How to fix broken packages in Ubuntu
Apt, Ubuntu's package manager, is one of the most powerful and intuitive tools, but that doesn't mean that this manager never happens to be a problem. Sometimes, installing packages fails on Ubuntu and forcing users to figure out how to fix them. The great thing is that Ubuntu's package utilities, including Apt itself, have built-in functionality to help remedy this situation and get things back to normal.
The following tips and tricks will help in most cases. However, they are common remedies that cannot be applied to all different situations. So keep this in mind when trying to solve your own situation.
Fix broken package in Ubuntu
- Fix errors with Apt / Apt-Get
- Fix error with DPKG
- DPKG lock
Fix errors with Apt / Apt-Get
Apt has a few flags that users can use to fix dependencies or packages that are corrupted for any reason during the installation. The most common way to do this is to install a third-party .deb and find out the dependencies are not available. Those dependencies cannot be pushed into place and dpkg will notice that the package is missing. In any case, users can try the following steps.

First, run an update to make sure there are newer versions for the required packages.
sudo apt update --fix-missing Next, users can try to force Apt to find and fix any missing dependencies or broken packages. This tool will actually install any missing packages and repair existing settings.
sudo apt install -f Fix error with DPKG
Another step where errors can arise during package installation is the configuration process. In fact, dpkg is in charge of this part, not Apt, so when a package fails while configuring, dpkg will be the most effective tool to fix.

Start by forcing dpkg to reconfigure all or part of the corrupted package.
sudo dpkg --configure -a If this tool does not solve the problem, users can apply a more robust approach. Let's start by listing packages marked as requiring reinstallation.
sudo dpkg -l | grep ^.r If the package (s) is found to be problematic, the user may force to remove the corrupted packages.
sudo dpkg --remove --force-remove--reinstreq When dpkg completes its work, try to 'clean up' everything with Apt.
sudo apt clean sudo apt update After that, everything will return to the starting point. This does not help regain damaged packages, but at least Apt will work again.
DPKG lock
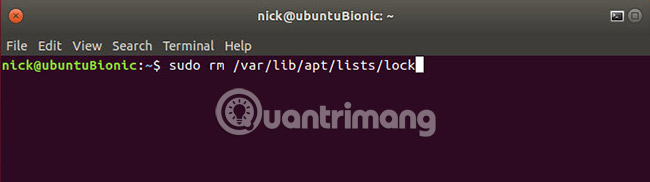
A rare problem is that the dpkg lock prevents users from doing anything. Whenever trying to use Apt or dpkg, users will get an error stating that an application is ready to use, while in fact it is not. It's easy to delete the lock file that prevents using Apt and go back to doing what is needed. Sometimes these lock files remain in place after an error during the installation process, interrupting the process and preventing the file from being deleted automatically. In this case, do it manually.
sudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/lock The best solution is to delete the lock in the cache.
sudo rm /var/cache/apt/archives/lock Hopefully, one of the ways to fix the above error will be effective in your case and everything works back to normal on Ubuntu. Remember that the best way to thoroughly handle a situation 'out of reach' is to try to bring things back to the starting point. Don't "try to eat away" or solve problems by adding more things, unless you know exactly what you're doing. Chances are you will make things worse.
Good luck!
See more:
- How to fix Ubuntu update errors
- How to troubleshoot Ubuntu problems does not start
- How to fix errors without sound in Ubuntu