What is VPN? Advantages and disadvantages of VPN virtual private network
For those who are new to school, new to the field of Information Technology - IT, to those who work. surely they have heard the word VPN, or virtual private network, virtual personal network many times. . So what really is VPN, what are the advantages and disadvantages of VPN? Let's discuss with TipsMake.com the definition of VPN and how to apply this model and system in work.
1. What is a VPN virtual private network?
VPN is a virtual private network, Virtual Private Network, which is a network technology that helps create a secure network connection when participating in a public network such as the Internet or a private network owned by a service provider. Large corporations, educational institutions, and government agencies use VPN technology to allow remote users to securely connect to their agency's private network.

A VPN system can connect many different sites, based on region, geographical area. similar to the Wide Area Network (WAN) standard . Besides, VPN is also used to "diffuse" and expand Intranet models to transmit information and data better. For example, schools still have to use VPNs to connect school campuses (or between branches and headquarters) together.
If you want to connect to the VPN system, each account must be authenticated (must have Username and Password ). These account authentication information are used to grant access through a data - Personal Identification Number (PIN) . These PIN codes are usually only valid for a certain period of time (30 seconds or 1 minute). .
When connecting a computer or another device such as a phone or tablet to a VPN, the computer acts as if it were on the same local network as the VPN. All traffic on the network is sent over a secure connection to the VPN. Thanks to that, you can securely access internal network resources even when you are far away.
You can also use the Internet as if you were in the VPN's location, which offers some benefits when using public WiFi or accessing blocked, geo-restricted websites.
When browsing the web with a VPN, your computer contacts the website through an encrypted VPN connection. All requests, information, and data exchanged between you and the website will be transmitted in a secure connection. If you use a VPN in the US to access Netflix, Netflix will see that your connection is from the US.
Although it sounds quite simple, in reality VPN is used to do many things:
- Access to business network while away: VPNs are often used by business people to access their business network, including all resources on the local network, while on the road, traveling or traveling. tourism,. Resources in the internal network do not need to be in direct contact with the Internet, thereby increasing security.
- Access your home network, even when away from home: You can set up a private VPN to access when away from home. This will allow you to remotely access Windows via the Internet, use files shared on the local network, and play games on your computer over the Internet as if you were on the same LAN.
- Browsing anonymously: If you are using public WiFi or browsing on non-https websites, the security of data exchanged on the network will be easily exposed. If you want to hide your browsing activity to keep your data more secure, you should connect to a VPN. All information transmitted over the network will now be encrypted.
- Access websites blocked by geo-restrictions, bypass Internet censorship, bypass firewalls,.
- Download files: Downloading BitTorrent on VPN will help increase file download speed. This also helps with traffic that your ISP may interfere with.
2. Important features of VPN
Encode

One of the main functions of a VPN is to block attempts by unauthorized users to intercept, read, or change the content of your Internet traffic. It achieves this by converting your actual data into an unreadable format, through a process called encoding.
Data is protected by encryption keys set only by authorized users. To decrypt data, you will need a similar decryption key. VPNs encrypt your data as it enters the VPN tunnel and then transform it back into its original format at the other end.
There are 3 types of encryption techniques that most VPNs use. That is:
Symmetric encryption : Symmetric encryption is an ancient form of cryptography that uses an algorithm to transform data. 'Key' is an element in the algorithm that changes the entire result of the encryption. Both the sender and receiver use the same key to encrypt or decrypt data.
These algorithms group data into a series of grids and then shift, swap, and shuffle the contents of the grids using keys. This technique is called block cipher and is the basis of frequently used key encryption systems including AES and Blowfish.
- AES : Advanced Encryption System or AES is a block encryption authorized by the US government and used by most VPN services worldwide. It breaks down the data stream into an array of 128 bits, equivalent to 16 bytes. Keys can be 128, 192, or 256 bits long while blocks are 4x4 byte grids. If you are not familiar with data units, you should learn to distinguish bits and bytes. The length of the key determines the number of encryption rounds or conversions. For example, AES-256 performs 14 rounds of encryption, making it extremely secure.
