PowerShell security
Derek Melber
If you've ever heard of PowerShell, you're probably wondering how powerful PowerShell is. With all the effort and effort spent, this scripting machine is now more mature with advanced security features. PowerShell is not just a routine scripting language. There are many security features built into it as well as some additional security you can configure in PowerShell.
PowerShell default security
First go to PowerShell's interface before doing what you want. In the interface there are a number of default security methods designed to ensure anyone who carries the malicious code will be denied any access attempts.
Path content
The first security method you will encounter is PowerShell that will not run scripts in the current directory. This is so that malicious scripts are trying to penetrate in order to break the cmdlet and the commands will fail.
For example, if you want to run a script named Example.ps1 from the C: scripts directory, you need to include the full path into the script, even if you are in the C folder : scripts in PowerShell. Figure 1 illustrates what happens when you try to run Example.ps1 without a path.

Figure 1: The script must contain the path
Observe what happens when the script runs with the path in the scenario in Figure 2.

Figure 2: When the path is inserted, the script will run without any problems
Why is limited?
The other default setting that relates directly to security is that all scripts must be run interactively. This is a security method to ensure that PowerShell scripts are not executed from a virus-implicated script. That means you must be in the PowerShell interface and run the script in real time.
This default setting is related to the ExecutionPolicy set within PowerShell. The ExecutionPolicy is set by default to Restricted, as shown in Figure 3.
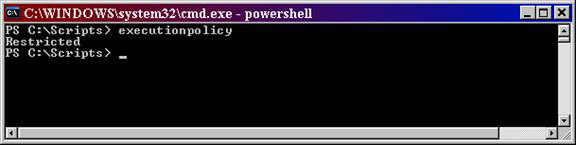
Figure 3: The default ExecutionPolicy is set to Restricted
to protect the execution of remote PowerShell scripts
The influence of the default security
The default ExecutionPolicy in PowerShell is very secure. It does not allow any script to run from anywhere. So the scripts you create and put in a system will not run. The scripts downloaded from the Internet will not run either. The scripts that have even been confirmed and secured to some extent will not run. Therefore, you need to reset the ExecutionPolicy level before running your scripts.
Set security level for ExecutionPolicy
There are four security levels for ExecutionPolicy that you can set up. These four security levels provide you with great security features on what your script can run and what needs are involved so that the script can run. These four levels and requirements include:
Restricted
This is the default configuration in PowerShell. This setting means that no script can run, regardless of its identity. The things that can be run in PowerShell with this setting are separate commands.
AllSigned
This setting allows scripts to run in PowerShell. However, scripts must have digital identifiers from a trusted publisher. There will be a prompt before running scripts from trusted publishers. This allows you to avoid malicious scripts.
RemoteSigned
This scenario allows scripts to run, but requires scripts and configuration files to be downloaded from the Internet with digital identifiers from a trusted publisher. The scripts running from the local computer do not need to be signed as such. There are no reminders before running the script. However, you can still avoid malicious scripts.
Unrestricted
This is not the recommended setting! This level of security allows scripts without identifiers, which may include all the scripts and configuration files downloaded from the Internet. The risk here is that you will probably guess, it is the malicious code can easily penetrate.
To set any security level, you must enter the security level () as shown in Figure 4.
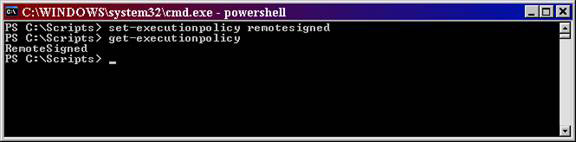
Figure 4: ExecutionPolicy setting
Use Group Policy
PowerShell is great, but if the script can't run on the computer in your environment, it clearly has limitations. First, you must have PowerShell on each computer. When PowerShell is set through an EXE file, it's easy to install the application. You can use a ZAP file and push it out with Group Policy, or you can use the current method of installing applications. However, you should note that PowerShell is reviewed as a hotfix, so Windows Update can also push PowerShell's installation.
After installing PowerShell for computers, you need to enable scripts to run. With the ExecutionPolicy set to Restricted by default, you need to configure each computer to run the scripts you want to run. This can take days if you want to do it manually.
Although you can also use Group Policy to get the above done. However, you can create your own Administrative Template (ADM file) to make this change, or download the ADM template that Microsoft provides. We recommend that you do this by downloading the ADM template.
After downloading, you need to install MSI. Although it is not the most efficient installation. But after installation, the ADM file is included in the folder C: program filesMicrosoft Group Policy . This is a great security! File to import into Group Policy Object Editor is PowerShellExtensionPolicy.ADM . After importing, you will have two new buttons in the Group Policy Object, one in Computer Configuration Administrative TemplatesWindows Components, Windows PowerShell and one in User Configuration Administrative TemplatesWindows Components Windows PowerShell , as shown in Figure 5.
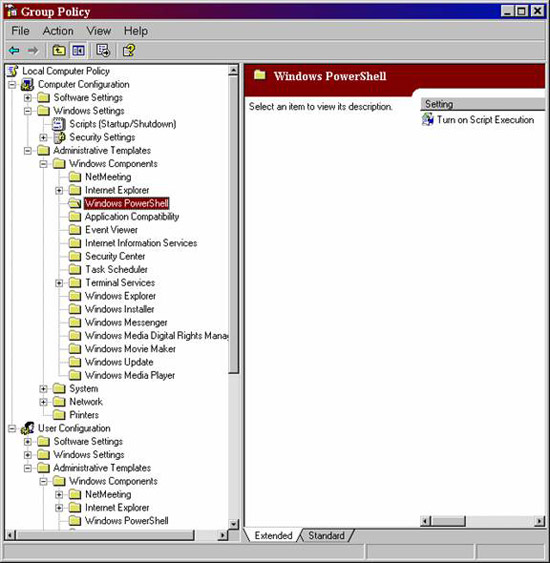
Figure 5: PowerShell ADM template adds settings to Computer Configuration
and User Configuration for script execution
When configuring this policy, you will have 3 options for a setting as shown in Figure 6.
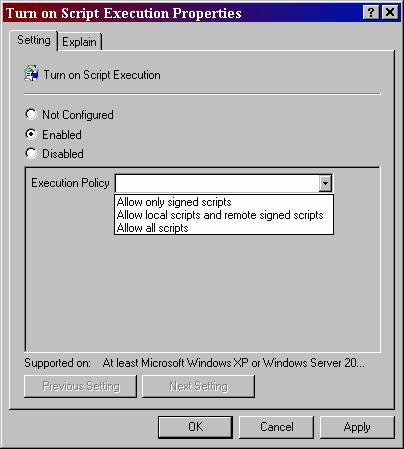
Figure 6: The ExecutionPolicy settings for PowerShell in the GPO
Conclude
PowerShell is an integrated component of Windows Server 2008 product, the operating system will be released in early 2008, and PowerShell will take off like a rocket engine spacecraft. With all the concerns PowerShell is trying, people hope that it is ready with advanced security features. The truth is that all scenarios set up to have a limited enforcement policy are unimaginable. Even if you have a .PS1 file, the existence of the script associated with Notepad is a good default security. Although you can have the PowerShell interface, the fact that the path for the script still needs to be added. In addition to the default security, you can also set execution policies and control PowerShell through Group Policy to centrally control PowerShell security.