8 Simple Ways to Browse the Web Safely
Nowadays, surfing the web to find information as well as serve your work is very necessary. However, along with it are dangers lurking, threatening you. If you implement one of the following tips, you can be sure that you will surf the web more safely on the Internet environment.
1. Always keep your browser updated
When you update your browser, you don't just get access to new features and bug fixes. You also get better protection against security flaws and malware thanks to the security fixes that come with each new release. Don't miss out on this update protection and put your data at risk. Update your browser to the latest version now.
But if you have turned off automatic updates to save bandwidth when traveling, you should update your browser manually. Using an updated browser on an unsupported version of your operating system can also be a security risk. Upgrade your operating system or at least find a more secure browser to browse the web.
2. Use HTTPS
Websites using the HTTPS protocol are capable of encrypting information as well as user activities on the Internet. Instead of only accessing websites using the http protocol, you can replace this phrase with https before each website address you want to view. However, not all websites support this protocol. So get into the habit of not accessing websites that do not use https in public places.

You can use the HTTPS Everywhere add-on to force your browser to make an encrypted connection to popular websites. The add-on is compatible with Chrome and Firefox on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
3. Expand the shortened URL
Be careful when clicking on short URLs as they may not always be safe. A short URL may be hiding a phishing link that downloads malware to your computer or redirects you to unwanted and/or inappropriate web content.
A web app like CheckShortURL is all you need to get rid of this. For any short URL you copy-paste into the app, it will display the corresponding long URL. If the extended URL doesn't match the site and content you're expecting, leave the shortened URL alone.
Additionally, you can use a browser extension like Unshorten.It to quickly check if a shortened URL is safe. You can even take a screenshot of the website before deciding to visit the link.
4. Browse anonymously if using a borrowed computer
Whether you're looking up information on a computer at the library or checking your email from a friend's computer, it's best to do so using your browser's private or incognito mode. When you surf the web in private mode, none of your browsing history is saved to that computer (but your downloads are).
Remember that private browsing does not make you anonymous online and you can still be tracked.
Private browsing is useful even on your computer - you can go incognito to check price differences, log into a second account on a website, buy surprise gifts, etc.
You'll also want to create a guest profile in your browser if you're allowing someone to browse from your computer. Setting up a guest user account with limited permissions is even better.
If you don't use your computer often and browse on shared computers, consider carrying a portable version of your browser on a USB stick. Your browsing data is backed up to the USB and no trace is left on the shared computer.
5. Enable security and privacy features in the app
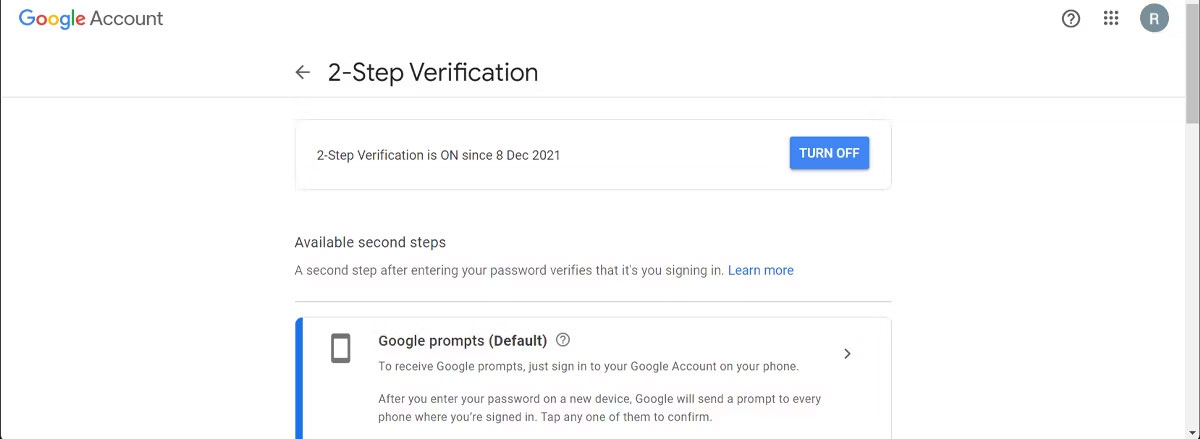
Most services, apps, and devices have at least a few basic settings designed to protect your online activity. Also, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) and add access codes to apps that contain sensitive information. Don't forget to secure your smartphone browser—it's just as vulnerable as your desktop browser.
If you're looking for a convenient solution while still keeping your account secure, there are a number of multi-factor authentication (MFA) apps you can try.
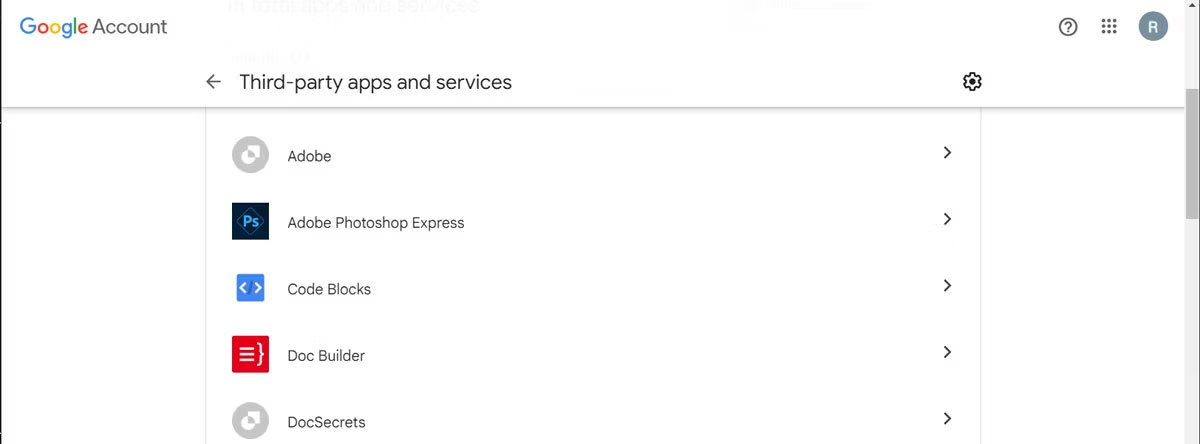
Every month or so, check your Google, Facebook, and Dropbox accounts (plus any others) and look through the list of third-party apps that can access them. If you find any apps that you haven't used in a while or are acting suspiciously, revoke their permissions.
6. Look carefully before clicking
What happens when you surf the web? Your eyes are bombarded with interesting links. You see them and you click on them. It's just this kind of impulsive behavior that can get you into serious trouble because you could be clicking on a virus-laden download link, a fake website, or a well-disguised scam.

