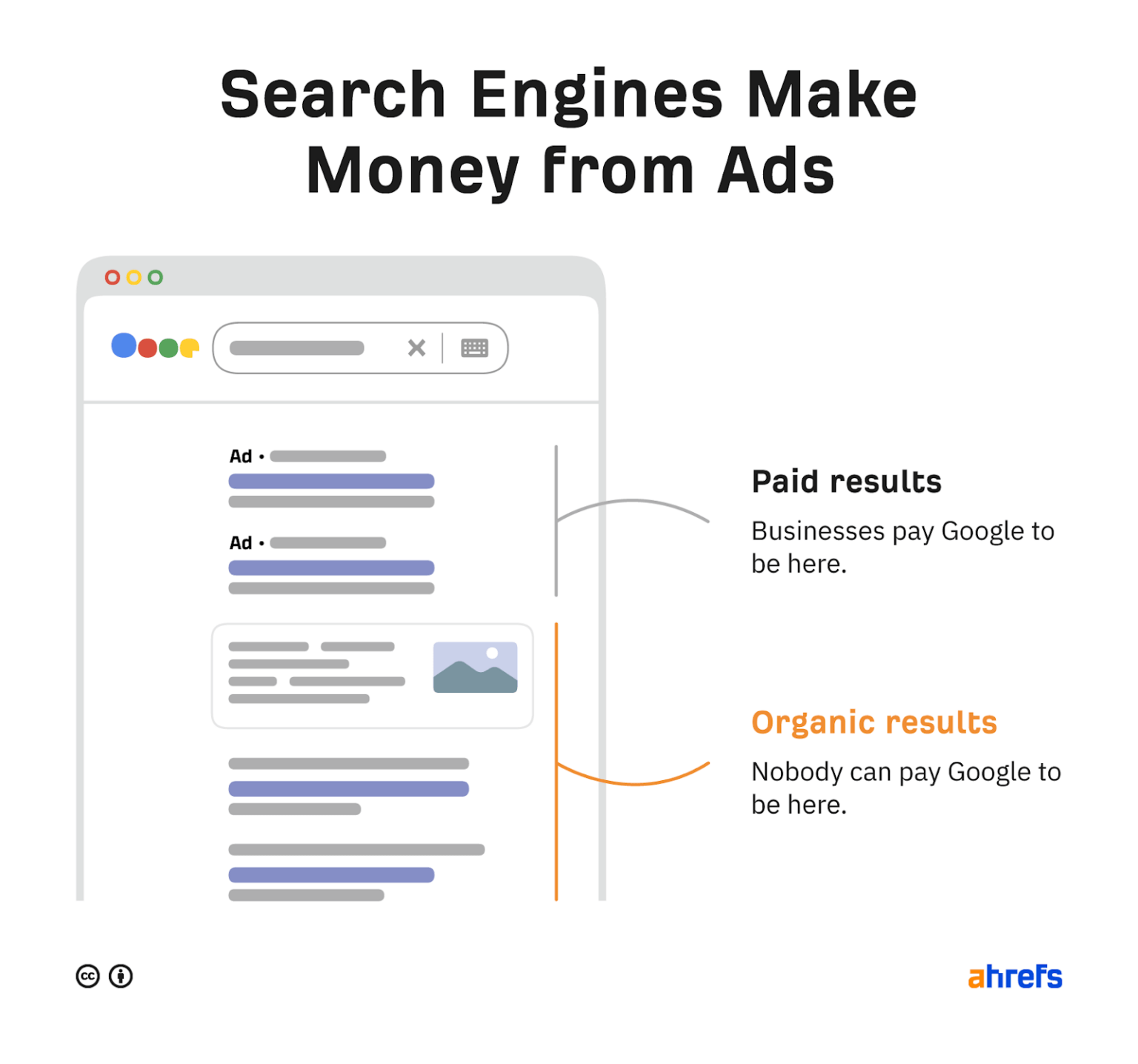
How do search engines make money?