- Blowfish : Users who do not trust the security provided by AES will use Blowfish. It uses an open source algorithm, which is why Blowfish is also included in the open source OpenVPN system. However, on a technical level, Blowfish is weaker than AES because it uses 64-bit blocks - only half the size of the AES grid. This is why most VPN services prefer AES over Blowfish.
Public key encryption : An obvious flaw with symmetric encryption systems is that both the sender and receiver need to have the same key. You will have to send the key to the VPN server to begin communication. If interceptors somehow obtain the key, they can decrypt all data encrypted with that key. Public key encryption provides a solution to security risks during key transmission. Public key encryption systems use two keys, one of which is public. Data encrypted with a public key can only be decrypted with the corresponding decryption key and vice versa.
Hashing : Hashing is the third encryption method used by VPNs. It uses Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) to preserve data integrity and confirm that the data came from the original source.
Split tunneling
Split tunneling is a popular VPN feature that allows you to choose which apps to secure with the VPN and which apps can function properly. This is a useful feature that helps you keep part of your Internet traffic private and route the rest through your local network.
Split tunneling can be a useful tool to save some bandwidth because it only sends part of your Internet traffic through the tunnel. So if you have sensitive data to transfer, you can protect it without experiencing the inevitable lag in other online activities caused by VPNs.
Data and bandwidth limits

Data and bandwidth limits are limits that determine the amount of data you can transfer or the bandwidth you can use at a time. VPN services use data and bandwidth limits to control the amount and speed of data flow across the network.
It is important for VPN service providers to maintain limits to prevent network congestion and outages. However, premium service providers with extensive infrastructure such as ExpressVPN, NordVPN, PIA, and Surfshark do not place any data and bandwidth limits on usage.
No-logs policy
A no-logs policy is a VPN service provider's promise to never keep records of its users' online activities. The no-logs policy is a major selling point for VPNs as it is one of the main reasons people use VPNs in the first place.
Not many VPNs offer complete no-logs, and even the ones that do strictly no-logs tend to store some logs. If you're not sure which VPN to choose that's truly zero-logging, look for services that only use server RAM. Such servers store temporary data that is deleted when the hardware is turned off.
Connect multiple devices simultaneously

Simultaneous connections refer to the number of devices that can connect to the VPN at the same time. Most VPNs set limits on simultaneous connections, and only a few of them can accommodate unlimited connections at a time.
One thing to remember with multiple device connections is that you can install VPNs on as many devices as you want, but you can't have them running on all of them at the same time.
Kill switch

VPN kill switch is a feature that disconnects your device from the Internet if the VPN connection is suddenly disconnected. This is an important VPN feature that prevents you from sending data outside the secure VPN tunnel.
Protection against IP leaks
The main purpose of using a VPN is to hide your real IP address from prying eyes. But sometimes your original IP address can be exposed, revealing your location, browsing history, and online Internet activity. Such an incident is called an IP leak and it defeats the purpose of using a VPN.
Many top VPNs have built-in IP/DNS leak protection enabled by default. They also provide tools to check your real IP and the address assigned to you by the VPN. With an active VPN connection, the two IP addresses should not match.
IP Shuffle
IP Shuffle is a VPN security feature that randomizes your IP address. VPNs do so by reconnecting you to another VPN server after a certain period of time. Most VPNs allow users to set this random connection frequency with a variety of options, from every 10 minutes to every 1 hour or once a day.
3. Commonly used protocols in VPN
VPN products often offer a wide variety of convenience, efficiency, and security. If security is a top concern, then an organization needs to pay attention to the protocols that the VPN service supports. Some widely used protocols have concerning weaknesses, while others offer state-of-the-art security. The best protocols today are OpenVPN and IKEv2.
Learn about VPN protocols

The nature of the VPN protocol is a set of protocols. There are several functions that every VPN must address:
- Tunneling (technique for transmitting data across multiple networks with different protocols) - The basic function of VPN is to distribute packets from one point to another without revealing them to anyone on the connection. . To do this, the VPN packages all data in a format that both the client and server understand. The sending side puts the data into tunnelling format and the receiving side extracts it to get the information.
- Encryption : Tunneling does not provide protection. Anyone can extract data. Data also needs to be encrypted in transit. The receiving party will know how to decrypt data from a given sender.
