How to integrate Google authentication in Next.js app using NextAuth
Integrating a secure authentication system is an important development that not only provides a secure environment for your users, but also gives them confidence in your product. This system ensures that the user's data is protected and that only authorized individuals can access the application.
Building secure authentication from scratch can be a time-consuming process, requiring a thorough understanding of authentication protocols and processes, especially when dealing with different authentication providers.
Using NextAuth, you can shift your focus to building core features. Read on to learn how to integrate Google logins in your apps using NextAuth.
How does NextAuth work?
NextAuth.js is an open source authentication library that simplifies the process of adding authentication and authorization functionality to Next.js applications and customizing the authentication process. It offers a wide range of features like email, passwordless authentication, and support for various authentication providers like Google, GitHub, etc.
At a high level, NextAuth acts as a middleware, facilitating the authentication process between your application and the provider. Basically, when a user tries to log in, they will be redirected to the Google login page. After successful authentication, Google returns a payload that includes the user's data, such as their name and email address. This data is used to grant access to the application and its resources.
Using payload data, NextAuth creates a session for each authenticated user and stores the session token in a secure HTTP-only cookie. Session tokens are used to verify the user's identity and maintain their authenticated state. This process also applies to other vendors with small changes to their implementation.
Register Next.js app on Google Developer Console
NextAuth provides support for Google's authentication service. However, in order for your app to interact with the Google APIs and allow users to authenticate with their Google credentials, you need to register your app on the Google Developer Console, get the Client ID and Client Secret.
To do that, navigate to the Google Developer Console. Next, sign in with your Google account to access the console. Once logged in, create a new project.
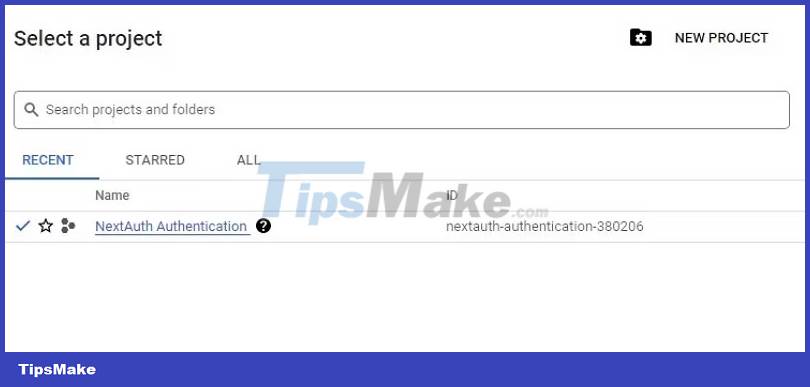
On the project dashboard, select the APIs and Services tab in the left menu pane and finally the Credentials option .
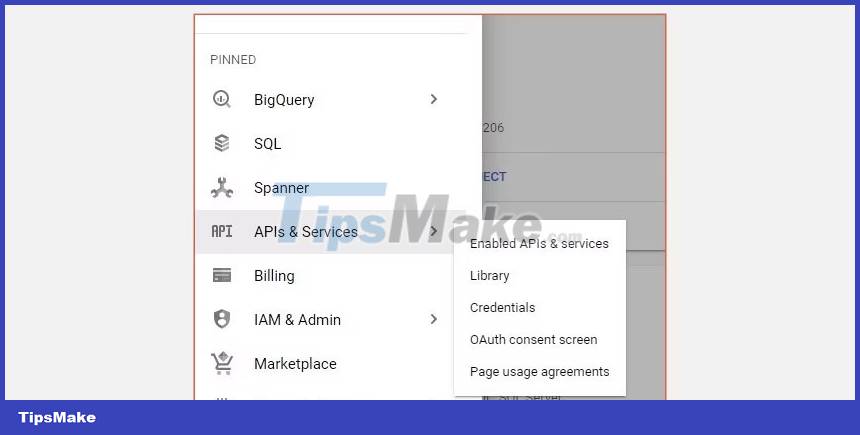
Click the Create Credentials button to generate Client ID and Client Secret. Next, specify the application type from the given options and then provide a name for your application.
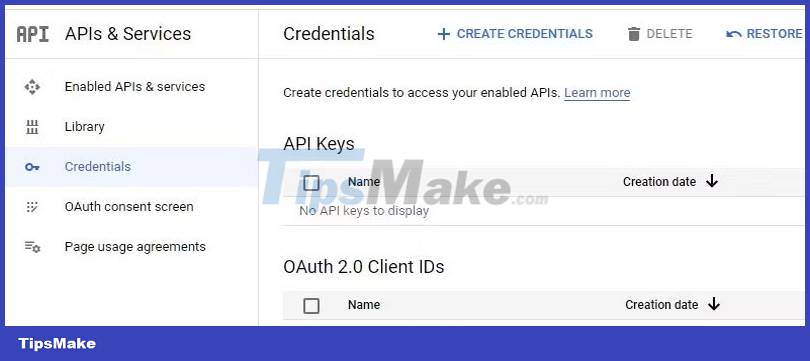
Then specify the URL back to the app's home page, and finally specify the authorized redirect URI for the app. For this case it should be http://localhost:3000/api/auth/callback/google as specified by NextAuth's Google service provider settings.
