6 Powerful Excel Features Most People Never Use
Even the simplest spreadsheets—budgets, lists, trackers, etc.—can benefit from powerful features in Microsoft Excel that people often avoid because they seem too complicated. In fact, they're easier than you think and can save hours of work.
6. Quick Analysis
Let's say you have a spreadsheet containing sales records. When you highlight some cells, the Quick Analysis tool in Excel will immediately suggest doing the following for you:
- Calculate total revenue or number of units sold
- Add a chart you can use to visualize total profit by region
- Apply color grading to highlight your most profitable orders
- Convert data into Excel tables for easier filtering and sorting
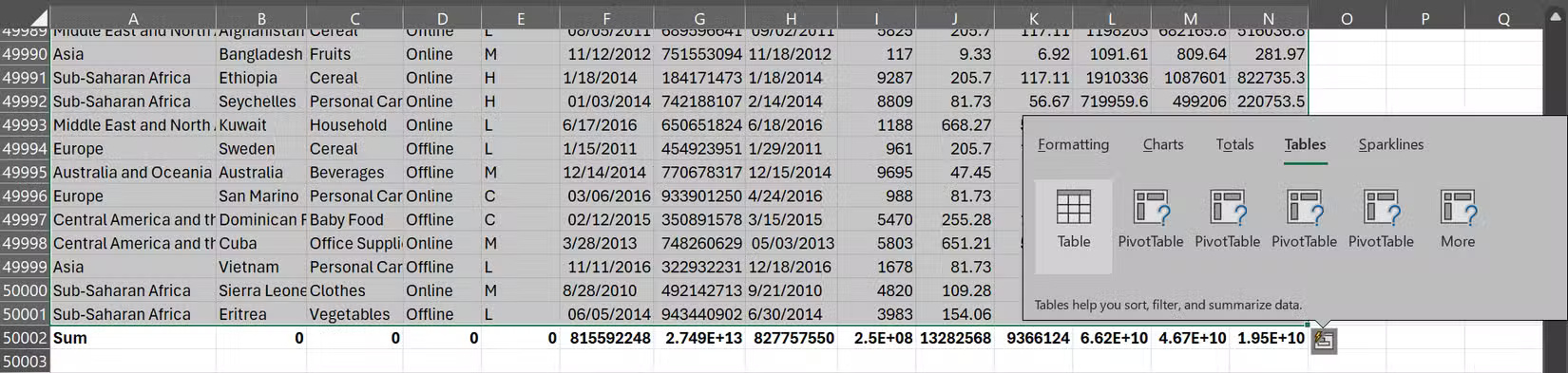
Here's how it works: When you select any range of cells in Excel, a small icon will appear in the lower-right corner (it looks like a square with three lines and a lightning bolt). Click this icon or simply press Ctrl + Q , Excel will immediately display a menu with five analysis categories: Formatting, Charts, Totals, Tables, and Sparklines.
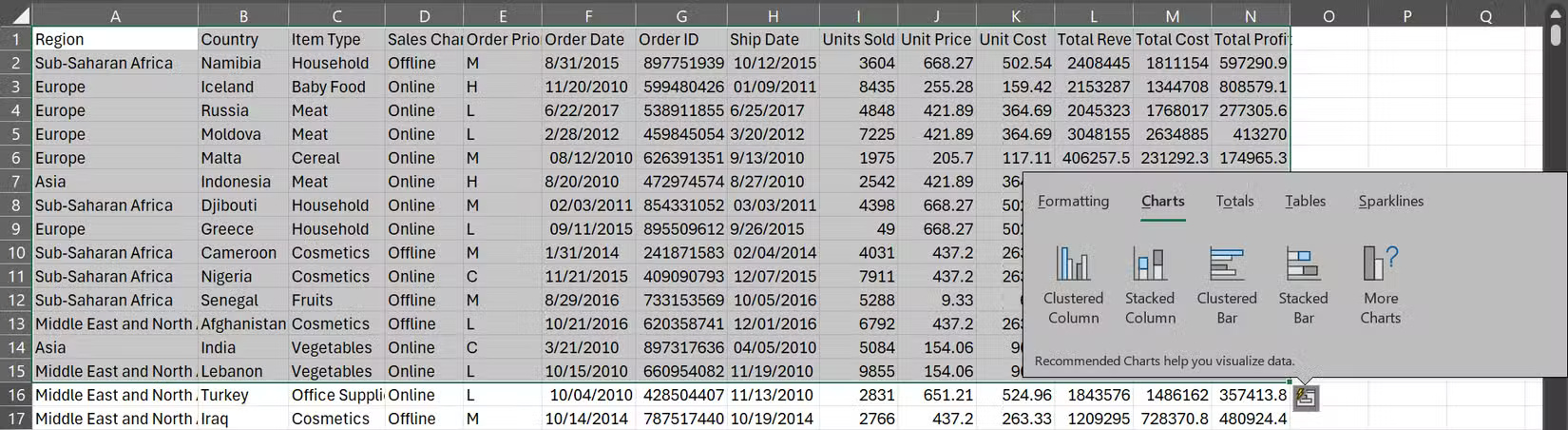
Within each of these categories, you'll find options tailored to your specific data. When you highlighted 15 rows with all 14 columns from your sales records spreadsheet, Excel suggested Clustered Column, Stacked Column, Clustered Bar, and Stacked Bar charts in the Charts category.