- Accuracy . For security, a VPN must confirm the identity of any client that attempts to 'communicate' with it. The client needs to confirm that it has reached the intended server.
- Session management : Once the user is authenticated, the VPN needs to maintain the session so that the client can continue to 'communicate' with it over a period of time.
Generally VPN protocols treat tunneling, authentication, and session management as one package. Weaknesses in any function are potential security holes in the protocol. Encryption is a specialty, it's also very difficult, so instead of trying to create something new, VPNs often use a combination of multiple reliable encryption protocols. Below are popular VPN protocols and their strengths and weaknesses.
Weak protocols
Point-To-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
The oldest protocol still in use is PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol). PPTP was first used in 1995. PPTP does not specify an encryption protocol but can use several protocols such as the powerful MPPE-128. The lack of strong protocol standardization is a risk, as it can only use the strongest encryption standard that both sides support. If one side only supports a weaker standard, then the connection must use weaker encryption than the user expects.
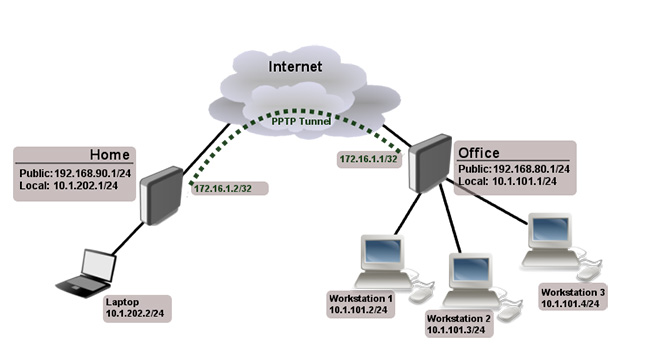
However, the real problem with PPTP is the authentication process. PPTP uses the MS-CHAP protocol, which can be easily cracked in today's time. An attacker can log in and impersonate an authorized user.
IP security (IPSec)
Used to secure communications and data flows in the Internet environment (environment outside the VPN). This is the key point, traffic via IPSec is mainly used by Transport modes , or tunnels (or tunnels - this concept is often used in Proxies, SOCKS) to ENCRYPlate data in VPN.
The differences between these modes are:
- Transport mode is only responsible for encrypting data inside packets (data package - or also known as payload). While Tunnels encrypt all those data packages.
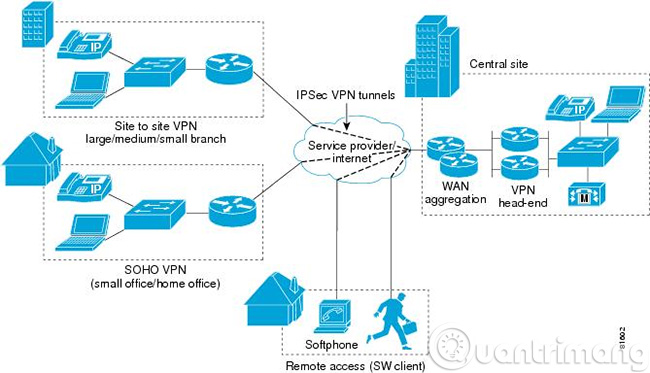
Therefore, IPSec is often considered a Security Overlay , because IPSec uses layers of security compared to other protocols.
L2TP

The L2TP protocol typically works with the IPSec encryption algorithm. It is significantly more powerful than PPTP but still causes concern among users. The main vulnerability in L2TP/IPSec is the public key exchange method. Diffie-Hellman public key exchange is a way for two parties to agree on the next encryption key and no one else knows about it. There is a method that can 'crack' this process, which requires quite a bit of computing power, but it then allows access to all communications on a given VPN.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Partly similar to IPSec, the above two protocols also use passwords to ensure security between connections in the Internet environment.
