How does the hard drive work?
Have you ever gone to buy a hard drive? You are familiar with the hard drive. But what is a hard drive and how does it work, not many people know. Let us consider the problem that seems so familiar and still be strange in this article.
If the CPU is the brain of a computer, then the hard drive is a long-term memory, which stores data permanently.
Wheels and gears! Without them, there would be no car or hard drive. Before gears appeared, people used magnetic tape to store data, on large mainframes, these tapes had to spin continuously to handle the huge amount of data stored. A very annoying problem encountered in magnetic tape is a sequential reading mechanism. For example, if you want to have data at the end of the tape, while you are at the tape head, what should you do? There is no way that you will have to sit and wait for the time to never seem to end so that the tape . turns from the beginning to the data you want. What if you need data at the tape then? Not talking but surely everyone could imagine your wrinkled face at that time!
Compared to magnetic tape, magnetic disks are much faster. The magnetic disc recording mechanism allows you to move the reader (recorder) directly to the data storage location, significantly improving the time compared to having to wait hundreds of meters of tape to turn on sequentially. desired data section.
Defining the hard drive
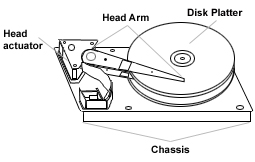 A hard drive is a storage device that can read and write data quickly with a set of magnetized molecules on rotating discs.
A hard drive is a storage device that can read and write data quickly with a set of magnetized molecules on rotating discs.
If the CPU is the computer's brain, then the hard drive is a long-term memory, storing program data and the operating system even when the machine is idle or off. Most people can't see the inside of the hard drive. Because it is covered by a metal shell (usually aluminum). You can refer to its construction at the PC panel (printed circuit board) at the end.
This PC panel provides us with the core components of a hard drive such as I / O controller, firmware, embedded software. These components are responsible for telling the hardware what to do and how to communicate with the computer. In the table you will also see another part that is the hard drive's buffer. This buffer is a temporary data container, waiting to be written or sent to computer memory. But the speed of modern hard drives today is slower than the data flow interface that is controllable.
If you have a removable hard drive, you will see that each hard drive has one to four platters , each of which is nearly 9cm in diameter. The diameter of the platters used in mobile devices is about 2.5 cm different from the platters in music players, about 4.5 cm with hard drive platter pocket and 6.3 cm with the platter used in notebooks. These platters, also known as disks, are coated with sensitive magnetic materials on both sides and arrange the millimeters to separate into a spindle. There is also an engine in the hard drive that alternates between spindle and platter. Hard disk drives used in notebooks with speeds of 4200, 5400 or 7200 rpm. Current desktop drives are usually 7200 or 10,000 rpm. In general, the higher the rotational speed, the faster the data read.
Magnetic recording
Data is read and written through bit ranges (the smallest unit of digital data). A bit has only two states 0, 1 or on / off. These bits are expressed vertically on the surface of a platter, in a magnetic coating. They are changed (recorded) or recognized (read) by the magnetic part on the reader (write). Data is not only stored on the hard disk in its raw form, but it is first processed with synthetic mathematical formulas. The base program in the drive adds extra bits to the data, allowing the drive to find and correct random errors.
In today's new drives, the vertical magnetic recording mechanism is replaced by a process called perpendicular magnetic recording . In this type of recording the elements are arranged perpendicular to the surface of the platter. Therefore they can be packed closer together with greater density, storing more data. The thicker bit density per inch means that the throughput of the data streams under the reader (write) will be faster.
 Source: Helpwithpcs
Source: Helpwithpcs
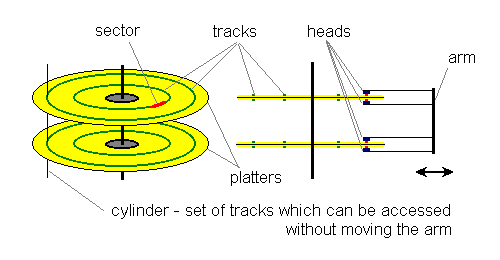
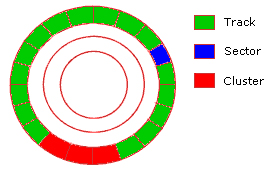
Information is recorded and read from both sides of the disk, using mechanisms mounted on arms , moving mechanically back and forth between the center and outer edges of the disc. This move is called 'seeking' and the speed of movement is called 'seek time'. The search (read) information on the tracks (tracks) is the concentric data circles on the drive. Tracks are divided into multiple logical units called sectors . Each sector has its own address (track number plus sector number), which is used to organize and locate data.
