Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 11
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 1
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 1
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 2
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 2
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 3
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 3
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 4
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 4
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 5
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 5
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 6
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 6
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 7
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 7
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 8
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 8
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 9
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 9
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 10
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 10
The MAK
Export output to XML
Part 10 of this article series showed how to use PowerShell scripts in conjunction with SMO and parameters to create SQL Server scripts.
In this section, we will show you how to use PowerShell cmdlets in conjunction with the SQL Server client and output saving to export to a text file or XML file.
Let's assume we want to query a certain SQL Server table with transact sql and save the output in text format or XML format. Using PowerShell cmdlets, connecting the SQL Server client and saving the output can be done very easily.
Let's create c: psoutput.ps1 as shown below (See Figure 1.1)
param
(
[string] $ SQLServer,
[string] $ Database,
[string] $ outputType,
[string] $ filename,
[string] $ Query
)
$ SqlConnection = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection
$ SqlConnection.ConnectionString =
"Server = $ SQLSERVER; Database = $ DATABASE; Integrated Security = True"
$ SqlCmd = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand
$ SqlCmd.CommandText = $ Query
$ SqlCmd.Connection = $ SqlConnection
$ SqlAdapter = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataAdapter
$ SqlAdapter.SelectCommand = $ SqlCmd
$ DataSet = New-Object System.Data.DataSet
$ SqlAdapter.Fill ($ DataSet)
$ SqlConnection.Close ()
if ($ outputType -eq "Text")
{
$ DataSet.Tables [0] | -auto format-table> $ filename
}
if ($ outputType -eq "xml")
{
$ DataSet.Tables [0] | Export-Clixml $ filename
}

Figure 1.1
This scenario can be executed as shown below (Figure 1.2)
./output "HOMESQLEXPRESS" "VixiaTrack" "TEXT" "c: test.txt" "Select dbid, name from sys.sysdatabases"
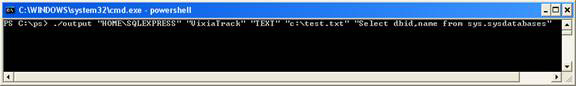
Figure 1.2
Explain the parameters :
- output is the script output.ps1 in the c: ps directory
- HOME is the hostname
- SQLEXPRESS is the name of the SQL Server instance in the HOME host
- VixiaTrack is the database name residing in SQLEXPRESS instance
- TEXT is the required output format. It can be TEXT or XML.
- C: test.txt is the file name and its location
- Select dbid, name from sys.sysdatabases is a Transact SQL query executed with the database
When the PowerShell script is executed, it queries the database and saves the output to a text file that has been passed as parameters (Refer to Figure 1.3 and Figure 1.4).

Figure 1.3
The contents of the test.txt file
dbid name
---- ----
1 master
2 tempdb
3 models
4 msdb
5 tests
6 VixiaTrack
7 XMLTest
8 admin
9 AdventureWorks
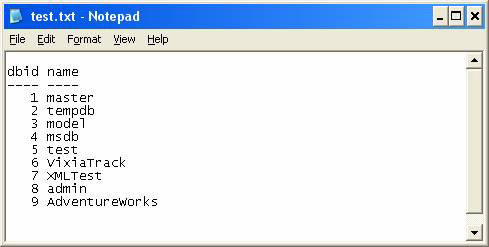
Figure 1.4
The same PowerShell script can be executed using XML as a parameter to create the XML format.
This scenario can be executed as shown below (Figure 1.5)
./output "HOMESQLEXPRESS" "VixiaTrack" "XML" "c: test.xml" "Select dbid, name from sys.sysdatabases"
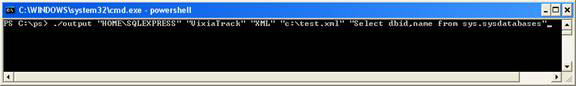
Figure 1.5
Explain the parameters :
- output is the script output.ps1 in the c: ps directory
- HOME is the hostname
- SQLEXPRESS is the name of the SQL Server instance in the HOME host
- VixiaTrack is the database name residing in SQLEXPRESS instance
- XML is the required output format. It can be TEXT or XML.
- C: test.txt is the file name and its location.
- Select dbid, name from sys.sysdatabases is a Transact SQL query executed with the database
When the PowerShell script is executed, it will query the database and save the output to an XML file that has been passed as a parameter (Figure 1.6 and Figure 1.7).

Figure 1.6
The contents of the test.xml file
-
-
-
System.Data.DataRow
System.Object
-
first
master
-
-
2
tempdb
-
-
3
model
-
-
4
msdb
-
-
5
kiểm TRA
-
-
6
VixiaTrack
-
-
7
XMLTest
-
-
8
admin
-
-
9
AdventureWorks

Figure 1.7
Conclude
Part 11 of this series illustrated how to use PowerShell cmdlets in conjunction with the SQL Server client and output saving to export to a text file or XML file.