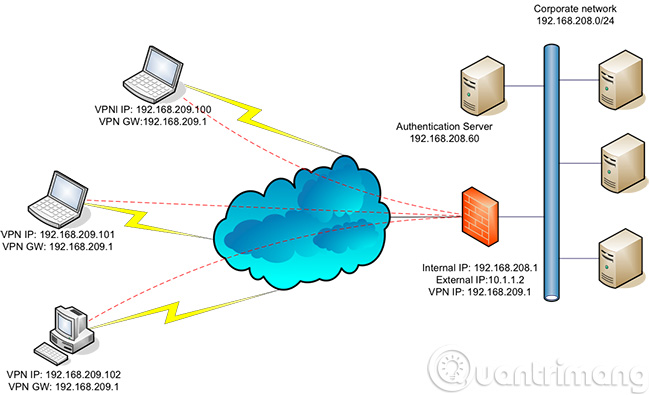
SSL VPN model
Besides, the above two protocols also use Handshake mode - related to the account authentication process between client and server. For a connection to be considered successful, this authentication process will use Certificates - which are account authentication keys stored on both the server and client.
These protocols have better security
IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange)
IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange) is ranked highly secure among current protocols. IKEv2 uses IPSec tunneling and has a wide selection of encryption protocols. IKEv2 is used with AES-256 encryption, making it very difficult to crack. IKEv2 uses strong certificate-based authentication and can use the HMAC algorithm to verify the integrity of transmitted data. IKEv2 supports fast communication and is especially robust at maintaining sessions, even when the Internet connection is interrupted. Windows, MacOS, iOS, and Android all support IKEv2. Several open source implementations are also available.
Version 1 of the protocol was introduced in 1998 and version 2 in 2005. IKEv2 is not one of the newest protocols, but is very well maintained.
SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol)

SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol) is a Microsoft product, mainly supported on Windows. When used with AES and SSL encryption, SSTP provides good security, in theory. Currently, no SSTP vulnerabilities have been found, but it is likely that a certain weakness still exists.
A practical problem with SSTP is its limited support on non-Windows systems.
OpenVPN

OpenVPN is an open protocol suite that provides strong security and has become very popular. OpenVPN was first released in 2001 under the GPL license. OpenVPN is open source, so vulnerability testing is guaranteed. OpenVPN's encryption function typically uses the OpenSSL library. OpenSSL supports many encryption algorithms, including AES.
There isn't any support for OpenVPN at the operating system level, but many packages include their own OpenVPN clients.
Achieving the most security with a protocol requires administrators to handle it correctly. The OpenVPN community provides recommendations to enhance OpenVPN security.
SoftEther (Software Ethernet)

SoftEther (Software Ethernet) is a new name, first launched in 2014. Like OpenVPN, SoftEther is also open source. SoftEther supports the strongest encryption protocols, including AES-256 and RSA 4096-bit. SoftEther provides greater communication speeds than most protocols, including OpenVPN, at a given data rate. It does not support its own operating system but can be installed on many operating systems, including Windows, Mac, Android, iOS, Linux and Unix.
As a new protocol, SoftEther is not supported as much as some other protocols. SoftEther has not been around as long as OpenVPN, so users have not had much time to test for possible weaknesses in this protocol. However, SoftEther is a strong contender for anyone who needs top quality security.
So which protocol should you choose?
The question 'Which protocol is the most secure?' it is difficult to give an answer. IKEv2, OpenVPN, and SoftEther are all strong candidates. OpenVPN and SoftEther have the advantage of being open source. IKEv2 has open source implementations but also proprietary implementations. The main security advantage of IKEv2 is its ease of installation, reducing the risk of configuration errors. SoftEther provides very good security, but users have not had as much experience with SoftEther as with the other two protocols, so it is possible that SoftEther still has problems that users have not discovered.
OpenVPN's code has been around for years for security experts to examine. OpenVPN is widely used and supports the strongest encryption protocols. The final decision also requires consideration of other factors, such as convenience and speed, or whether security is the biggest concern.
4. Advantages and disadvantages of VPN
That's the theory, but when applied in practice, what are the advantages and disadvantages of VPN? We invite you to continue the discussion with TipsMake.com.
To build a private network or virtual personal network, using VPN is an inexpensive solution. We can imagine this, the Internet environment is the bridge, the main communication to transmit data. In terms of cost, it is completely reasonable compared to paying to establish a separate connection with the Internet. high price. Besides, having to use software and hardware systems to support the account authentication process is not cheap. Comparing the convenience that VPN brings with the cost for you to set up a system as you want, it is clear that VPN has the upper hand.
