What is a Honeypot? The Benefits and Risks of Honeypots
Honeypot is a term commonly used in the field of cybersecurity to refer to a tool or simulation system designed to attract attacks from hackers, thereby helping security experts better understand the behavior and attack techniques used by bad guys. If you do not know what a honeypot is, let's find out with Bizfly Cloud in the following article.
What is a honeypot?
Honeypot is an important tool in preventing and detecting cyber attacks. It acts as a "decoy" for hackers, creating a safe environment that can be attacked without affecting the main system.
The main goal of a honeypot is to collect data about attackers and their attack methods, thereby providing valuable information to improve security measures. This not only raises awareness about cybersecurity but also helps build more effective defense strategies.
What is a honeypot?
The origin of Honeypot
The concept of honeypots is not new; they have been around since the 1990s. They were originally developed as a research tool to help cybersecurity researchers gain a deeper understanding of cyberattacks.
As the Internet became more popular and online applications and services grew, the number of cyber attacks increased rapidly. Tracking and analyzing real attacks on critical systems was often difficult. Honeypot was developed as a solution to create a simulated environment to attract attackers.
Over time, honeypots have evolved from simple models to more complex systems that are capable of automating data collection and analysis. Today, honeypots are not only used for research but are also widely used in organizations to enhance defense capabilities.
How does Honeypot work?
Honeypots work by creating an attractive environment for attackers. When a hacker tries to attack the honeypot, their every move is recorded and analyzed.
The honeypot operation process can be divided into three main steps:
- Deploying a simulated environment: Security experts set up a simulated system or application that appears to be a real system. This system often has security vulnerabilities to attract attackers.
- Monitoring and recording: When there is any activity on the honeypot, the system will record all the information, including the attacker's IP address, attack type, and related factors.
- Data analysis: The collected data will be analyzed to better understand the attacker's methods and behavior, thereby providing appropriate defense measures.
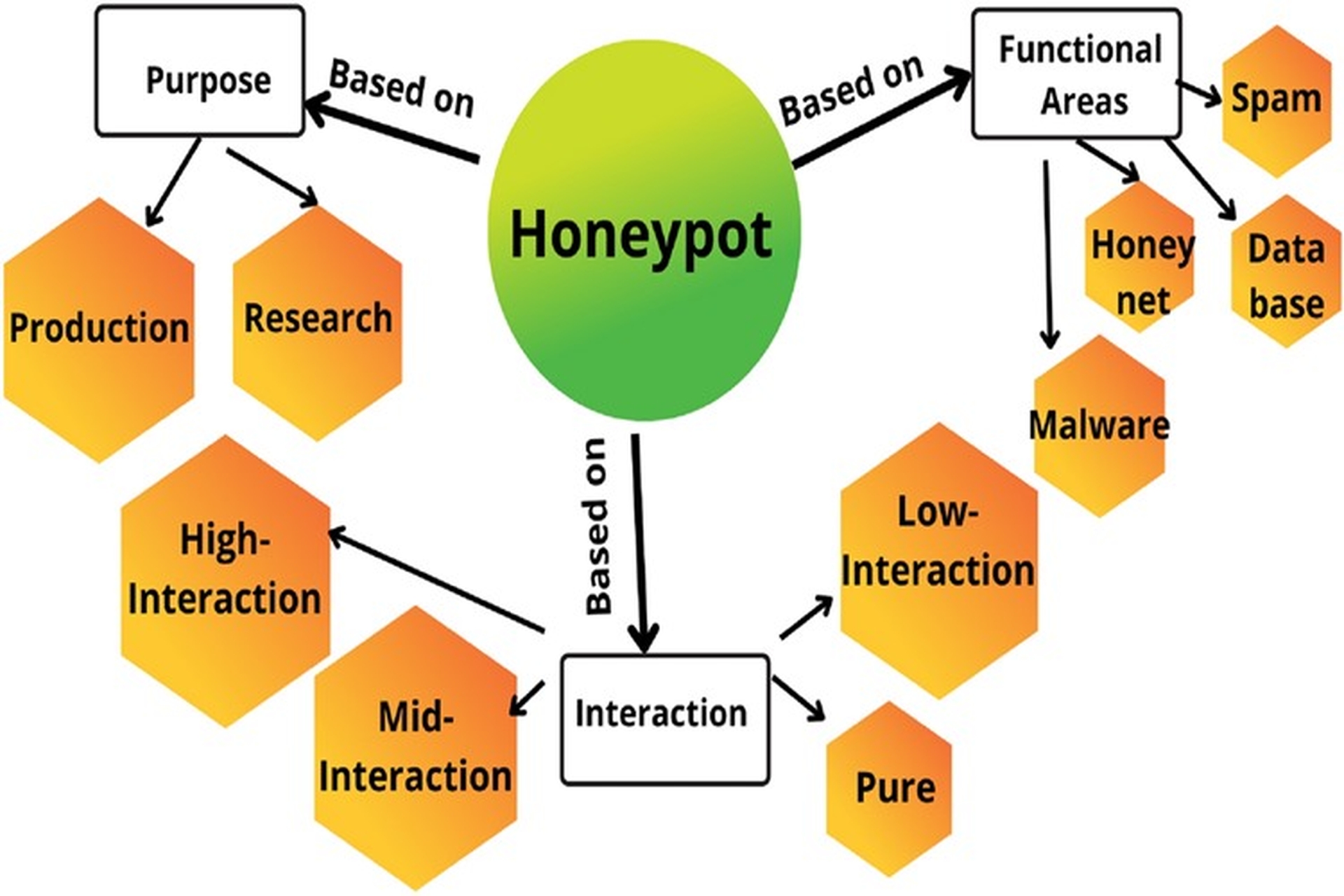
Current types of Honeypots
There are many different types of honeypots available today, each serving its own purpose and needs in a cybersecurity strategy. Here are some common types of honeypots:
- Production Honeypot: Placed next to production servers and running similar services, helps detect internal network intrusions and fool malicious actors.
