As powerful as computers, why don't smartphones need cooling fans?
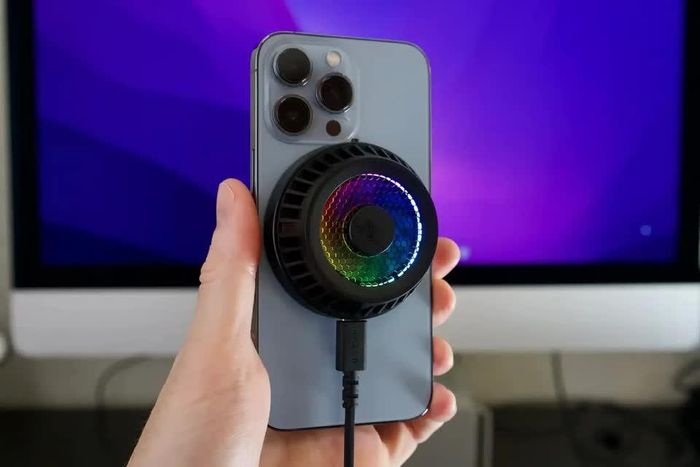

The processing power of smartphones gradually increases over time. If you take into account some performance evaluations (benchmarks), some high-end phones today are more powerful than mid-range desktop computers, and even have graphics capabilities that surpass ultrabooks using integrated Intel graphics cards. .
However, for many different reasons, most smartphones do not have cooling fans like computers.
Design does not allow it
Phone manufacturers spend years making products as thin as possible. These handheld devices would not be able to reach a thickness of a few millimeters if they had to contain a cooling fan.
This is a bulky component that requires space to move the fan blades and is easily damaged if impacted. Normal actions when using a smartphone such as putting it in your pocket while jogging, throwing it on the bed. can all cause damage to the fan.
If you place the device in a cramped place that doesn't dissipate heat well like a pocket, it will cause the fan to operate at full capacity and make loud noises, while the device's processing ability will gradually deteriorate. This situation is similar to the user placing the laptop on a pillow, causing the cooling slots to be blocked and performing intense work.
Besides, imagine you're carrying a miniature version of your laptop in your pocket. If it is not so hot that it makes you feel uncomfortable, it will turn off automatically after a certain period of time, instead of operating continuously like a smartphone.
Cooler mobile CPU
When mentioning the power saving ability of CPUs, we will come across the term "thermal design power" (Thermal Design Power - TDP). TDP is often measured in W, representing the maximum heat that the CPU generates when operating at its highest power level.
Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 is a mobile chip designed for high-end smartphones, able to play games that require strong processing capabilities. It has a TDP of 12.5 W, a figure higher than the 5 W of early Snapdragon CPUs but only on par with lower-power Intel CPUs.
The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 graphics card has a TDP of 450 W, and that's just one component of the PC. That level of power usage is unfeasible for a mobile device with a limited battery, which also generates more heat than passive cooling can handle.
That's part of the reason desktops and laptops need fans, while phones don't. At the same time, this is also the reason why smartphones, no matter how powerful, cannot match the graphics capabilities of specialized gaming computers.
So how can the phone's CPU be both powerful and cool?
There are various methods, including throttling CPU activity to keep temperatures consistent, controlling network traffic, and clocking (stopping processor logic for a few microseconds at a time).
Mobile applications generate little heat
Software does not take up physical space, but it greatly affects heat generation. Some forms of software or sub-optimal code will require more power.
If the application constantly requests a network connection and calls background processes, the device will need more power and generate a lot of heat. When creating a mobile app, developers need to pay attention to this factor.
If the application causes the battery life to decrease, the device becomes hotter and requires frequent charging, the user will not like to use it. Therefore, usually mobile apps will focus on this issue.
Passive cooling system
Some phones are equipped with fans, such as the Lenovo Legion Phone Duel 2, but this design is very rare. Smartphone manufacturers consider other options to make devices in case the device operates at high capacity.
One method used is vapor chamber cooling, which uses evaporation and condensation of liquid to cool components.
For example, the Samsung Galaxy S23 series uses a vapor chamber cooling system. Previously, the Galaxy Note 9 also had a liquid cooling system inside a carbon tube. Similarly, Xiaomi also introduced Loop LiquidCool passive cooling technology for high-end smartphones.
Additionally, instead of placing the fan inside the phone, users have the option of mounting it on the back. That's Asus' approach with the AeroActive Cooler 6. This is an accessory for the ROG Phone 6, a phone that uses graphite panels inside to conduct heat. The company has now launched the AeroActive Cooler 7 version.
You should read it
- How can smartphones change our way of thinking?
- What was the 'first smartphone' like?
- 10 super useful new features of smartphones that few people know
- Sony will use MediaTek processor for high-end smartphones
- 5G Qualcomm modem will be available on mid-range smartphones next year, officially opening the era of 5G universalization
- 10 beautiful photography tips with smartphones
 New features on iOS 17.5 help iPhone users limit being tracked
New features on iOS 17.5 help iPhone users limit being tracked Millions of iPhones will be 'transformed' thanks to iOS 18
Millions of iPhones will be 'transformed' thanks to iOS 18 What was the 'first smartphone' like?
What was the 'first smartphone' like? Apple's cheapest iPhone was revealed, inherited from iPhone 14 and iPhone 15
Apple's cheapest iPhone was revealed, inherited from iPhone 14 and iPhone 15 Should I buy an iPhone with 128 GB internal memory?
Should I buy an iPhone with 128 GB internal memory? Samsung's Bixby virtual assistant is smarter thanks to AI creation
Samsung's Bixby virtual assistant is smarter thanks to AI creation