But besides that, there are easily noticeable disadvantages such as:
VPN is not capable of managing Quality of Service (QoS) over the Internet environment, so data packages - Data packages are still at risk of being lost. The management ability of VPN providers is limited, no one can predict what can happen to their customers, or in short, being hacked.
5. Why do you need a VPN service?
Surfing or banking on an unsecured WiFi network means you could be exposing your personal information and browsing habits. That's why a VPN is a must for anyone concerned about online privacy and security.
Have you ever logged into your online banking account in your hotel lobby? Or maybe you paid your credit card bill online while sipping a mocha at your favorite coffee shop. If you did this without logging into the VPN first, you may have exposed your personal information and browsing habits to hackers and cybercriminals.
Unless you log in to a private WiFi network that requires a password, any data transmitted during your online sessions can be vulnerable to eavesdropping by strangers using the same network.
That's where VPNs come in: VPNs encrypt your data online, scrambling it so strangers can't read it. The encryption that VPNs provide keeps your online activities private, including everything from emailing and online shopping to paying bills or chatting with your doctor.
A VPN can also hide your IP address so snoopers don't know that you're surfing the net, downloading files, and commenting on Reddit groups. A VPN encrypts the data you send and receive on whatever device you're using, including your phone, laptop, or tablet. It sends your data through a secure tunnel to the VPN service provider's servers. Your data is encrypted and rerouted to whatever website you are trying to visit.
6. What to expect in VPN services?
The VPN market is full of options, so it's important to consider your needs when purchasing a VPN.
Think about what is important to you. Do you want to surf the web anonymously by hiding your IP address? Are you afraid that your information could be stolen on public WiFi? Are you a frequent traveler who wants to be able to watch your favorite shows on the go?
A good VPN can help you meet all of those needs, but there are a few other things to consider.
7. How to choose a VPN
A smart way to stay safe when using public WiFi is to use a VPN solution. But what is the best way to choose a virtual private network? Here are some questions to ask when you choose a VPN provider.
- Do they respect your privacy? The purpose of using a VPN is to protect your privacy, so it's important that the VPN provider respects your privacy as well. They should have a no-logs policy, meaning they never track or log your online activities.
- Are they running the latest protocol? OpenVPN provides stronger security than other protocols, such as PPTP. OpenVPN is an open source software that supports all major operating systems.
- Do they set data limits? Depending on your Internet usage, bandwidth may be a big deciding factor for you. Make sure their services suit your needs by checking to see if you're getting full bandwidth, unlimited data.
- Where are the servers located? Decide which server location is important to you. If you want to appear as if you're accessing the web from a certain locale, make sure there's a server in that country.
- Can you set up VPN access on multiple devices? If you're like the average consumer, you typically use three to five devices. Ideally, you can use a VPN on all of them at the same time.
- How much does a VPN cost? If price is important to you then you might think that a free VPN is the best choice. However, keep in mind that some VPN services may not cost you money, but you may have to make trade-offs in other ways, such as showing frequent ads or having your personal information collected and sell to third parties. If you compare the paid and free options, you can see that free VPNs:
- Does not provide the latest or most secure protocols
- Does not provide the highest bandwidth and connection speed for free users
- There is a higher disconnection rate
- There are not many servers in many countries around the globe
- No support provided
There are many things to consider when choosing a VPN, so test it out at home to make sure you get the right VPN for your needs. Regardless of which provider you choose, rest assured that a good VPN will provide greater security, privacy, and anonymity online than a public WiFi hotspot.
VPN Price
It's right to choose your VPN provider based on price. After all, we all want to spend as little as possible each month, right?
But focusing only on price can be a mistake. You want a VPN provider to protect your online privacy and encrypt the data you send and receive. You want it to be reliable and connect quickly. All of these factors are as important - if not more important - than price.
That means most VPN service providers charge similar prices, typically ranging from $9.99 to $12.99/month, with some exceptions. However, when considering the price, make sure you understand what you're getting.
