Learn about 'Honeypot' and 'honeynet'
In the myriad of measures to prevent hackers from breaking into the system, the "honeypot" and "honeynet" are considered as one of the pitfalls designed with the item. this destination.
I. HONEYPOT
1. What is Honeypot :
- Honeypot is an information resource system built with the aim of deceiving illegal users and intruders, attracting their attention, preventing them from contacting the real system.
- Information resource system means Honeypot can disguise any kind of resource server such as Mail Server, Domain Name Server, Web Server . Honeypot will directly interact with hackers and find ways to exploit information information about hackers such as attack, attack tools or how to proceed instead of being attacked.
2. Types of Honeypot :
Consists of two main categories : Low interaction and high interaction
+ Low interaction: Simulate fake services, applications, and operating systems. Low risk level, easy to deploy and maintain but limited in service.
+ High interaction: Are real services, applications and operating systems. The level of information collected is high. But the risk is high and time consuming to operate and maintain.
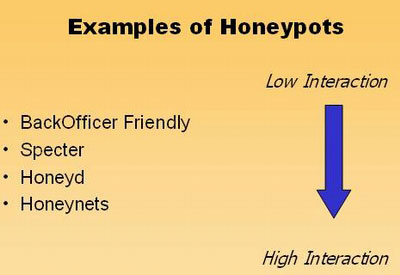
VD model of honeypot types
- BackOfficer Friendly (BOF) : A type of Honeypot is easy to operate and configure and can operate on any version of Windows and Unix but only interacts with some simple services like FTP, Telnet, SMTP .
- Specter : It is also the type of Honeypot with low interaction but better ability to interact with BOF, emulation of over 14 ports, can be warned and managed remotely. However, like BOF, specter has limited number of services and is not flexible.
- Honeyd :
+ Honeyd listens on all TCP and UDP ports, simulation services designed with the purpose of preventing and recording attacks, interacting with attackers as a victim system.
+ Honeyd can simulate many different operating systems simultaneously.
+ Currently, Honeyd has many versions and can simulate about 473 operating systems.
+ Honeyd is a low-interaction Honeypot type that has many advantages but Honeyd has the disadvantage of being unable to provide a real operating system to interact with hackers and there is no warning mechanism when detecting a compromised system. or in danger.
II. HONEYNET
1. What is Honeynet :
- Honeynet is a highly interactive form of honeypot. Unlike honeypots, Honeynet is a real system, exactly like a normal network. Honeynet provides real systems, applications and services.
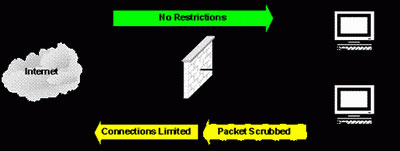
- The most important thing when building a honeynet is the honeywall. Honeywall is the gateway between honeypots and external networks. It works on the 2nd floor as Bridged. Data streams when entering and exiting honeypots must go through honeywall.
2. honeynet architecture model (GenII)

3. Honeynet functions
a. Control data :
- When malicious codes infiltrate the honeynet, operations will be controlled.
- The data flow when entering is not limited, but when going out, it will be limited.
b. Data acquisition :
When data enters, the honeynet will review and record all destructive activities and then analyze the motives of hackers.
c. Data analysis : The main purpose of the main honey net is to collect information. Once the information is available, users need to be able to analyze this information.
d. Data collection : Collect data from honeynets to a centralized source. Applies only to organizations with multiple honeynets. Most organizations have only one honeynet.
DuyLong
You should read it
- ★ What you need to know about an information security analyst
- ★ DNA information leaks are worse than leaking many credit card information
- ★ How to use Bitlocker to encrypt data on Windows 10 (Part 1)
- ★ Should we worry about location access?
- ★ Windows Information Protection (WIP) price, marketcap, chart, and fundamentals info