If the read (write) drive does not reach the track you are looking for, you will experience something called latency (latency) or rotational delay, which is mostly average. This delay occurs before a sector rotates below the reader (write) and after it finds the track to look for.
What is a coupling circuit?
Typically, computers use the connection of PATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment) or SATA (Serial ATA) on the hard drive. You can even use both of these connections at the same time as most modern motherboards now offer both types of interfaces. We are in the transition period between PATA and SATA so it is very reasonable to arrange it. PATA interface is still needed in the connection of optical drive in (internal optical drive) to the computer. Parallel in PATA means that data is sent in parallel to multiple data streams. SATA sends data in a series of ways between single twisted pair.
PATA drives (commonly referred to as IDE drives) are developed at different speeds. The original ATA coupling circuit of the 80s supports the largest transfer rate of 8.3 MB / sec, a very fast speed at that time. ATA-2 raised the maximum throughput to 16.6 MB / sec. The next step is Ultra ATA with speeds of 33 MB / sec, 66 MB / sec, 100 MB / sec. And up to 133 MB / sec of Ultra DMA-33 (Direct Memory Access - Direct memory access) via Ultra DMA-133 or Ultra ATA-33 via Ultra ATA-133. The majority then use Ultra ATA-66 or more.
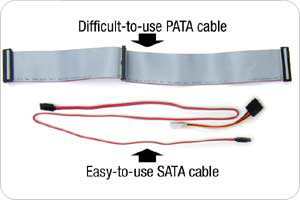
Cable PATA and SATA ( Source: Seagate )
A typical ATA drive uses a 2 inch, 40 or 80 (fiber) cable, although some 40-foot cables are ring-shaped. Desktop drives mainly use 40-pin connectors, 80 extension cables are to physically separate data strands to avoid crosstalk at ATA-100 and ATA-133. Notebook with a 2.5-inch drive uses a 44-pin connector, a 1.8-inch drive uses a 50-pin connector.
At 133 MB / sec, the ATA coupling circuit gradually fails to address the technical challenges. SATA circuit was born to solve ATA problems. Currently SATA has two main speeds: 150MBps and 300MBps and two new 1.5 gigabit / second (gbps) SATA and 3 gbps SATA. But the algorithm of these new versions is quite fuzzy: 3gbps is divided into 8 (the total number of bits in a byte) becomes 375 MBps (not 300MBps). The reason is that the gbps speed is the signal speed; 300MBps is the largest data transfer rate. And so far the connection speed has not been duplicated again. The data transfer rate of single SATA drives is usually maintained at 150MBps. If using RAID mode, providing data from two or more drives to the pipeline will use a larger bandwidth from the 300MBps interface.
SATA drives have a compact cable and smaller connectors than ATA drives. That allows for more connections in the main board and more airflow inside the case. SATA also simplifies installation by using a point-to-point network structure, allowing the use of one connection per port and cable. This structure is much improved compared to jumpers and master / slave connections of the PATA drive, in the structure of a PATA drive a cable is used to connect two drives. Unlike PATA, SATA is suitable for external drives directly attached, allowing the use of 2m cable in one interface, contributing to significantly faster speed improvements than USB 2.0 and FireWire. External SATA has a slightly different connector, improved speed, designed to lock in one place, many corrected errors and complete compatibility.
Another connection interface was quite popular in the past, but is no longer mentioned as SCSI (for Small Computer System Interface). At the time of development, SCSI was a means of storing desktop hard drive execution programs quite quickly. But SATA has gradually replaced SCSI.
Future hard drive
It can be said later that all desktop and mobile hard drives will use SATA communication circuit with orthogonal magnetic recording mechanism. Any new PC will have at least one SATA circuit; You can upgrade your drive to an orthogonal drive when the price is low. Drive capacity will continue to grow with exponential level while execution speed will only grow at an average level.