For example, a provider could charge you as little as $4.99/month to provide VPN protection on a single device. However, the provider can charge $9.99/month to provide the same service for 10 devices. You can also reduce your monthly costs by signing up for a longer term. Typically, you'll spend less each month if you sign up for a 1-year VPN plan than if you choose to pay monthly.
Is there a free version?
Many leading providers offer free versions of VPNs. However, free versions may have limitations - for example, on the amount of data you can use.
Some VPN providers offer free trials of their paid versions. The trial period usually lasts about a month. Some allow access to most of the paid service's VPN features, although there may be data restrictions.
If you sign up for a free trial, you will provide the same personal and payment information that you would use if you signed up for a paid service. You can cancel your account before the end of the trial period. If you don't cancel, the provider will start charging you to continue using the service.
Please note that some free VPNs may collect and share or sell your data to third parties for marketing purposes, while others may not block ads.
Number of servers
More important than price is the number of servers your VPN provider offers. In general, the more servers, the better.
Why? VPNs that don't offer multiple servers will often struggle with slow online speeds. That can be a problem if you connect to a VPN for the first time and then download files or stream videos.
If there are too many users on the same server, the server may become overloaded. When that happens, you'll notice your browsing speed slow down.
When considering a VPN provider, make sure you sign up with one that has a high server count. How many servers is enough? No one answered for that. But VPN services with 1,000 servers or more may be less prone to overload.
8. How does a VPN protect your IP address and privacy?
Essentially, a VPN creates a data tunnel between the local network and an exit node in another location, possibly thousands of miles away, making it appear as if you are somewhere else. This benefit allows for online freedom, or the ability to access your favorite apps and websites on the go.
Here's a closer look at how virtual private networks work. VPNs use encryption to scramble data as it is sent over a WiFi network. Encryption makes data unreadable. Data security is especially important when using public WiFi networks because it prevents anyone else on the network from eavesdropping on your Internet activity.
There is another aspect to privacy. Without a VPN, your Internet service provider can know your entire browsing history. With a VPN, your search history will be hidden. That's because your web activity will be linked to the VPN server's IP address, not yours.
A VPN service provider may have servers worldwide. That means your search activity could originate from any of them. Please note that search engines also track your search history, but they associate that information with an IP address that is not yours. Again, a VPN will keep your online activity private.
9. What does a VPN hide?
VPNs can hide a lot of information that could put your privacy at risk, including.
Your browsing history
It's no secret when you're on the Internet. Your Internet service provider and web browser can track everything you do on the Internet. Many of the websites you visit may also keep a history. Web browsers can track your search history and associate that information with your IP address.
Here are two examples why you might want to keep your browsing history private. Maybe you have a medical condition and you're searching the web for information about treatment options. Without a VPN, you're automatically sharing that information and may start receiving targeted ads that can draw more attention to your condition.
Or maybe you just want to see airfare prices for a flight next month. The travel sites you visit know you're looking for tickets, and they may display fares that aren't the cheapest available.
These are just a few individual examples. Remember that your Internet service provider may sell your browsing history. Even so-called private browsing may not be as private as you think.
Your IP address and location
Whenever you connect to the internet, your IP address is visible to everyone on the web. This makes it easy for hackers, ISPs, and other organizations to track your online activities. IP addresses can be used by ISPs to collect data about your web browsing activities, restrict access to certain sites, and even throttle your Internet connection speed. Cybercriminals can use it for malicious purposes. Even if you use the web anonymously and don't use your real name, your IP address can still be used to identify you.
Anyone who gets your IP address can access what you're searching for on the Internet and where you are when you search. Think of your IP address as the return address you put on a letter. It may lead back to your device.
Luckily, a VPN can hide your IP address by rerouting your traffic through one of its servers. This ensures that any web snoopers won't be able to trace your online activity or location.
Because a VPN uses an IP address that is not your own, it allows you to maintain your online privacy and search the web anonymously. You're also protected from having your search history collected, viewed, or sold. Please note that your search history can still be viewed if you are using a public computer or a computer provided by your employer, school or other organization.
Your streaming location
You can pay for streaming services that let you watch things like professional sports. When you travel abroad, this streaming service may not be available. There are good reasons for this, including contractual terms and regulations in other countries. A VPN will let you choose an IP address in your country, though. That can give you access to any event shown on your streaming service. You can also avoid data logging or speed adjustment.