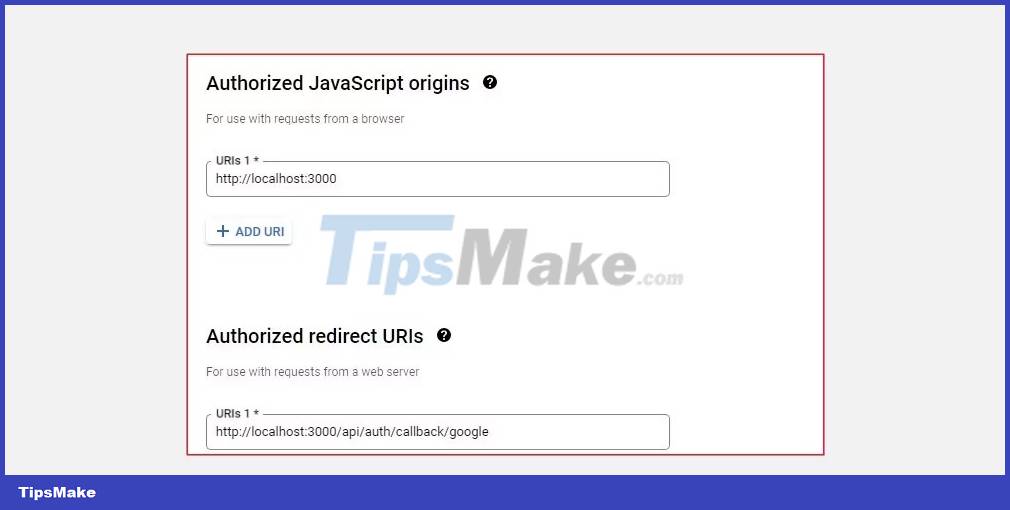
After successful registration, Google will provide you with Client ID and Client Secret to use in the application.
NextJS Application Setup
To get started, create a Next.js project locally:
npx create-next-app next-auth-appOnce the setup is complete, navigate to the newly created project directory and run this command to start the development server.
npm run devOpen a browser and navigate to http://localhost:3000. The expected result will be as follows.
Note: You can find the code for this project in its GitHub repository.
Set up the .env . file
In the root directory of the project, create a new file and name it .env to contain the Client ID, Client Secret and base URL.
NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID= 'client ID' NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET= 'secret' NEXT_PUBLIC_NEXTAUTH_URL= 'http://localhost:3000'The NextAUTH URL is used to specify the base URL of the application, which is used to redirect the user after the authentication is complete.
NextAuth integration in Next.js . application
First, install NextAuth's library into your project.
npm install next-authNext, in the /pages folder , create a new folder and name it api. Change directory to api directory and create another directory named auth. In the auth folder, add a new file named [.nextauth].js and add the following lines of code.
import NextAuth from "next-auth/next"; import GoogleProvider from "next-auth/providers/google"; export default NextAuth({ providers:[ GoogleProvider({ clientId:process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID, clientSecret: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET, }), ] });This code configures Google as the authentication provider. The NextAuth function defines a Google provider configuration object that has two properties: Client ID and Client Secret that initializes the provider.
Next, open the pages/_app.js file and make the following changes to the code.
import './styles/globals.css' import { SessionProvider } from "next-auth/react" function MyApp({ Component, pageProps: { session, .pageProps } }) { return ( ) } export default MyApp The NextAuth SessionProvider component provides authentication state management for the Next.js application. Needs a session prop that promises the authentication session data returned from the Google API, including user details like their ID, email, and access token.
By wrapping the MyApp component with a SessionProvider component, the session object authenticates with the user details provided in the application, allowing the application to maintain and render pages based on their authentication state.
Configure the index.js . file
Open the pages/index.js file , remove the boilerplate code and add the code below to create a login button that routes the user to the login page.
import Head from 'next/head' import styles from './styles/Home.module.css' import { useRouter } from 'next/router'; export default function Home() { const router = useRouter(); return ( Create Next App Welcome to Next.js!
Get started by signing in{' '} with your Google Account
) }This code uses the Next.js useRouter hook to handle routing in the application by defining the router object. When the login button is clicked, the handler will call the router.push method to redirect the user to the login page.
Create a login authentication page
In the pages folder , create a new Login.js file , then add the following lines of code.
import { useSession, signIn, signOut } from "next-auth/react" import { useRouter } from 'next/router'; import styles from './styles/Login.module.css' export default function Login() { const { data: session } = useSession() const router = useRouter(); if (session) { return ( Create Next App
Signed in as {session.user.email}
router.push('/Profile')}> User Profile { signOut() }}> Sign out ) } return ( Create Next App
You are not signed in!!
signIn()}>Sign in ) }useSession, signIn and signOut are hooks provided by next-auth. The useSession hook is used to access the current user session object after the user is logged in and successfully authenticated by Google.
This allows Next.js to maintain authentication state and dump user details on the client side of the application, in this case email.
In addition, using the session object, you can easily create custom user profiles for your application and store the data in a database like PostgreSQL. You can connect a PostgreSQL database to your Next.js application using Prisma.
The signOut hook allows the user to sign out of the application. This hook will delete the session object created during login and the user will be logged out.
Go ahead and start the development server to update the changes and go to the Next.js application running in the browser to test the authentication functionality.
npm run devAlternatively, you can use Tailwind CSS with your Next.js application to style validation models.
You should read it
- ★ More than 90% of Gmail users still don't use the two-factor authentication feature
- ★ Integrate download support into Chrome's right-click menu
- ★ Google: 2-factor authentication can prevent 100% of automated bot hacks
- ★ Integrate Google Calendar into Thunderbird
- ★ Google now allows G Suite administrators to disable unsafe 2FA authentication