Pay attention to the links you click. Take a quick look at your browser's status bar to see the URL behind the link and see exactly what you're clicking. If it's a shortened URL, expand it as discussed above.
To protect yourself from unsafe areas of the web, you should install Web of Trust (WOT). It's a browser extension that scores websites on their trustworthiness, making it easy for you to decide whether it's safe to visit them.
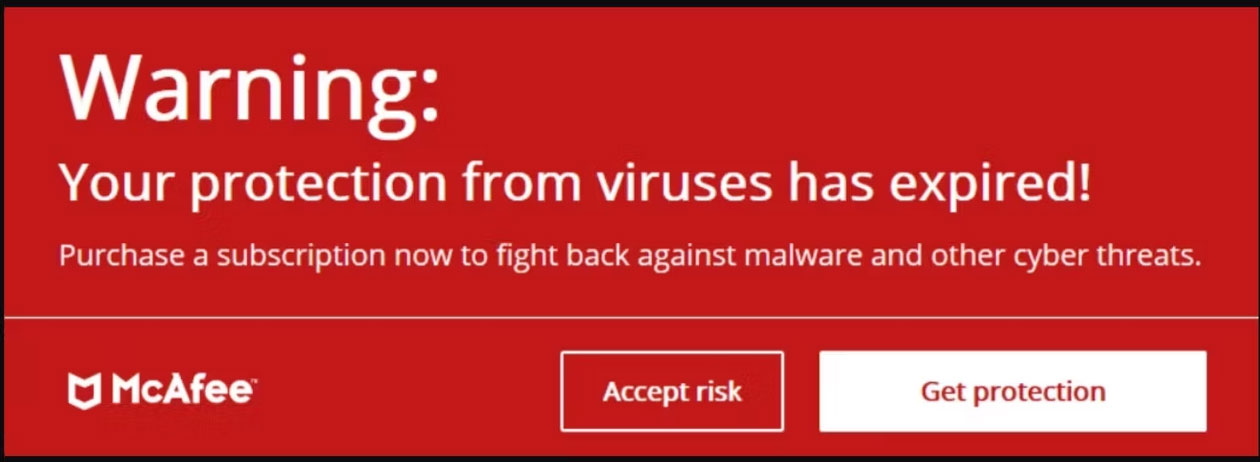
Stay away from alarm banners that claim your computer is at risk or is full of viruses and that you need to download this or that cleaner to fix things. Also, learn what security symbols to look out for and how to deal with security certificate errors.
All your efforts to protect your privacy will be undermined if you are not careful about what you post on social media and other sites. Be careful about leaving important information like your home location, travel destinations, or credit card number on public platforms.
7. Install the appropriate extensions
Feel free to delegate some of your browser security duties to extensions. For example, if Google Chrome is your default browser, check out TipsMake.com's list of the best security add-ons.
A word of warning here: Even extensions can be scams. Try to stay informed about the latest security and privacy threats that are emerging so you can avoid them in time.
8. Use a VPN
VPN or Virtual Private Network is a technology that allows users to create their own secure connection over a public network (usually the Internet). With VPN, all of the user's Internet traffic is encrypted; and the traffic is rerouted through a VPN server instead of using the usual ISP. In short, all of the user's data is protected when they are online.

VPNs not only protect user data, but are also used to access geographically restricted websites. Users can choose to use free or paid VPN applications. Of course, paid VPN applications will support more features and provide faster data transmission speeds.
Among the paid apps, HideMyAss is a recommended choice. As for the free product, CyberGhost is also a simple and easy-to-use option. The only limitation of VPN is the connection speed. However, considering the advantages that this technology brings, this sacrifice is worth it.
Website security should be a top priority for both website owners and Internet users. Never take security for granted when browsing the web. Check for certificates, customer reviews, trust seals, and legal compliance. Also, make sure you equip yourself and your business with the best tools to prevent and deal with cyberattacks of all kinds.
Refer to the red flags on unsafe websites for additional points to watch out for.