Use Wireshark to analyze data packets in the network
Wireshark, also known as Ethereal, this tool is probably not so strange to most of our users, which is considered one of the network data analysis applications, with monitoring and monitoring capabilities. Real-time monitoring of packets, accurate display of user reports via the interface is simple and user-friendly.In the following article, we will introduce you some basic characteristics as well as how to use, analyze and test network systems using Wireshark.
You can download the latest version of Wireshark here or directly at the homepage. If you use Linux or other UNIX systems, you can find Wireshark in the Package Repositories section. For example, with Ubuntu , Wireshark will be available in the Ubuntu Software Center. However, you should note that it should not be used freely, because companies, organizations or businesses do not allow the use of Wireshark in their networks.
1. Start with Wireshark
You can download Wireshark for Windows or macOS from the official website: https://www.wireshark.org/ . If you are using Linux or another UNIX-like system, you may find Wireshark in the repository package. For example, if you are using Ubuntu, you will find Wireshark in Ubuntu Software Center.
Quick warning: Many organizations do not allow Wireshark and similar tools to work on their networks. Therefore, be careful not to use this tool at work unless you have permission.
2. Capturing Packets
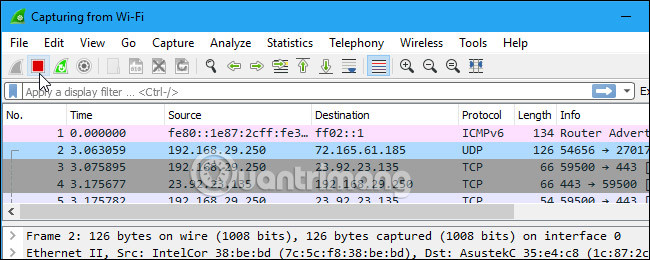
After installation, start the program and select the Interface List component to start working. For example, if you want to monitor network traffic via a wireless network, select the corresponding Wifi network card. Click the Capture Options button to display more options.

Soon after, we will see packets begin to appear, Wireshark will 'catch' each packet - the package comes and goes into the network. If you are monitoring information on the Wireless in Promiscuous mode, you will see other data packets in the entire system.
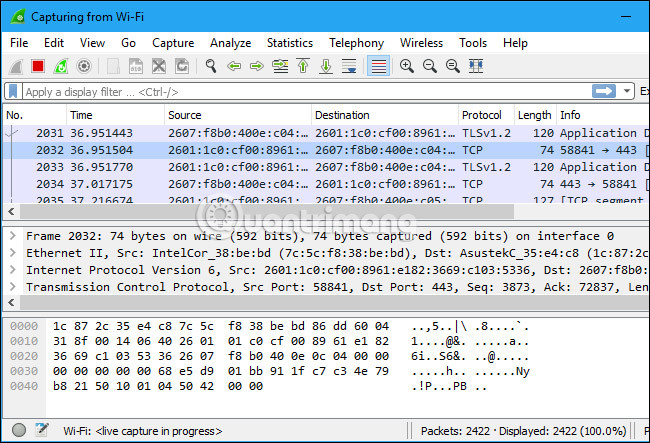
If you want to suspend this process, then click the Stop button at the top.
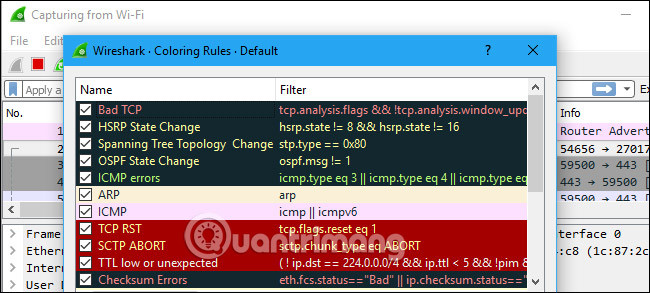
3. Color Coding
You may see packets marked with different colors. Wireshark uses colors to help you identify traffic types at a glance. For example, by default, light purple is TCP traffic, light blue is UDP traffic and black is the packet with errors. They can be distributed in order.
To see the exact meaning of the color codes, click View> Coloring Rules . You can also customize and modify the color rules from here, if you want.
4. Sample Captures
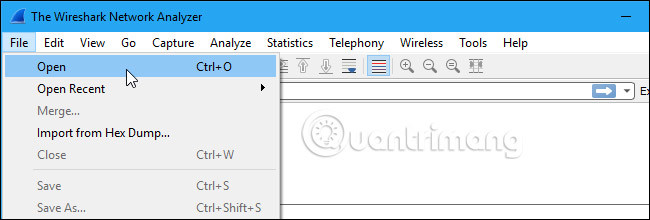
If there is nothing interesting to check on your own network, you can check out Wireshark's wiki (wiki.wireshark.org/SampleCaptures). The wiki contains a page of sample files that you can download and test. Click File> Open in Wireshark and browse for the downloaded file to open it.
