Three simple and economical ways for network protection
Zack Stern
Network Administration - Whether the Conficker worm or failures go away, let's take that as a reminder to keep your network safe. It can cost a lot of security advice - it's really not an inefficient investment if useful - but there are a number of other ways, which are free tools introduced in This article, three ways to do it in conjunction with the free tool below can increase the security of your network.
Use OpenDNS
Using OpenDNS, Internet traffic will be routed through IP addresses, the parts of the characters you type (such as a URL) are only the upper part of this transmission. Normally, when you type 'quangtrimang.com', it will be referenced in a domain server directory, then it will be routed allowing you to get to a real IP address. But what if that structure is compromised and an attacker can send your request to another IP address?
Last year there was an attack using that technology. You should type a trusted URL but instead of being routed to the correct server, you are taken somewhere. You may even see the name of a bank in the URL bar but don't think you're entering personal data directly into a hacker site.
Domain servers and operating systems are still patched to protect you against these attacks. However, the OpenDNS server anticipated the problem and quickly responded to the threats. Use it instead of relying on your service provider's DNS servers.
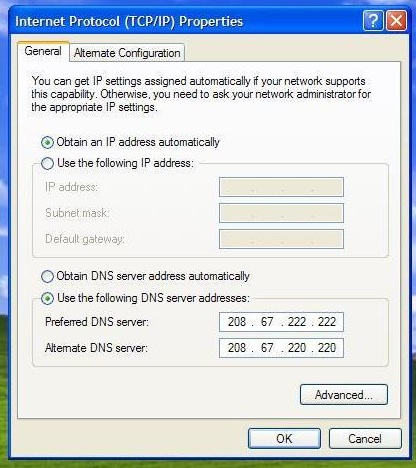
On the other side of the process, you can open the Network Connections Control Panel. Right-click on the active connection and select Properties. Select Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) and click Properties. Click the select button Use the following DNS server addresses and enter the addresses 208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220 .
Or you can enable it on your router, send this DHCP client these details without any extra intervention. The specific process may vary, but you will log in and enter those IP addresses in the NAT area. Visit OpenDNS.org for more details on specific hardware.
Upgrade the router's software
Psyb0t is a worm written to attack the router's hardware directly, embedded itself inside. It will guess the password and login for a variety of routers, starting from the default. Therefore you should use 'strong' passwords, especially many routers that do not allow you to change login ID. (Try setting a password of about 12 characters to mix numbers, letters and symbols).
Like your operating system, hardware companies also patch their routers, especially when security errors are detected. Look up your specific model and see if there are any upgrades to the router software. If there is a new upgrade, please download and use this new version immediately; It can protect you from many harmful attacks.
Disable remote administration issues
In addition to upgrading the software for the router and setting a 'strong' password, you can close other doors by disabling remote administration. This option is usually turned off by default, check the router's settings to ensure that.
When remote administration rights are enabled, someone can log in from offsite. They also need a valid password, although this access still shows another weakness in your defensive strategy.
If you need to administer a remote network, set up a secure connection to the VPN gateway at your network because of the connection as that open method. (Or you can use the router's built-in security connection if available).