How is MS-DOS used when Windows has not yet appeared?
As we all know, desktop computers don't always run every Windows.Before Windows came along and 'claimed profanity' as it is today, desktop computers are often accompanied by Microsoft's MS-DOS operating system.This is really the right environment for using command-line.However, using MS-DOS is not the same as using a terminal in Linux or Command Prompt on Windows.
Experience DOS PC
DOS is a command line operating system with no graphical window.You start your computer and then see a DOS prompt.It is important that you understand the commands to type in this command prompt to start programs, run integrated utilities, generally perform tasks with your computer.
You must know some basic cmd commands to be able to use this operating system as well as to switch between different drives.For example, to access the floppy drive on drive A: type something like A: at the prompt and press Enter. To change the directories, you will use the CD command. To view the files in the current directory, you will use the DIR command.To run the program, you will enter the executable file name of that program into the prompt.
For example, if you want to select a new floppy disk with a great program installed on it, you'll push the floppy disk into your drive, waiting for the magnetic drive to read the contents of your disc and proceed. run the following commands:
A:
DIR
SETUP or INSTALL (depending on the name of the program's installer)
After that, you will go to the installer and install the program.Basically, just extract the files into a folder on your small hard drive.You often have to use multiple floppy disks for a while because larger programs cannot be enough with just a single floppy, but after the installation is complete, you can run the program without using a floppy disk. half.
Then, run the C: command to return to drive C, use the CD command to access the directory containing your installed program and run the program with the command like PROGNAME.The name of the program file must also be a short-term file name by MS-DOS, limiting the names of the files to only stop at 8 characters, followed by a dot and an extension consisting of three letters.For example, PROGNAME.EXE is the longest file name you can set.
Some programs have tried to make it easier for ordinary users to use it.For example, you have file managers like Norton Commander that are provided to view and manage files without commands, simply sorting all the text on the screen.This is the usual style of most DOS programs.
No multitasking
For DOS, forget the multitasking.DOS only allows you to work with one task at a time.When you open a program, that program takes up your entire screen.If you want to use another program, you need to close the current program and enter the command to open the program.
To cope with this limitation, DOS provided a function called 'terminate and stay resident' (TSR).A program that supports this feature will be accessible with a keyboard shortcut.You will press the appropriate shortcut and the current program will be temporarily turned off and saved in memory.Another program (corresponding to the shortcut) will then be uploaded.
TSR is not really a pure multitasking feature.The programs that support TSR are not actually run in the background.Instead, it is temporarily disabled and can be relaunched quickly.After all, DOS can only run one program at a time.
This is one of DOS's most significant differences compared to more modern operating systems like Linux, which allows you to run programs and services in the background and perform many other advanced tasks.And DOS is not nearly as strong.

Hardware support and real mode (Real Mode)
DOS does not really support hardware devices in the way that operating systems are still in use today.Programs will need direct hardware access, for example, a DOS game that wants to use your sound card to output sound - it must directly support that hardware.That means if you are developing games on DOS or similar applications, you must conduct encryption so that your program can support all types of sound cards that your users may be use.Fortunately, many sound cards are compatible with Sound Blaster.You will use the SETUP program to configure this setting for each program you have used.

Due to the way that DOS operates, programs that want to access memory directly and peripheral devices need to be run in real mode (Real Mode) or real address mode (real address mode).In real mode, a program can write to any memory address on computer hardware without any protection.The reason for this is because you can only run one program at a time.
To this day, you still cannot run multiple DOS games in Command Prompt on Windows.Command Prompt runs applications in protected mode, but these games require real mode.This is why you need DOSBox to run old DOS games.
Windows is just a DOS program
The initial popular versions of Windows, such as Windows 3.0 and Windows 3.1, were in fact the programs running under the MS-DOS platform.Therefore, if you start your computer, go to the DOS prompt, and then type the WIN command to start the Windows program, it will show you a Windows 3-style desktop interface, called a chapter manager. Program Manager.Of course, you can also install your DOS computer to automatically start Windows by adding the WIN command to the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, and DOS will automatically run the Windows command when you start.
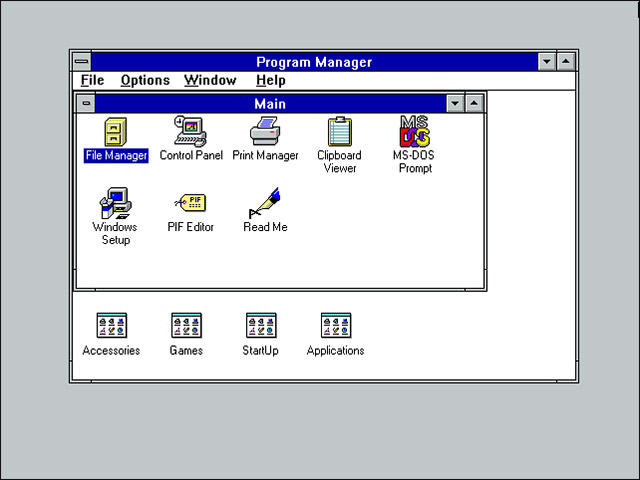
As mentioned above, DOS applications and games require real mode and cannot be run from within Windows, so if you want to open a DOS application, you must exit Windows.
The advent of Windows 95, 98, 98 SE and ME dropped DOS backward.Windows 95 works like a standalone operating system, but DOS always hides in the background run because these Windows versions are still built on DOS.Until Windows XP, the commercial versions of Windows finally came out of the shadow of DOS and switched to using a modern Windows NT 32-bit kernel.
Computer desktop DOS is now widely appreciated by many and even Microsoft itself as an outdated relic in the era of simple mobile interfaces and touch screens.But there was a time when DOS desktops were a new, user-friendly interface and dominated the global computer industry.
See more:
- 7 commands to manipulate the most basic files and folders everyone must know
- How to install and use Kali Linux on VmWare virtual machine
- History of Microsoft Windows operating system throughout the ages
You should read it
- ★ How to run Linux commands when starting Windows Subsystem for Linux on Windows 10
- ★ Extremely dangerous commands on Windows, Linux, Mac, don't try even once
- ★ Guide to network operation for Linux users: 11 commands to know
- ★ 14 interesting Linux commands in Terminal
- ★ 15 Tar commands should try in Linux