The Wormhole attack in wireless sensor networks
The idea behind the Wormhole attack is to forward data from one compromised node to another malicious node on the other end of the network through a tunnel. Therefore, other nodes in WSN may be tricked into believing that they are closer to other nodes than they really are, which can cause problems in the routing algorithm.
In addition, the compromised nodes can intercept the packets. The Wormhole attack can also be combined with a Sinkhole attack to make it more effective.
Wormhole attacks
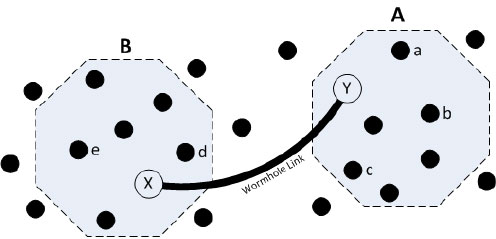 The Wormhole attack is a type of network layer attack that is performed using multiple malicious nodes
The Wormhole attack is a type of network layer attack that is performed using multiple malicious nodes
The Wormhole attack can be classified into three main categories:
1. Attack the open Wormhole
In this case, the data packets are first sent from the source to a wormhole to move them to another wormhole, and then to the destination. The other nodes in the network are ignored and cannot be used to transmit data.
2. Attack the half-open Wormhole
In this case, data packets are sent from the source to a wormhole to transmit them directly to the destination.
3. Attack the closed Wormhole
In this case, the data packets are passed directly from source to destination in a single hop, making them fake neighbors.
How to cope with Wormhole attacks?
Some of the countermeasures for Wormhole attacks are:

1. Watchdog model
According to the Watchdog model if some information is passed from one node to another through a central node, the sending node checks the middle node. If the middle node does not send a packet within the set time limit it is declared fake, and a new path to the destination node is created.
Although in this method, the Watchdog node is not always accurate in wormhole detection and can be deceived easily, if the Wormhole attack is combined with a Selective Forwarding attack (selective forwarding). ). The probability of an inaccurate warning is also quite high here.
2. The Delphi technique
In this method, the latency per hop in the WSN is calculated and it is clear that the tunnel will be longer than the normal path. So if the latency per hop of any path is significantly greater than the average then the network is considered under attack. This method is not very successful if there is a large number of wormholes in WSN, because with the increase of wormholes the average latency per hop will increase significantly.
3. Wormhole Resistant Hybrid technique
This model is a combination of Watchdog and Delphi methods and also overcomes their limitations. This method tracks both: data loss and latency per hop, and is designed to detect all types of wormholes.
4. Explore separate route algorithm
This algorithm discovers different paths between two nodes to identify a Wormhole attack. It finds all single and double hop neighbors, as well as most routes between nodes. So it can be easy to check if a node that claims to be the shortest path to the destination is correct.
5. Packet Leash
The Packet Leash prevents the transmission of packets over long distances. They are also divided into:
(i) Geographical Leash - Ensures that data cannot be transmitted more than a specific distance in a hop.
(ii) Temporal Leash - Set a limit for the total distance the data packet can travel even with multiple hops.