Search engines have two types of search results:
- Organic results from search index. You can't pay to stay here.
- Paid results from advertisers. You can pay to be here.
Every time someone clicks on a paid search result, the advertiser pays the search engine. This is called pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and it's why market share matters. More users means more ad clicks and more revenue.
Part 2: How search engines build indexes
Each search engine has its own process for building search indexes. Below is a simplified version of the process Google uses.
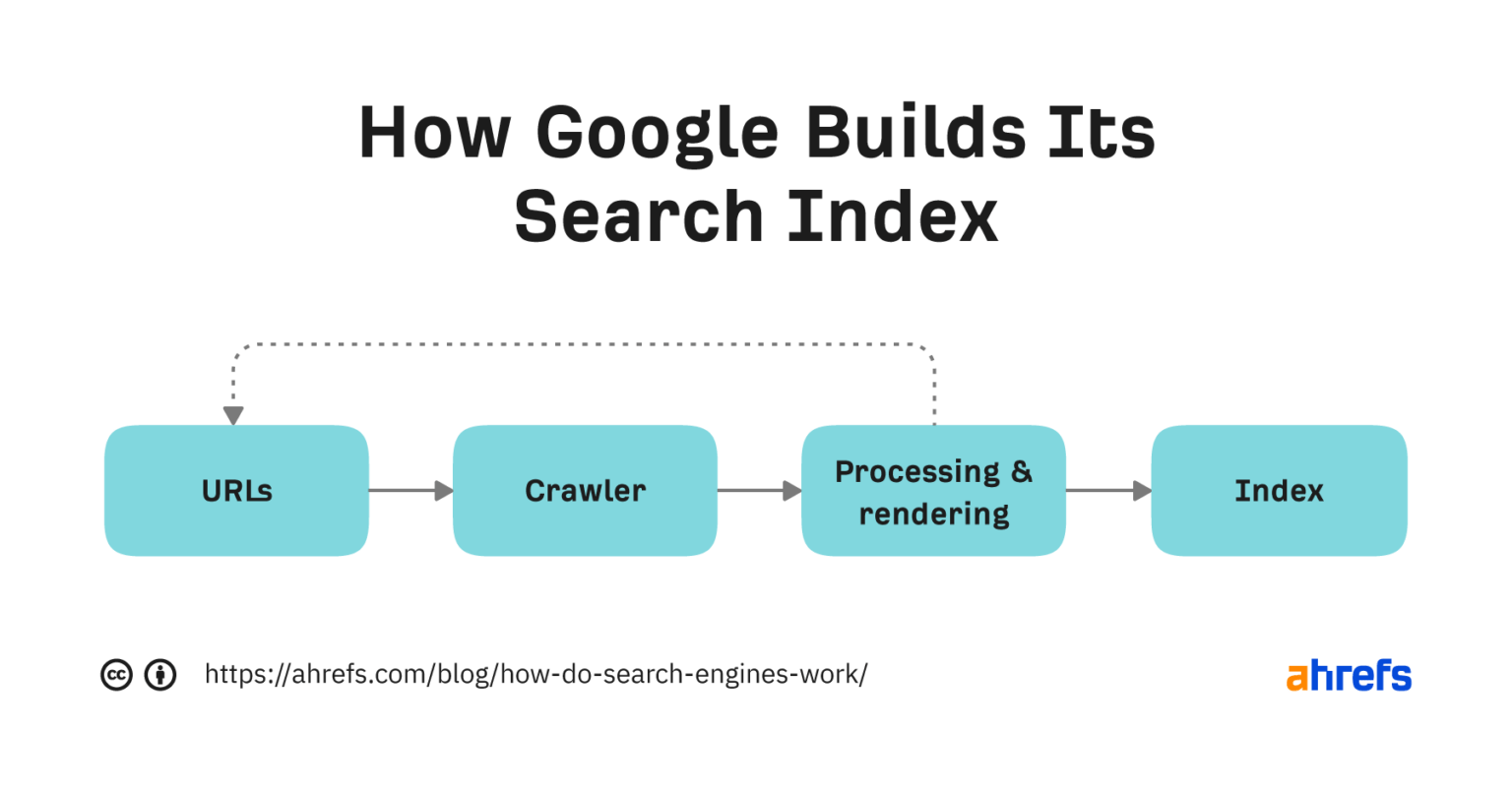
Let's break down every factor to understand better.