5. Data Validation
Imagine you're collecting RSVPs for your wedding. You'll need guests to confirm their attendance, select their preferred food, and possibly indicate whether they're bringing someone else. Without Data Validation, you'll likely get a chaotic array of responses: Yes, y, Attending, Chicken, Veggie, 1, one , or even fields that are completely blank.
Here's an example of how you can avoid such a data cleanup headache:
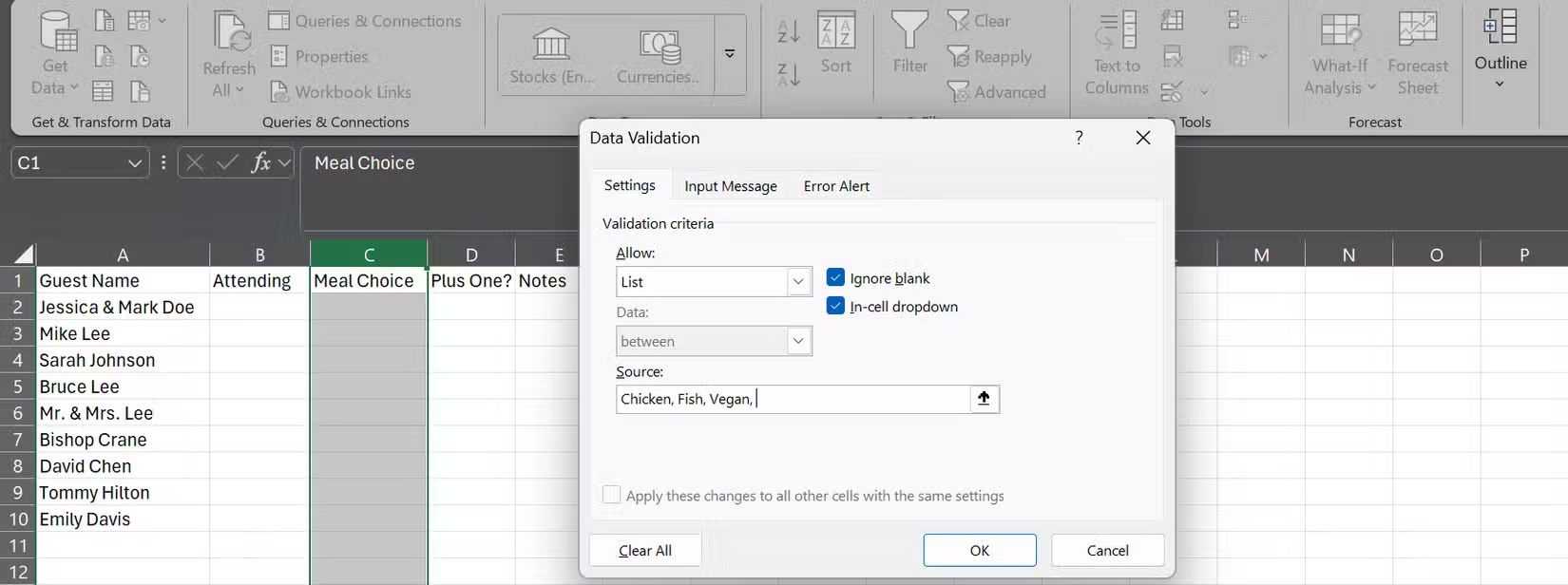
- Highlight the Meal Choice column and go to the Data tab .
- Find Data Validation in Data Tools . You'll recognize it by the icon with two rectangles, one showing a green check mark and the other showing a red error mark.
