Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 4
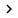 Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 1
Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 1
 Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 2
Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 2
 Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 3
Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 3
In this article, I will show you some more tests that can be performed on the Domain Controller Diagnostic Tool.
We finished the previous section in this series by talking about some of the individual tests that you can do with the Domain Controller Diagnostic tool. In this section, we will continue and mention some other tests.
DCPROMO
Some of the tests available through the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility are often unknown. In contrast to the fact that they are very useful, the DCPROMO test is one of them. It is designed to allow you to test server readiness before strengthening to a domain controller. This makes it easier to enhance a server to a domain controller. Just enter the DCPROMO command, click Next a few times to find the issues that need to be adjusted.
If you use the DCPROMO test, you will have to use at least two additional command conversions with it. The first switch that you need to use is / DNSDomain. You must use this command switch to tell the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility which domain the server will be creating a Domain Controller inside.
Next, switch the command / DNSDomain to switch the second command to tell the utility what is the intent of your server. For example, if the server will be a Domain Controller in a new forest, it needs to be tested differently than the server will be an extended Domain Controller in the existing domain.
The command switch you use here is to tell how the Domain Controller diagnostic utility will fit into an existing Active Directory structure. The order conversion is:
/ NewForest
/ NewTree
/ ChildDomain
/ ReplicaDC
For example, if you want to use the server as an extended Domain Controller in an existing domain called Contoso.com, the full syntax of the command will be:
DCDIAG / test: DCPROMO / DNSDomain: Contoso / ReplicaDC
However, there is one problem that I want to mention is that if you use the / NewTree command switch, you will have to use the third command switch named / ForestRoot. Simply put after converting / ForestRoot a colon and the name of the root domain (/ForestRoot:Contoso.com).
DNS
There may be many friends for the Domain Controller diagnostic utility as a mechanism for running diagnostic tests on Domain Controllers. However, this utility has a series of tests designed to help you diagnose problems with your DNS server. This is not surprising because the Active Directory completely depends on the Domain Name Services and the first Domain Controller in the forest is usually configured to act as a DNS server.
DNS tests are used for many different tests, any test can be done separately. If you call a DNS test but don't specify any additional conversions, the diagnostic tool will run all as small tests within it. The ignored test includes external domains. We will introduce this test in a few moments. Before we do, however, we want to give you a list of tests that can be performed when the DNS test runs without any extra command switching. Figure A below shows some of the default DNS test types when executed.
Test typeConvert commands for test execution
Description for test
Basic diagnostic test
/ DNSBasic
This is a basic diagnostic test, done at any time when performing a DNS test. This test cannot be ignored, regardless of which command switch is used.
Hiệu lực và root hint thử
/ DNSForwarders
Check who 's forwarding its DNS and root hint server.
Delegation test
/ DNSDelegation
Check the DNS server delegation
Dynamic Update Test
/ DNSDynamicUpdate
Check to see which part of the DNS namespace is authorized by the DNS server.
Record Registration Test
/ DNSRecordRegistration
Verify that the logs can be registered on the DNS server.
Picture A
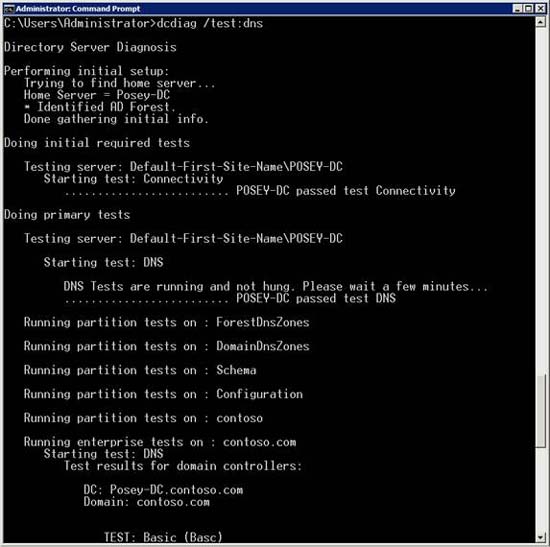
Figure B: This is what you see when you perform the default DNS test
We mentioned above that only the test is not run by default when you specify that you want to test the DNS configuration to test the external name solution. There are some command conversions you can use if you want to run this test.
One option is to use the / DNAAll command switch. Converting this command tells the diagnostic utility to run all DNS-related tests, including testing an external name solution. The syntax of this command is as follows:
DCDIAG / TEST: DNS / DNSAll
You also have an option to call an external name test instead of wrapping tests with any DNS-related tests that the utility can run. If you want to call some external name test, you can do so by specifying the / DNSResolveExtName command switch.
In case you're still wondering, the external name resolution test might try to resolve with the Microsoft.com domain. However, you can specify another external domain name to be resolved by adding the switch / DNSInternetName switch, associated with the name you want to resolve.
SysVolCheck
One of the simplest tests that the diagnostic utility can perform is SysVolCheck. This test performs some basic tests for different Active Directory partitions including the forest DNS zones, the domain DNS zone, the schema, the configuration partition, and on the domain partitions. You can see what this SysVolCheck test type does when executed in Figure C.
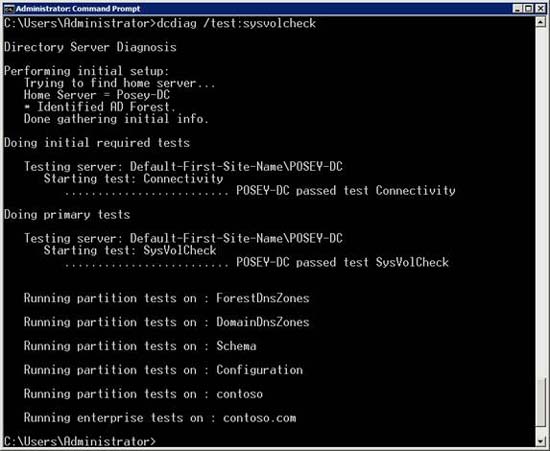
Figure C
The SysVolCheck test type performs some initial connection tests, then tests other Active Directory partitions.
FrsEvent
The last test we want to mention here is FRSEvent. FRS stands for File Replication Service. This test will check if the File Replication Service feels any operational errors. This is important because if the FRS crashes, the domain controllers may lose synchronization, which may prevent policies from being applied properly until the problem is fixed.
Conclude
In this section, I have shown you some tests that you can run using the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility. In the next part of this series, we will introduce some more tests.
You should read it
- ★ Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 1
- ★ Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 5
- ★ Working with the Domain Controller Diagnostic Utility - Part 2
- ★ Fix Xbox One game console not working
- ★ Instructions for creating a Domain Controller - DC on Windows Server 2012