URL
Everything starts with a list of known URLs. Google detects these in many ways, but the 3 most common are:
- From backlinks. Google has an index of hundreds of billions of web pages. If someone links to a new page from a known page, Google can find it from there.
- From sitemap. Sitemaps tell Google which pages and files you consider important on your website.
- From submitting the URL. Google allows site owners to request crawling of individual URLs in Google Search Console.
Collect information
Crawling is where computer bots (spiders) access and download known URLs. Google's crawler is Googlebot.
Processing and rendering
Processing is where Google works to understand and extract key information from crawled pages. To do this, it must render the page, which is where it runs the page's code to understand how the page looks to the user.
No one outside of Google knows all the details about this process. But it doesn't matter. All we really need to know is that it involves extracting links and storing content for indexing.
Indexing
Indexing is where processed information from crawled pages is added to the search index.
The search index is what you search for when using a search engine. That's why being indexed in major search engines like Google and Bing is so important. Users cannot find you unless you are in the index.
Part 3: How search engines rank pages
Discovering, crawling, and indexing content is just the first part of the puzzle. Search engines also need a way to rank relevant results when users perform searches. This is the job of search algorithms.
What is a search algorithm?
Search algorithms are formulas that match and rank relevant results from an index. Google uses many factors in its algorithm.
Key Google ranking factors
No one knows every Google ranking factor because Google hasn't revealed them yet. But there are some important things as follows:
Backlinks
Backlinks are links from one page on one website to another website. They are one of Google's strongest ranking factors. This is probably why we saw a strong correlation between linking domains and organic traffic in our study of over a billion pages.
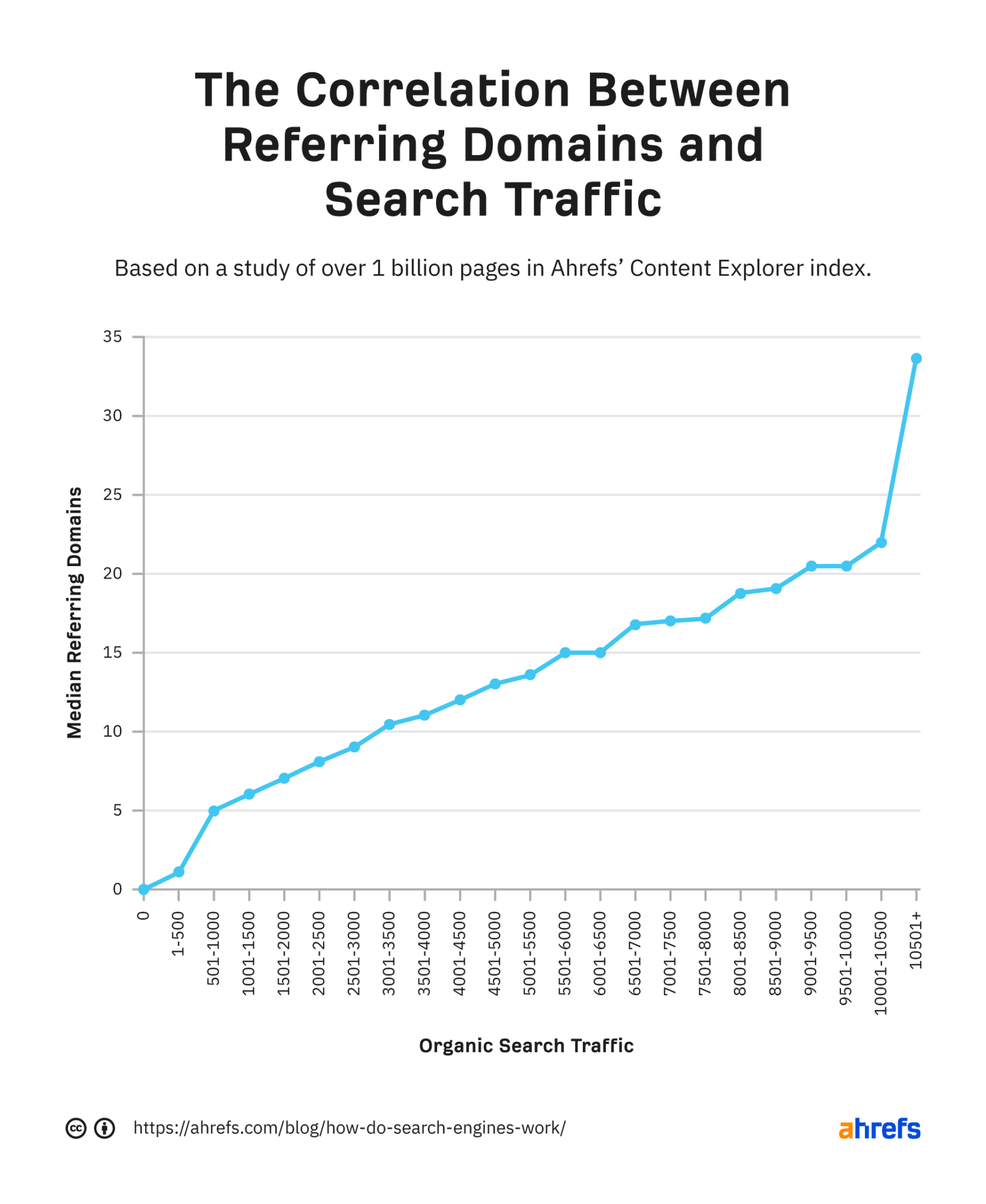
However, quantity is not everything. The same goes for quality. Pages with a few high-quality backlinks often rank higher than pages with many low-quality backlinks.
Relevance level