Your device
A VPN can help protect your devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones, from prying eyes. Your device can be a prime target for cybercriminals when you access the Internet, especially if you're using a public WiFi network. In short, a VPN helps protect the data you send and receive on your device so hackers can't track your every move.
Works on the web to maintain freedom on the Internet
Hopefully you are not the subject of surveillance by some organization, but anything is possible. Remember that a VPN protects against your Internet service provider seeing your browsing history. So you're protected if an organization asks your service provider for records of your Internet activity. Assuming your VPN provider doesn't log your browsing history, it can help protect your Internet freedom.
10. What does a VPN not hide?
A VPN offers many advantages when it comes to online privacy and security, but it does not provide full privacy protection, as there are still some things that a VPN cannot hide.
Account activity
A VPN can encrypt your web traffic, hide your IP address, and spoof your location, but it cannot protect you from being tracked by online services. When you sign up for a website or an online service, the company can still track your activities within their own platform. So if you use Gmail, Facebook or Twitter with a VPN enabled, your account activities won't actually be hidden.
Billing Information
A man enters payment details from a card on a laptop
Enabling a VPN can help protect you from hackers and snoopers, but it cannot protect you from financial fraud. When you make online purchases using a credit card or PayPal, the company can still access your payment information. Even if you're using a VPN, it's important to take extra precautions when making online purchases and always use a secure payment method.
Malware and viruses
A VPN can do a lot to protect your system from intruders, but can it protect you from malware? Unfortunately, using a VPN while browsing the Internet cannot prevent malware or viruses from infecting your device. It can actually make the situation worse because a VPN can route you through untrusted networks that may contain malware.
Even if you are using a VPN, it is important to have a good antivirus program installed on your device, if you want to stay safe from malicious attacks.
Device MAC address
Your VPN can hide your IP address but cannot hide your device's MAC (Media Access Control) address. This is a unique identifier assigned to every device on the network and can be used to track your activities.
Data usage
Your ISP will still be able to see how much data you're using, even if you're using a VPN. Additionally, some ISPs have data caps that limit the amount of data you can use each month, and these restrictions will still apply even if you're using a VPN.
11. Can VPN access be set up on multiple devices?
If you are a normal consumer, you usually use 3 to 5 devices. Ideally, you can use a VPN on all of them at the same time.
How much does this option cost? If price is an important factor for you, then you might think that a free VPN is the best choice. However, keep in mind that some VPN services may not nominally charge you money, but you have to make trade-offs in other ways,
such as seeing ads displayed regularly or having your personal information accessed. collect and sell to third parties. If you compare paid and free options, you can see that free VPNs:
- Does not provide the newest or most secure protocols
- Does not provide the highest bandwidth and connection speed for free users
- There is a higher disconnection rate
- There are not many servers in many countries around the globe
- No support provided
There are many things to consider when you choose a VPN, so think carefully to make sure you're getting the right VPN for your needs. Regardless of which provider you choose, rest assured that a good VPN will provide more security, privacy, and anonymity online than a public WiFi hotspot can.
12. Do you need a VPN at home?
What if you're logging onto the Internet from home? Do you need a VPN?
Sure is not. When setting up your home WiFi network, you likely protected your network with a password. Therefore, you may not need the additional security of a VPN to protect your online activity.
Investing in a VPN for home use can be a waste of money, unless you want to keep your web surfing private from your Internet service provider (ISP) or if you choose to access Access streaming content or sports news that you can't access from your location.
You could invest in a VPN service provider to access the Internet at home, but that's not a wise move financially. It's worth noting that you might consider a free VPN, but those services can cover their costs in other ways, such as selling your data to third parties for marketing purposes. .
There are exceptions where you might consider using a VPN at home. You may want to use a VPN if you're worried about your ISP tracking your online activity. If you connect to the internet through a VPN, your internet service provider won't be able to see what you're doing online. However, your VPN provider does. If you trust that company more than your Internet service provider, then using a VPN at home may make sense.
There's another reason to use a VPN. It can help you stream content or watch sporting events that aren't available in your location. Remember that you should understand any contractual agreements you have accepted with your streaming provider. Furthermore, government regulations in other regions or countries may make this a bad idea.
