Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 10
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 1
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 1
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 2
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 2
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 3
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 3
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 4
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 4
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 5
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 5
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 6
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 6
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 7
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 7
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 8
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 8
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 9
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 9
The MAK
Use PowerShell scripts to create SQL Server scripts for databases and tables
In Part 10, I will show you how to use PowerShell scripts in conjunction with SMO and parameters to create SQL Server scripts. Creating SQL Server scripts is an important task for administrators and SQL Server database development professionals.
Let's assume that we want a PowerShell script to create a 'Create Database' script for a database or a 'Create object' script for all objects from an existing database. In addition, the server name and database name will be passed as parameters to the PowerShell script.
We can do this by creating a PowerShell script as shown below.
Create C: PSScriptSQL.ps1 as shown below. Refer to Figure 1.0
param
(
[string] $ ServerName,
[string] $ DatabaseName,
[string] $ scriptType
)
[reflection.assembly] :: LoadWithPartialName ("Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo") | out-null
$ MyScripter = new-object ("Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Scripter")
$ srv = New-Object "Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server" "$ ServerName"
$ db = $ srv.Databases ["$ DatabaseName"]
$ MyScripter.Server = $ srv
if ($ scriptType -eq "Database")
{
echo "Database Scripts"
echo "-----------------"
$ MyScripter.Script ($ srv.databases ["$ DatabaseName"])
}
if ($ scriptType -eq "Tables")
{
echo "Table Scripts"
echo "-----------------"
$ MyScripter.Script ($ srv.Databases ["$ DatabaseName"]. Tables)
}

Figure 1.0
Execute the PowerShell script as shown below (Figure 1.1)
./ScriptSQL "HOMESQLEXPRESS" "Admin" "Database"
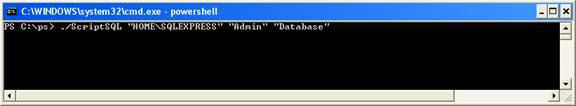
Figure 1.1
Explain the parameters :
- ScriptSQL is the script of ScriptSQL.ps1 in the c: ps directory
- HOME is the hostname
- SQLEXPRESS is the SQL server name instance on the HOME host
- Admin is the database name residing in SQLEXPRESS
- Database is the parameter when passed, will create the script 'Create database'
This script creates the 'Create Database' script below (Figure 1.2)
Database Scripts
-----------------
CREATE DATABASE [Admin] ON PRIMARY
(NAME = N'admin ', FILENAME = N'C: Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL.1MSSQLDATAadmin.mdf', SIZE = 2240KB, M
AXSIZE = UNLIMITED, FILEGROWTH = 1024KB)
LOG ON
(NAME = N'admin_log ', FILENAME = N'C: Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL.1MSSQLDATAadmin_log.LDF', SIZE = 76
8KB, MAXSIZE = 2048GB, FILEGROWTH = 10%)
COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
EXEC dbo.sp_dbcmptlevel @ dbname = N'Admin ', @ new_cmptlevel = 90
IF (1 = FULLTEXTSERVICEPROPERTY ('IsFullTextInstalled'))
begin
EXEC [Admin]. [Dbo]. [Sp_fulltext_database] @action = 'enable'
end
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET ANSI_NULL_DEFAULT OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET ANSI_NULLS OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET ANSI_PADDING OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET ANSI_WARNINGS OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET ARITHABORT OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET AUTO_CLOSE ON
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET AUTO_CREATE_STATISTICS ON
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET AUTO_SHRINK OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS ON
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET CURSOR_CLOSE_ON_COMMIT OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET CURSOR_DEFAULT GLOBAL
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET CONCAT_NULL_YIELDS_NULL OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET NUMERIC_ROUNDABORT OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET RECURSIVE_TRIGGERS OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET ENABLE_BROKER
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS_ASYNC OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET DATE_CORRELATION_OPTIMIZATION OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET TRUSTWORTHY OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET ALLOW_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION OFF
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET PARAMETERIZATION SIMPLE
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET READ_WRITE
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET RECOVERY FULL
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET MULTI_USER
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET PAGE_VERIFY CHECKSUM
ALTER DATABASE [Admin] SET DB_CHAINING OFF

Figure 1.2
Now execute the PowerShell script as shown below (Figure 1.3).
./ScriptSQL "HOMESQLEXPRESS" "VixiaTrack" "Tables"

Figure 1.3
Explain the parameters :
- ScriptSQL is ScriptSQL.ps1 script in c: ps directory
- HOME is the hostname
- SQLEXPRESS is the SQL Server instance server name on the HOME host
- VixiaTrack is the database name residing in SQLEXPRESS
- 'Tables' is the parameter when prompted to create the 'Create table' script.
This script will create the 'Create Database' script below (Figure 1.4)
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
CREATE TABLE [dbo]. [StockCriteriaHistory] (
[StockCriteriaHistoryID] [int] IDENTITY (1,1) NOT NULL,
[LocationID] [int] NULL,
[LocationDescription] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[SiteID] [int] NULL,
[Site] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[WingID] [int] NULL,
[Wing] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[BuildingID] [int] NULL,
[Building] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[FloorNo] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[DepartmentID] [int] NULL,
[Department] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[RoomNo] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[RoomTypeID] [int] NULL,
[RoomType] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[VixiaLocationType] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[VixiaLocationNo] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[TargetCount] [int] NULL,
[LowAlertCount] [int] NULL,
[LowAlarmCount] [int] NULL,
[HighAlertCount] [int] NULL,
[HighAlarmCount] [int] NULL,
[EquipCategoryID] [int] NULL,
[EquipCategory] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[EquipTypeID] [int] NULL,
[EquipType] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[CreatedDt] [datetime] NULL,
[CreatedID] [int] NULL,
[UserName] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
SET ANSI_NULLS OFF
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
CREATE TABLE [dbo]. [Wing] (
[WingID] [int] IDENTITY (1,1) NOT NULL,
[Description] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[CreatedID] [int] NULL,
[CreatedDt] [datetime] NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
CREATE TABLE [dbo]. [XMLStaging] (
[rdt] [nvarchar] (364) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[us] [nvarchar] (364) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[ltid] [nvarchar] (364) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[ls] [nvarchar] (364) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[eqtid] [nvarchar] (364) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[es] [nvarchar] (364) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[tp] [nvarchar] (364) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
SET ANSI_NULLS OFF
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
CREATE TABLE [dbo]. [UploadedFile] (
[UploadedFileID] [int] IDENTITY (1,1) NOT NULL,
[Description] [varchar] (100) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NULL,
[UploadedUserID] [int] NULL,
[UploadedDt] [datetime] NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]

Figure 1.4
You can send the output to a file as shown below (Figure 1.5).
./ScriptSQL "HOMESQLEXPRESS" "VixiaTrack" "Tables"> C: MyScript1.sql
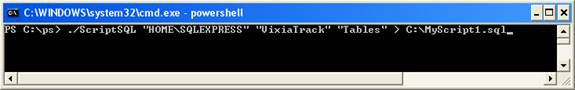
Figure 1.5
The created script is not saved in C: MyScript1.sql. (Refer to Figure 1.6)

Figure 1.6
Conclude
Part 10 of this series showed how to use PowerShell script in conjunction with SMO to create a script for a database and tables by passing parameters.
 Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 11
Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 11