Relevance is the usefulness of a given result to searchers. Google has many ways to determine this. At the most basic level, it searches for pages that contain the same keywords as the search query. It also looks at engagement data to see if others find the results useful.
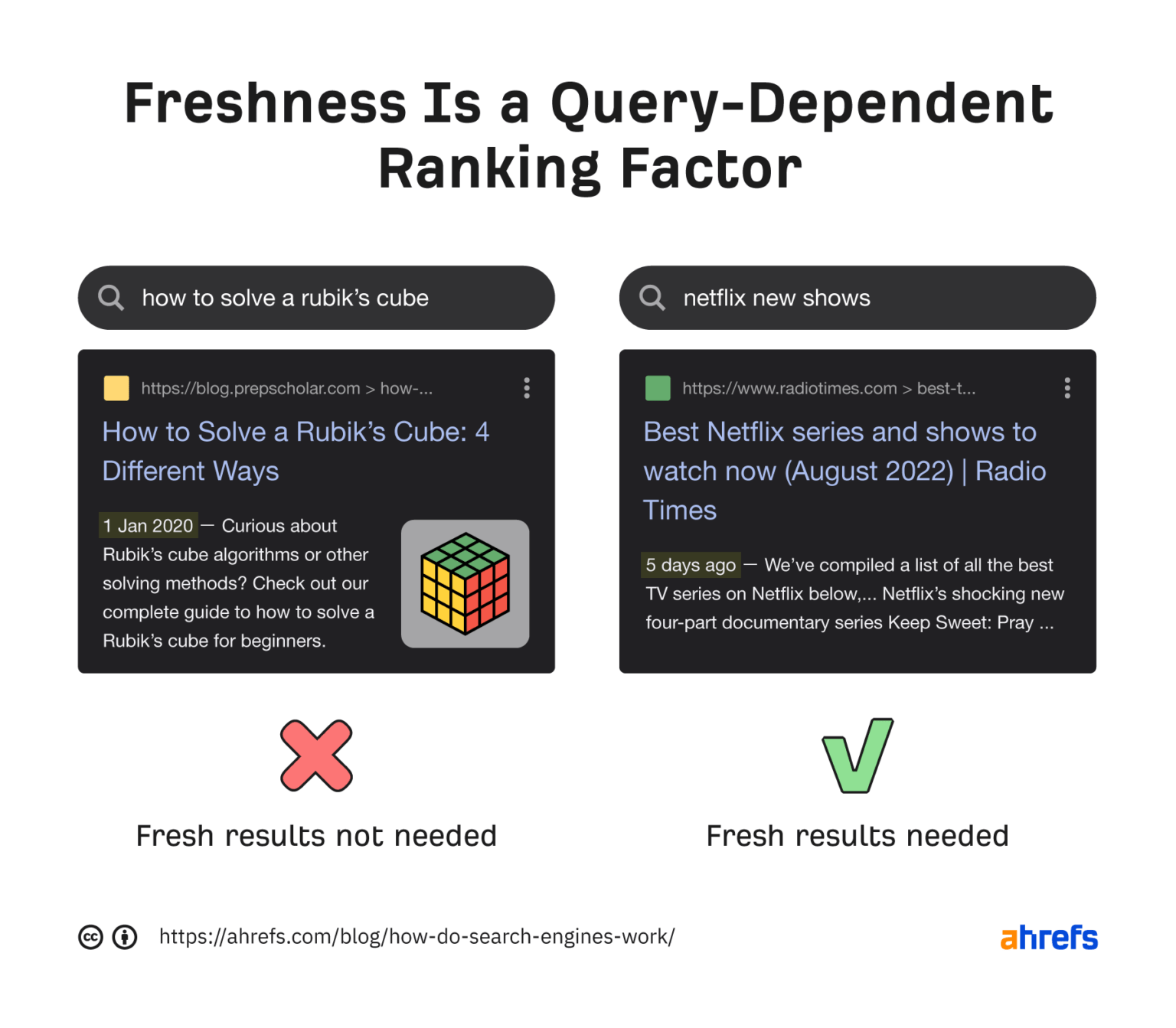
Freshness
Freshness is a query-dependent ranking factor. It is more powerful for searches that require new results. That's why you saw the top result published recently for 'new Netflix series' and not 'how to solve a Rubik's cube'.
Page speed
Page speed is a ranking factor on desktop and mobile. But that's more of a negative ranking factor than a positive one. This is because it negatively affects the slowest pages more than it positively affects the lightning-fast pages.
Mobile-friendly
Mobile-friendliness has been a ranking factor on mobile and desktop since Google switched to mobile-first indexing in 2019.
Part 4: How search engines personalize results
Google tailors search results to each user. It uses information like your location, language, and search history to do this. Let's take a closer look at these.
Location
Google uses your location to personalize results for searches with local intent. That's why all the results for 'Italian restaurant' come from or about local restaurants. Google knows you can't fly halfway around the world for lunch.