13. VPN terminology
Learning about VPNs seems to require specialized vocabulary. Here is a glossary with definitions of some of the most common terms you will see.
AES encryption
Encryption is essential to help keep your data from being read by hackers, private companies, and possibly government agencies. Encryption scrambles your data so that it cannot be understood by others without a specific decryption key. AES, short for Advanced Encryption Standard, is an encryption method developed by Belgian cryptographers Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen. In 2002, AES became the US federal standard for encryption. Since then, it has also become the standard form of encryption for the rest of the world.
Browser history
A record of all your Internet activity using a particular web browser, including the keywords you searched for and the websites you visited.
Geographic restrictions
One of the main reasons why users trust VPNs? They want to overcome geographical limitations. These restrictions are often put in place by entertainment companies that only want to distribute content to certain regions.
For example, Netflix may offer content in the US but not in the UK. It can offer UK programming that US Netflix users cannot access. By using a VPN with a UK-based IP address, US viewers can try to access Netflix programming that is not available in their country.
VPN services - and VPN connections - hide the location from which the Internet connection is made. Check your streaming service agreement for terms of service, and also note that some countries may impose penalties for using a VPN to circumvent its rules.
Google search history
A record of all your Internet searches using the Google search engine.
IP address
IP stands for Internet Protocol, and an IP address is a series of numbers and dots that identifies a computer that is using the Internet protocol to send and receive data over a network.
IPsec
IPsec is a series of protocols or rules that virtual private networks use to secure a private connection between two points, usually a device such as a laptop or smartphone, and the Internet. Without these protocols, a VPN would not be able to encrypt data and ensure user data privacy. IPsec stands for Internet Protocol Security.
ISP
Short for Internet Service Provider, this is a service you have to pay to connect to the Internet. ISPs may record your browsing history and may sell it to third parties for marketing or other purposes.
Kill switch
Users sign up with a VPN provider for data security and online privacy. But what happens if the VPN provider's network connection fails? Your computer or mobile device will default back to the public IP address provided by your ISP. This means your online activity can now be tracked. However, the kill switch will prevent this from happening. If your VPN provider's connection fails, the kill-switch feature will completely cut off your connection to the Internet. This way, your online activity will not be tracked by others. Not all VPN providers offer this feature, so look for it when shopping around.
L2TP
The acronym L2TP stands for Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol and is a series of rules that allow Internet service providers to enable VPNs. However, L2TP itself does not encrypt data, so it does not provide complete privacy to users. That's why L2TP is often used with IPsec to help protect users' online privacy.
Public WiFi
Wireless networks in public places allow you to connect your computer or other device to the Internet. Public WiFi is often unprotected and vulnerable to hackers.
Search
A service that allows you to search for information using keywords on the Internet. Many popular search engines record your search history and can monetize that information.
Service Provider
A company that offers virtual private networks - essentially routing your connection through a remote server and encrypting the data.
Connect simultaneously
You probably have a lot of devices connected to the Internet at the same time, everything from smartphones to laptops to desktops in your home office. Many VPN providers now offer protection for all your simultaneous Internet connections under one account. This is important: You might think about logging into a VPN before searching the Internet with your laptop. But if your smartphone isn't protected by a secure VPN, your browsing activity on that device won't be protected.
Virtual private network
VPNs give you online privacy and anonymity by creating a private network from a public Internet connection. It masks your Internet protocol address to keep your online actions private. It provides secure and encrypted connections to provide greater privacy and security for the data you send and receive.
VPN connection
A virtual private network connection allows you to access the Internet through a remote server, hiding your physical location and browser history and encrypting your data.
VPN Privacy
This refers to the privacy that using a VPN provides. For example, VPNs encrypt your data, disguise your location, and hide your browsing history and the data you transmit over the Internet.
VPN client
VPN client helps users connect to virtual private networks more easily. That's because it's the actual software installed on your computer, phone, or tablet. The most popular operating systems, such as Android, Windows and iOS, come with VPN client software pre-installed. However, many users choose to work with third-party VPN clients that offer a variety of features and user interfaces.
Hope the above article is useful to you!