How does Linux Inode work?
If you use Linux long enough, you will know the term 'inode'. It does appear occasionally, but does not affect what you are doing. The following article will explain what an inode is and how it works.
What is inode?
In a library, all books are sorted by genre, author name or audience age. Like a library, all files in the Linux system are organized for efficient retrieval and use. Inode is an entity that supports file organization in Linux systems.
What is file metadata?
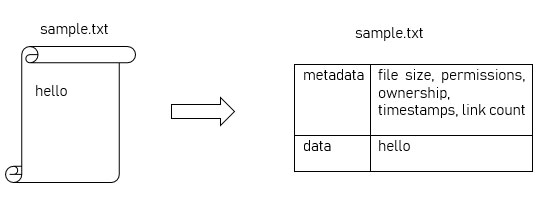
Suppose we have a file named 'sample.txt' containing the data 'hello'.
This file has some data and related information such as file size, permissions, group and user ownership, timestamp created / accessed / modified, number of links, etc. All of this information is collectively referred to as file metadata.
What is the file system?
Refer to the article: Basic File System in Unix / Linux for more details.
Combining concepts together
Inode is a data structure on Ext4 that contains all the metadata for a file.
Of course there will be many files on a file system. As you can guess, each file has its own inode and each inode is numbered.
Inode numbering like?
The number of inodes on a file system starts from the first 1.10 inodes are reserved for system usage. User files have metadata stored from inode 11. All inodes are neatly stacked in an inode table.
An entry in the inode table will have a capacity of 256 bytes. For one file, Linux intelligently sorts all the metadata within this 256-byte range! In addition, each inode for a file will have information about the location of the data in the file system. Remember, only the metadata of the file is stored in the inode.
The total number of inodes in a file system depends on the available space and the number of files that can be stored on the partition.
How are inodes allocated and freed?
When users add files to the newly formatted file system, inodes starting at 11 are allocated to hold file metadata.
There is another data structure called Inode Bitmap , used to track the allocation status of an inode. It is a set of bits that act as a map.
Consider the 8 bits in the inode bitmap to indicate the allocation status of 11 to 18 inodes as shown in the table below. A value of 1 in the bitmap means that the inode has been allocated to hold metadata for a file. A value of 0 in the bitmap means that the inode is currently not in use. Here, you can see that inode 17 is being used.

In the case of a file whose metadata in inode 17 is deleted, its corresponding bitmap status becomes 0 , indicating that it can be freely used by another file.

How to view the inode number for a file?
There are two ways to do this.
The first is to use the ls command with switch -i, followed by the name of the file. The first field in the output is the inode number that has metadata of sample.txt.
The same information can be obtained by stat command followed by the file name.

To see the total number of inodes available for a partition, the df command can be used with the -i switch .
In the '/ dev / sda4' partition, 404854480 inode is available for use, of which only 359044 inode is used.
Inode, inode tables organize metadata of all files meticulously in inodes, along with information about the location of the file data. Note all that the article discussed about Linux inode is just the tip of the iceberg.
 How to make the script executable anywhere in Linux
How to make the script executable anywhere in Linux How Linux stores and manages user passwords
How Linux stores and manages user passwords How to find the MAC address using the command line in Linux
How to find the MAC address using the command line in Linux How to format a hard drive into NTFS in Linux
How to format a hard drive into NTFS in Linux 4 interfaces and Linux distros that can be run on PinePhone
4 interfaces and Linux distros that can be run on PinePhone How to set Terminal as a transparent wallpaper in Kubuntu
How to set Terminal as a transparent wallpaper in Kubuntu