Setting up VPN yourself does not need support from expensive software
In this tutorial we will show you how to set up a VPN server on Windows 7 or Vista and make connections from remote clients Windows XP, Vista, or Windows 7.
If you want to securely access the corporate network when away from your office, you can set up a virtual private network (VPN). With this virtual private network, you can connect via the Internet and access shared files and your resources securely. Not buying expensive VPN servers if your organization doesn't have many users. The Windows operating system also allows us to set up a VPN server and client.
In this tutorial we will show you how to set up a VPN server on Windows 7 or Vista and connect to Windows XP, Vista, or Windows 7. Here's how to do it specifically:
Avoid IP conflicts
Because VPN connections are associated with networks, be careful of typing IP addresses and subnets so that they do not conflict with each other. On the network hosting the VPN server, you should use a different IP address than the router's IP addresses, such as 192.168.50.1. If there are multiple offices, assign each office a separate IP / subnet, such as 192.168.51.1, 192.168.52.1, .

Figure 1
Create connection incoming VPN in Windows
To configure the Windows VPN server, you need to create an incoming connection. This computer will be the VPN server or host. Also, need to specify the user you want them to be able to make a VPN connection. Follow these steps to create incoming connections:
- Right-click the network icon in the system tray and select Open Network and Sharing Center .
- Click Manage network connections (Windows Vista) or Change adapter settings (Windows 7).
- Press Alt to display the File Menu and click File > New Incoming connection .
- Choose the person you like to allow VPN access or create custom accounts by clicking Add someone . See the example in Figure 2. When done, click Next .
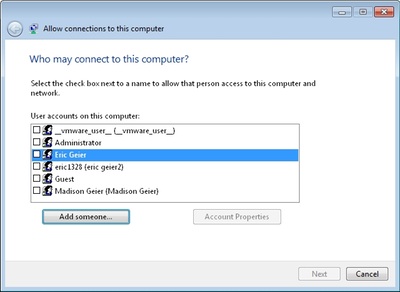
Figure 2
- Select Through the Internet and click Next .
As shown in Figure 3, select the protocols you want to use for this connection. Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4) so that remote users will receive the IP address and can access the network or the Internet. In addition, if you want remote users to access shared files and printers, select File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks . Once done, click Allow access .
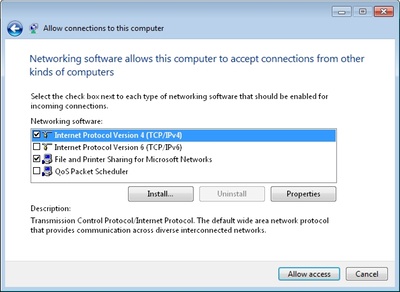
Figure 3
- In the next window, click Close .
At this point, access the incoming connection properties page that has just been created and define the IP address range for VPN clients:
- In the Network Connections window, double-click Incoming Connections .
- Select the Networking tab and double-click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4) .
- Select Specify IP addresses then enter the beginning and end addresses of your local subnet range, but do not conflict with the DHCP range. For example, if the router's IP address is 192.168.50.1, you can import 192.168.50.50 to 192.168.50.59 as shown in Figure 4, this address range supports 10 clients. If you want the clients to manually assign IP addresses, select that option.
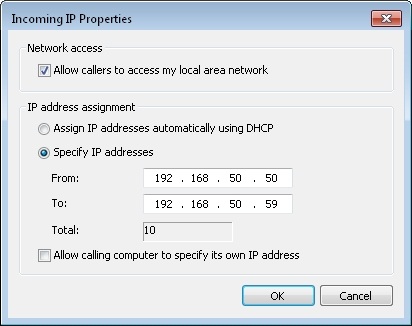
Figure 4
- Click OK in the two dialog boxes to save the changes.
Configure third-party firewalls
Windows will automatically allow VPN connections through Windows Firewall when you configure incoming incoming on the host computer. However, if you use a third-party firewall on this computer, you need to make sure it allows this VPN traffic. You may have to manually enter port numbers 47 and 1723.
Configure IP address, dynamic DNS and router
To enable VPN connections for the host computer from the Internet, you must configure the router to forward them to a Windows computer that accepts incoming connections. Specify the host machine by entering its local IP address. So, before setting up port forwarding, you should make sure the IP address is not changed.
Start by logging into the router's web console. Then go to Network or DHCP settings and see if you can maintain an IP address for the computer so that it doesn't change. This is called DHCP reservation or Static DHCP. Some routers do not have this feature. In that case, it is necessary to assign the computer a static IP in the TCP / IP settings of the network connection in Windows.
Once you have specified the IP address, find the virtual server or set up port forwarding in the router's web console. Then create port 1723 forwarding entry to the computer's local IP address, as shown in Figure 5. Don't forget to save the changes!