Language
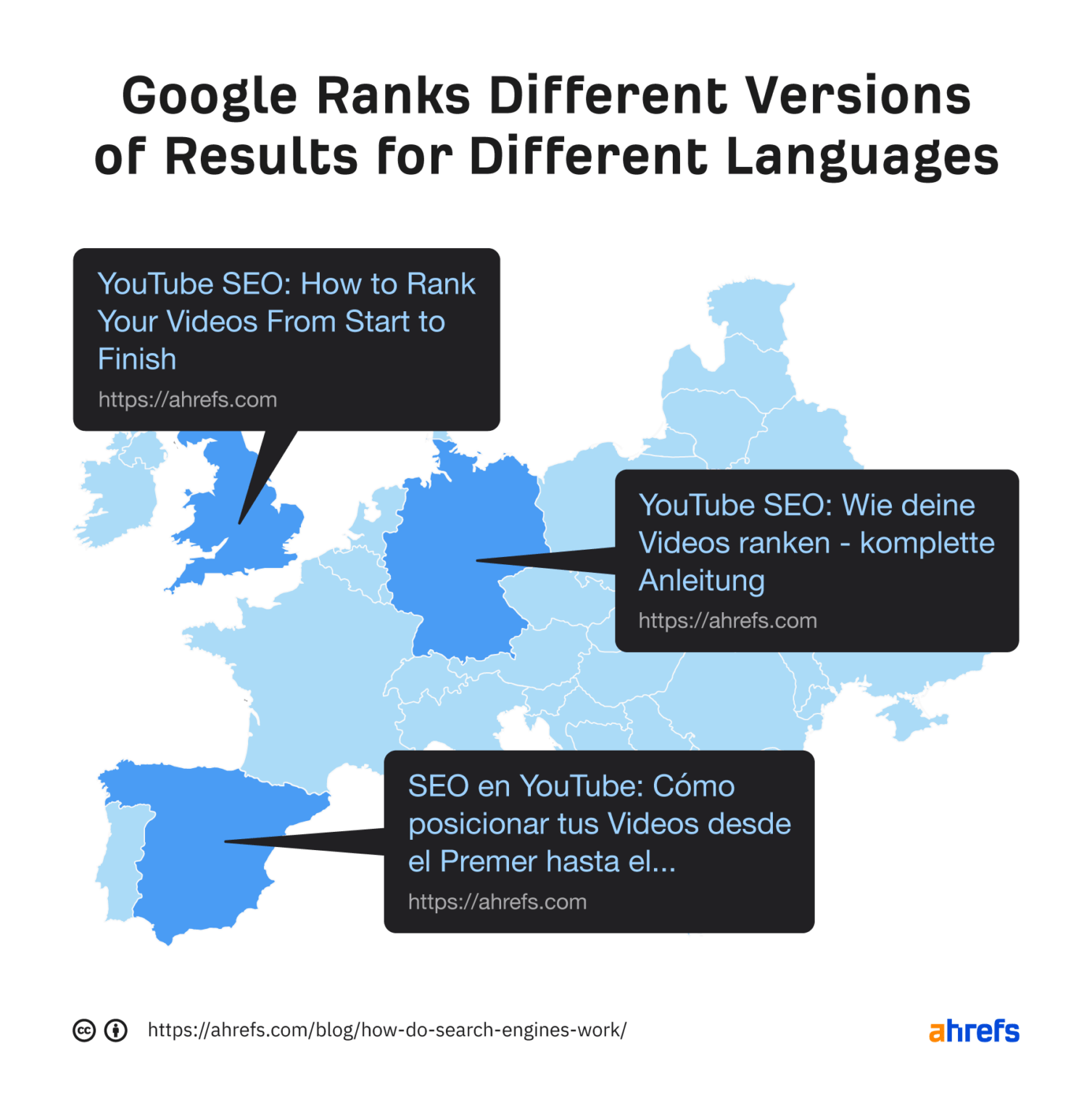
Google knows that there's no point in showing results in English to Spanish users. That's why it ranks localized versions of content (if available) for users speaking different languages.
Search history
Google saves what you do and where you go to give you a more personalized search experience. You can decline this, but most people won't.
summary
- A search engine consists of two main parts: Index and algorithm.
- To build the index, it crawls known pages and follows those links to find new pages.
- The purpose of the search algorithm is to return the best and most relevant results.
- The quality of search results is important for building market share.
- No one knows all the Google ranking factors for organic results.
- Key ranking factors include backlinks, relevance, and freshness.
- Google personalizes results based on your location, language, and search history.