- Click on it, select List under Allow and enter the allowed values, separated by commas.
- Click OK > Apply , depending on your version, and you're done!
Now, when someone tries to insert a meal outside the allowed list, they will get an error message.
4. PivotTables
PivotTables in Excel may seem complicated, but they are actually one of the easiest ways to make sense of large data sets. Most people avoid them because they think only advanced users need them. But that's not the case.
Let's say you have a 30,000-row sales spreadsheet and your boss wants to see total profits by region.
Instead of spending hours writing formulas and filtering data, you can create a PivotTable in about 30 seconds:
- Select any cell in the data.
- Go to Insert > PivotTable > From Table/Range .
- Select New Worksheet and click OK .
- Drag Region to the Rows area and Total Profit to the Values area .
Immediately, you'll see each region and its total profit neatly summarized.
3. Flash Fill
This feature is basically a way for Excel to read your mind. You tell Excel what you want by entering an example or two, and Excel automatically figures out the pattern and does the rest.
If you have a column of full names, such as Jessica Doe and Sarah Lee, and need to separate the last name into a separate column, you don't need to type each name manually. Just type Doe in the cell next to Jessica Doe, press Enter , then start typing Lee in the next cell. Excel will recognize the action and offer to complete the entire column for you.
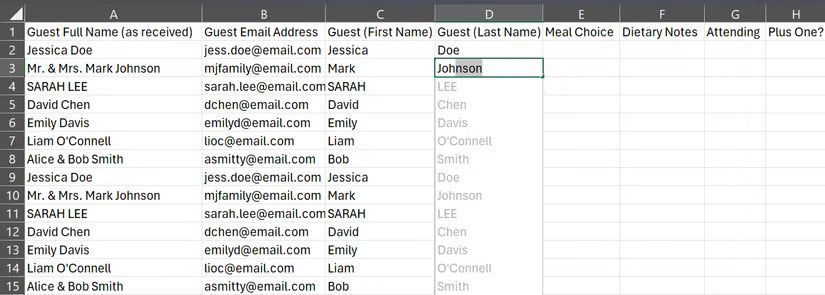
2. Formula Auditing
We've all been there: A formula suddenly throws a weird error, and you wonder if you made a typo somewhere in row 247. Luckily, Excel's Formula Auditing tool can pinpoint the exact error in just a few seconds.
Let's say you're calculating profit margins across hundreds of rows. You might have a Total Margin column (divide Total Profit by Total Revenue) and an Adjusted Margin column (multiply Total Margin by 0.9).
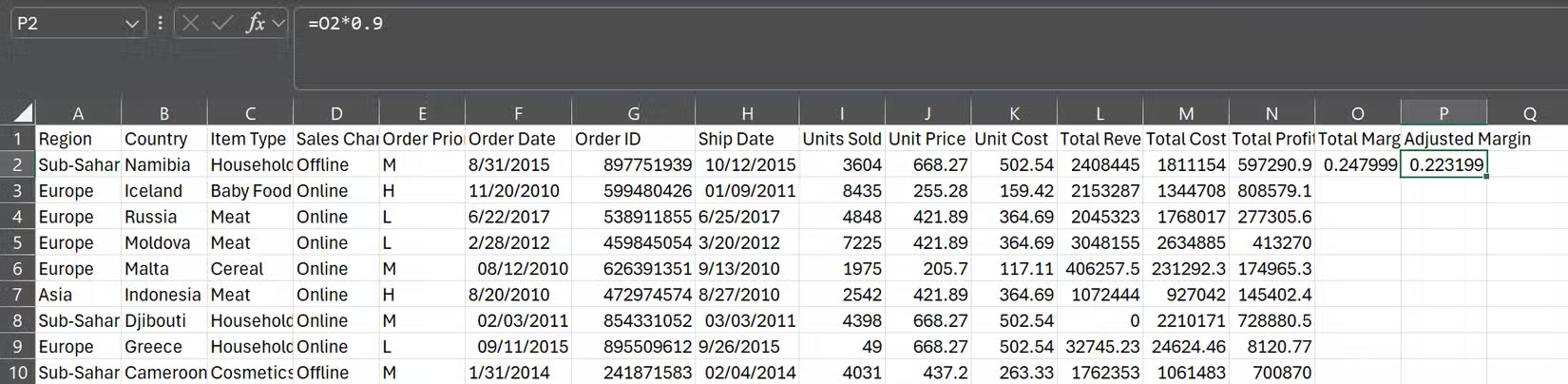
Everything looks perfect until you scroll down and see error messages scattered throughout the data. That's where Formula Auditing comes in.