- Research Honeypot: Provides information on the latest cybercriminal attack techniques and tools, used to improve security measures and develop defense strategies.
- Low-Interaction Honeypot: Allows limited interaction with the system, running only limited simulated services. This is an early detection mechanism, often used in production environments.
- High-Interaction Honeypot: More complex, allowing for greater interaction with the attacker's actual operating system. They are more resource-intensive and require higher maintenance than low-interaction honeypots.
- Pure Honeypot: A large-scale system running on multiple servers that completely simulates a production system. User information and data are faked to appear confidential and sensitive, and sensors monitor threat actors' activity.
- Client Honeypot: Simulates vulnerable client systems, such as web browsers or email applications, to detect and analyze client-side attacks.
- Virtual Honeypot: A virtual machine that simulates a real system, used to detect and analyze attacks in a virtualized environment.
Benefits and risks of Honeypots
Benefits of Honeypots in Network Security
Benefits of Honeypots in Network Security
- Early threat detection: Honeypots detect attacks and system vulnerabilities before they cause harm.
- Gathering insights: Honeypots record attacker behavior, techniques, tools, and methods, providing useful information for security strategy.
- Protect the real system: Honeypot simulates fake targets, minimizing the impact of attacks on the real system, keeping the infrastructure safer.
- Easy to analyze: Honeypot traffic is primarily from attackers, making it easy for security teams to analyze without having to filter between legitimate and malicious traffic.
- Provide insider threat intelligence: Honeypots help detect threats from within the organization.
Risks of using Honeypot
- No complete protection: Honeypot does not guarantee complete protection. If detected, the attacker can switch targets.
- Misconfiguration: A misconfigured honeypot can make it easier for attackers to identify and move to other parts of the network, creating even more risk.
- Misinformation: Attackers may intentionally provide false information, confusing the analysis.
- Increased risk of compromise: If the honeypot runs in a real environment with real services, it can become a real attack target if not managed carefully.
Conclude
Honeypots are a useful tool in cybersecurity, attracting attackers and providing valuable information to security professionals. However, organizations need to carefully consider the risks when deploying honeypots. This article hopes to provide a clearer view of honeypots, their benefits, and their risks in the context of modern cybersecurity.