You can also save your own files in Wireshark and open them later. Click File> Save to save your packets.
5. Filtering Packets
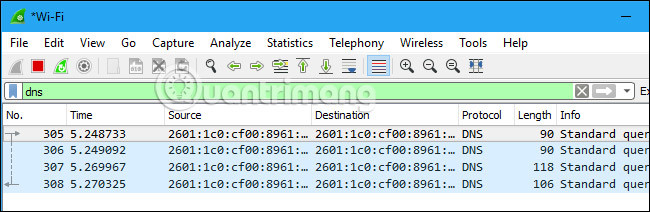
The most basic way to apply a filter is to enter the information in the Filter box, then click Apply or press Enter . For example, if we type dns, we will only see DNS packets. As soon as the keyword is entered, Wireshark will automatically complete this information sequence based on the corresponding suggestion.
Or press the Analyze> Display Filters menu to create a new filter.
Right-click on each package and select Follow TCP Stream.
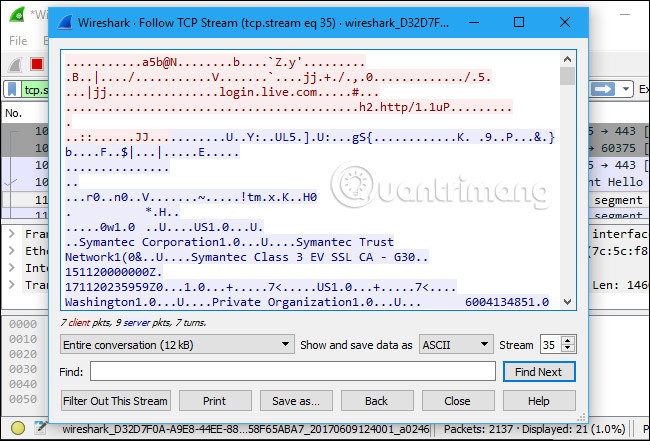
We will see the entire communication time between the server and the client.
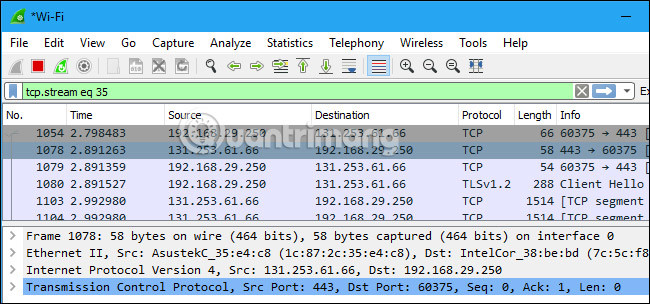
Closing this window and the filter will automatically be applied, Wireshark continues to display the full and exact packages involved.
6. Inspecting Packets
Click and select any package to check for more specific pieces of information.
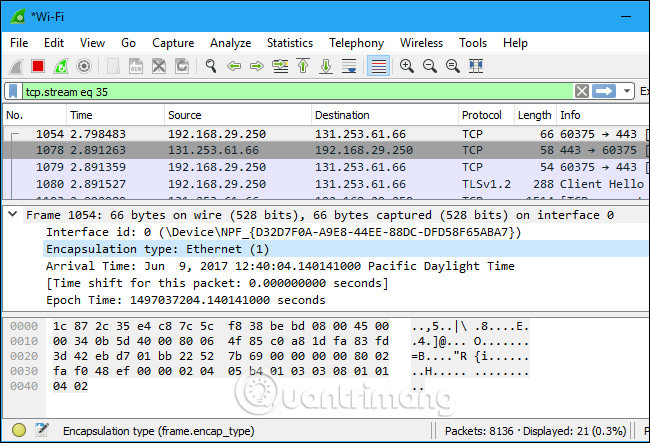
Or you can directly create a filter here, right-click on the details section and select Apply as Filter to apply.

Here are some basic information on how to use Wireshark to check, analyze data and packets in the network. We will continue to dive into WireShark's features with other tutorials on QuanTriMang.com. Invite you to read!
See more:
- Data analysis with Network Monitor
- Fix basic network applications with Wireshark (Ethereal)
- Network analysis with Wireshark on Ubuntu 9.10