Highlight any cells that show errors and go to the Formulas tab . Click Trace Precedents , and Excel will draw arrows pointing to the exact cells where the formula entered the error. With experience, you'll usually spot the problem right away - maybe the total sales are zero, you're referencing an empty cell, or the cell contains text instead of numbers.
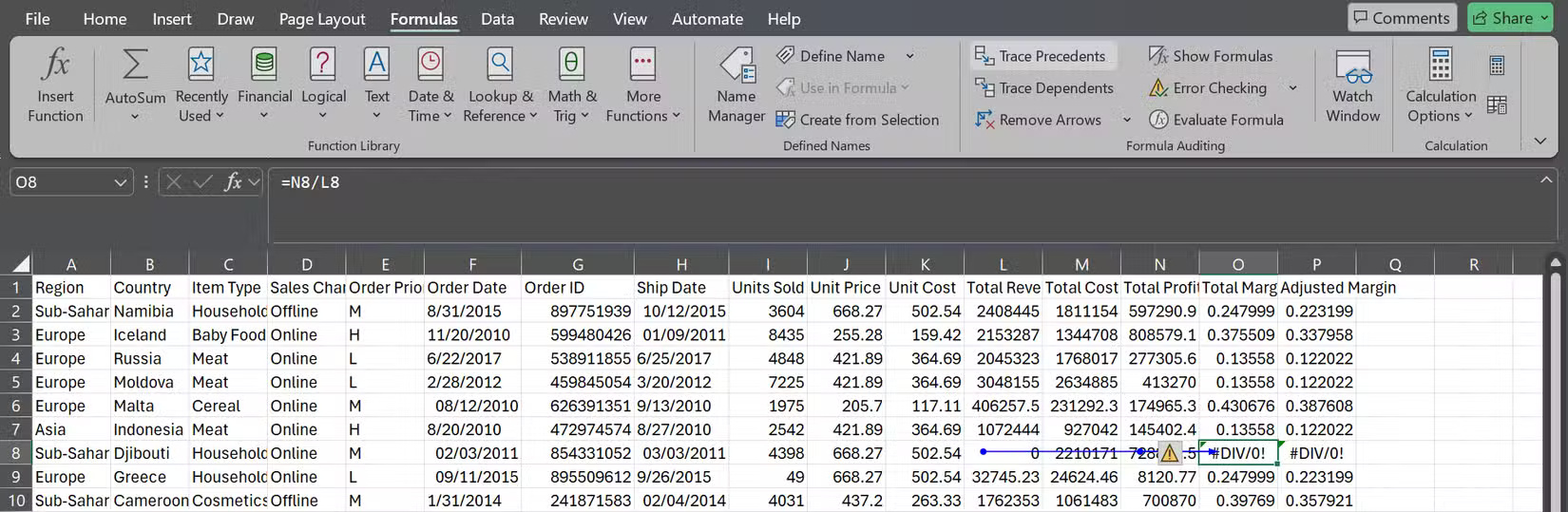
Trace Dependents works in reverse and can be even more useful. You can highlight any cell to see what other formulas rely on that cell. This is extremely useful when you are about to delete or modify a cell and want to know what else might be wrong.
1. Conditional Formatting
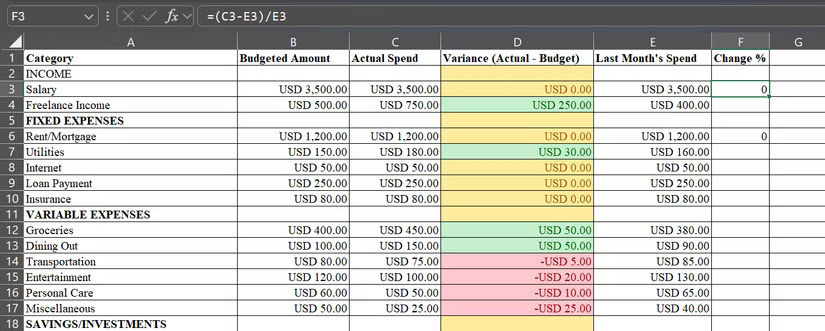
Spreadsheets are just numbers until you put them into context. Take a budget spreadsheet, for example. You'll have to look at it for a while before you can understand how much you've actually spent throughout the month.