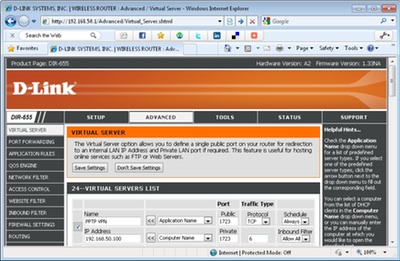
Figure 5
If an Internet connection uses a dynamic IP address, you should register and configure a dynamic DNS service. The reason is because, when configuring remote clients, you must enter the Internet IP address of the host machine host. This will cause problems if the IP changes. However, you can register for a free service, such as from No-IP and enter account information into the router so that it updates the hostname with your IP address. You will then have a hostname (such as yourname.no-ip.org) to import to the remote client, which will always point to the current Internet IP address of the host machine.
Now everything on the server side has been configured. Next we need to set up the clients.
Create an outbound VPN connection in Windows
Now that we have set up the server, we need to configure the clients that want to remotely access the VPN connection, called VPN clients. Here's how to do it in Windows Vista and Windows 7:
- Right-click the network icon in the system tray and select Open Network and Sharing Center .
- Click Set up a connection or network (Windows Vista) or Set up a new connection or network (Windows 7, as shown in Figure 6).
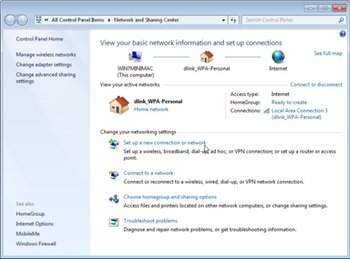
Figure 6
- On the wizard, select Connect to a workplace and click Next .
- Select Use my internet connection (VPN) .
- Type the Internet IP address or hostname into Internet address and enter the description in the Destination name section. See the example in Figure 7. Other options should be disabled and then click Next to continue.
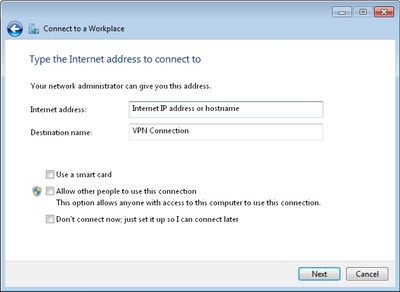
Figure 7
- Enter the selected User name and password when creating the incoming VPN connection and click Next to try connecting. This will perform a connection attempt using the following protocols: SSTP, PPTP, and then L2TP.
- When connecting successfully, click Close .
By default Windows will assign the connection type to Public Network, which is a connection type that limits sharing. So if you want to change this, you need to open the Network and Sharing Center, click Customize (Windows Vista) or link Public network under the connection name (Windows 7). Then on the window that appears, select Work Network .
Here's how to create an outgoing VPN connection in Windows XP:
- Open the Network Connections window and click Create a new connection .
- Select Connect to the network at my workplace and click Next .
- Select the Virtual Private Network connection and click Next .
- Enter the connection name and click Next .
- Select Do not dial the initial connection and click Next .
- Type the Internet IP address or hostname and click Next.
- Click Finish .
Limit VPN traffic
By default, all Internet traffic on the VPN client will be transmitted over VPN instead of the local Internet that they connect to. This is a great technique if we use a public connection, like a certain access port in a hotel or a Wi-Fi access point, this time it will make browsing more private. . However, if these computers are on a trusted network, like at home or remote offices, this method can waste bandwidth. So we can restrict traffic through a VPN connection:
- On the Network Connections window , right-click the VPN connection and select Properties .
- Select the Network tab and double-click Internet Protocol (TCP / IP).
- Click the Advanced button and uncheck Use default gateway on remote network (see Figure 8).
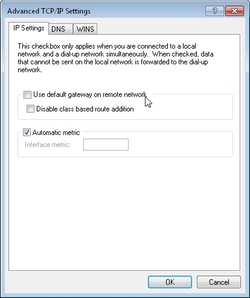
Figure 8
- Click OK on the dialog boxes to save the changes.
Now the VPN client will use the local Internet connection when browsing. It will only use the VPN connection when the server or IP address cannot connect via the Internet, such as when accessing shared files named network hosting VPN.
Connect with VPN
In Windows XP, you can connect and disconnect by opening the Network Connections window and right-clicking on the VPN connection. In Windows Vista, you can click the network icon in the system tray, click Connect to and select the connection. In Windows 7, click the network icon in the system tray and select the VPN connection.
Once connected, you can access shared resources on the VPN hosting network. Note that you may have to access shared folders manually (such as: the computer's IP address or file: // computer_name / ) instead of browsing in My Network Places or Network.