Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 2)
Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 1)
In the first part of this series, we introduced some concepts related to Network Access Protection. In this second part we want to start discussing some basic network requirements and other decision conditions. Then the configuration process is like.
Network Access Protection infrastructure
Implementing NAP needs to use some servers, each server has its own role. You can see in Figure A to get an overview of this issue.
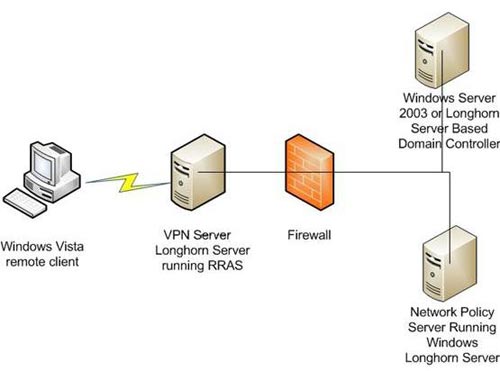
Figure A : NAP implementation requires some servers to use
As you can see in the diagram, the Windows Vista client is connecting to a Longhorn Server running Remote Access Service (RRAS). This server works as a VPN server for the network. The Windows Vista client establishes a connection to this VPN server in the usual way.
When the remote user connects to the VPN server, the domain controller will check the validity of the user's computer to see if it meets the network policy and indicate which security policies have been met. , a server is used to configure both the Remote Access Service and the Network Policy Server. In the real world, VPN servers operate at the perimeter network layer and should not configure the network policy server on the perimeter server.
Domain controller
If you look at the diagram shown in Figure A, you will see that one of the required servers is a domain controller. It should not be thought of as just a single server, it can be quite like a complete Active Directory infrastructure. An Active Directory cannot operate without a DNS server, if the diagram presented represents exactly one network, the domain controller will be configuring DNS services. Of course in real world organizations typically use many domain controllers and dedicated DNS servers.
Another factor to consider for the ambiguity in the diagram is the right to grant a business activity certificate is also required. In the case of this diagram, certificate services can easily be configured on domain controllers. In the real world, a dedicated server is often used as a certificate authority because of the sensitive nature of digital certificates.
In case you are wondering, the reason why the right to grant a business license is required is because the VPN server uses the PEAP-MSCHAPv2 protocol for authentication. PEAP protocol is the original certificate. The VPN server will use a machine certificate next to the server, but clients will use user certificates instead.
Setting the right to grant business operation certificates
The procedure for deploying a business certificate authority changes depending on whether you are installing services on Windows 2003 Server or Longhorn Server. One of my purposes in this article is for readers who are quite friendly with Longhorn Server. The following procedures are intended for installing certificate services on Longhorn Server.
Before demonstrating how to install certificate services, you need to remember 2 things. First of all, Longhorn Server is still a test version, so it can be changed until the final product is released, a major change in the development process of this application is unlikely. .
The second thing to note is that when deployed in the real world, you always want to get effective measurements to ensure the right to grant business activity certificates is safe. Best of all, if someone has obtained the right to grant your business certificate, they can master the network. Since this article is only focused on NAP, I will show you a bit about this certification service and its operation. In the real world deployment, you will want to get back to the server's configuration.
Start the deployment process by opening Longhorn Server's Server Manager and selecting the Manage Roles option. Next, click the Add Roles link found in the Roles Summary section. This will be for Windows to start the Add Roles Wizard . Click Next to skip this window. You will see a list of all the available components. Select the Active Directory Certificate Server option from the list. Sometimes items may not appear listed alphabetically, so you may have to read through the entire list to find the appropriate service. Click Next to continue.
This window will introduce you to certification services and provide some attention. Click Next , you will see another window asking you which component you want to install. Select the Certification Authority and Certificate Authority Web Enrollment checkboxes and click Next .
You should now see a window asking whether you want to create a business certificate authority or an independent certificate authority. Select the Enterprise Certificate Authority option and click Next . You will be prompted to see if this server should act as a Root CA or Subordinate CA. If this is the first time that the certificate authority is granted in the room, you should select the Root CA option. Click Next to continue.
The wizard will ask if you want to create a new private key or use an existing private key. If this is again an experiment, you choose the option to create a new private key and click Next to continue.
The next window will ask you to choose a cryptographic service provider, key length and hash algorithm. In the real world deployment, there are many things to consider carefully. When we are setting this certificate authority for demonstration purposes, we should leave the default and click Next .
The next window lets you define a generic name and special name suffix for the certificate authority. Again choose the default and click Next .
Now you should see how long the window is asking for valid certificate time, by default this period is 5 years, that's pretty good for our purposes, so click Next to continue. . The next window will ask where the certificate databases and their respective session logs will be located. In a production environment, choosing a suitable location has a limited effect on error and security resistance. If it is tested, leave the default and click Next .
Finally, the window details the options you have selected. Click the Install button then Windows will copy the necessary files and configure the services below.
Conclude
So we showed you how to configure the certificate of business operation, and the moment you start configuring the VPN server. Please see part 3.
Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 3)
Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 4)
Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 5)
Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 6)
Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 7)
You should read it
- ★ Installing and configuring the 2004 ISA Server Firewall - Chapter 2 Installing Certificate Services
- ★ Configure Windows Server 2008 to remotely access SSL VPN Server (Part 2)
- ★ Introduction to Network Access Protection (Part 3)
- ★ What kind of SSL certificate does your website need?
- ★ HOW TO INSTALL ISA SERVER ENTERPRISE 2000