Instead of manually comparing your actual spending to your budget across twenty different categories, you can use Conditional Formatting to bring your spreadsheet to life, so you can see at a glance where you overspent and where you could save. In your monthly budget, have a Variance column that shows the difference between your budgeted amount and your actual spending. Then let Conditional Formatting do the hard work.
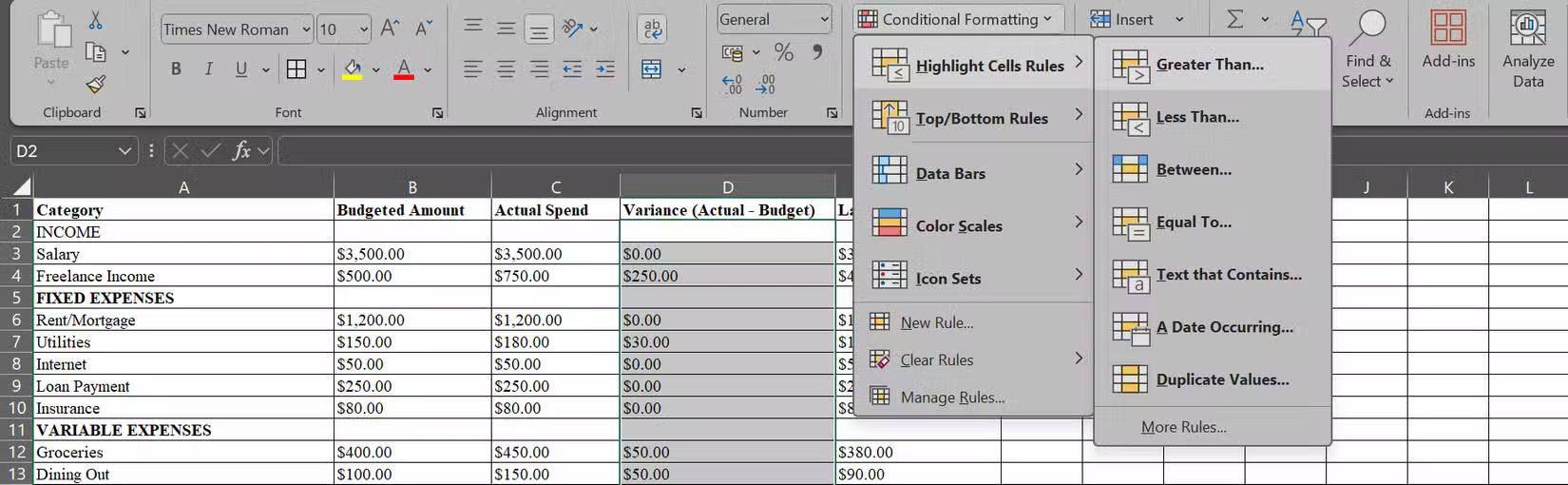
First, select all the cells in the Variance column and click Conditional Formatting on the Home tab before doing this:
- For overspending: Click Highlight Cells Rules > Greater Than , enter 0 in the cell, and choose a highlight color (perhaps a light red fill with bold red text).
- For underspending: Go back to Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cells Rules > Less Than , enter 0 again, and choose a different color.
- For exact spending: Use Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cells Rules > Equal To , enter 0 again and choose a different color.
Instantly, positive numbers (overspending) turn green, negative numbers (savings) turn red, and exact matches stay yellow. At a glance, you can see everything you need to know about your monthly spending.
Mastering even a few of these features can change the way you work in Excel. They're not just power tools, they can save you time and help you work like a pro.
You should read it
- Link download Microsoft Excel 2019
- MS Excel 2007 - Lesson 7: Create Macros in Excel 2007
- MS Excel - Lesson 11: Solving the problem of Excel Help feature?
- Use 300 powerful features in Excel with the Kutools utility
- Difference between function and formula in Excel
- Summary of expensive shortcuts in Microsoft Excel
 Here's What Hackers Hope You Never Do With Your Email!
Here's What Hackers Hope You Never Do With Your Email! 5 Ways to Get YouTube Premium for Cheap
5 Ways to Get YouTube Premium for Cheap How to convert images to text in Google Sheets
How to convert images to text in Google Sheets How to Improve Spotify 10x With This Simple Mod
How to Improve Spotify 10x With This Simple Mod How to show Outlook notifications without time limit
How to show Outlook notifications without time limit 7 Best Hacking Apps for Android
7 Best Hacking Apps for Android