Hard drive industry 'stands between two streams'
Orthogonal recording technology allows for increased storage capacity but still has many limitations. A flash memory that dominates the laptop. Meanwhile, hard drive manufacturers are conflicting when choosing between two new solutions.
" We need to maintain a data density growth of at least 40% to ensure a safe distance from the flash, " said Mark Kryder, Seagate's technical director.

Seagate thermal magnetic recording technology.Photo: CNet .
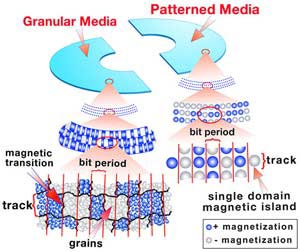
The hard drive stores data in bits (tiny spots on the hard disk). Each bit is made up of about 50-100 platinum cobalt particles. When particles are magnetized, the bits will be displayed as 1 or 0. In order to increase the area density, engineers must shrink bits and particles year by year, allowing the storage capacity of the hard drive to be expanded. from several megabytes to over 100 gigabytes.
However, reducing the size of particles can cause problems when they operate at room temperature. This phenomenon is called "superparamagnetic effect" by experts. Some manufacturing companies have spent a lot of time developing orthogonal technology, but this solution has not eliminated this limitation.
In the face of this situation, the largest hard drive manufacturer Seagate has introduced "magnetic thermal recording" technology, converting cobalt particles into platinum ions. The integrated laser in the drive will heat a specific bit during the system recording or deleting the data. After that, this bit will quickly be cooled again.
However, " the above method requires the use of new materials, smaller dot dot design and more flexible thermal gradients ," commented John Best, Hitachi's technical director.
Therefore, Hitachi Global Storage Technologies, the world's second-largest hard drive manufacturer, is studying an "intermediate" solution. Intermediate technology still uses traditional platinum particles but can reduce the number of particles per bit from 100 to 10 by separating the bits into dots (showing bits close to each other, forming a chain of interlayer link).
Hitachi's intermediate technology.Photo: CNet .
This method should be done with e-beam lithography (electron beam). But the introduction of e-beam and lithography technology into mass production lines is not simple and relatively expensive.
If Seagate and Hitachi combine heat and intermediate technology, they can produce hard drives with the capacity to store up to 50 - 100 terabit / inch2, 280 fold - 560 times 178.8 gigabit / inch2 density in upcoming products. was released by Toshiba.
However, both methods are only discussed in paper and the data given are only true in the laboratory, but none of the companies have released a simulation model.