Things to know when choosing to buy mainboard
TipsMake.com - As we all know, the most important and complex component in the computer is the motherboard, also known as the Motherboard, motherboard . Made up of many different components, And with many different models, series as well as different manufacturers, choosing to buy a really satisfactory product with a need to use is quite a difficult thing for most users. If you are planning to build your own computer and choose a motherboard for your device, refer to the following key factors, before deciding which type of motherboard to choose accordingly.
The size of the mainboard
This is the basic element but also few people pay attention to the most, they often only care about the name of the manufacturer and the model of the mainboard. In fact, there are standards dedicated to the size of the motherboard and the case to be able to create a suitable system.
Most of the removable parts are quite well adapted to the Desktops , but there are a number of separate product lines from A to Z (also known as All-in-one, synchronous computers ) from vendors. like HP, Acer, Dell . do not follow the above rules. Therefore, users will find it difficult to replace each part of this synchronous computer.
Currently, the most popular on the main motherboard market is Intel's Advanced Technology Extended (ATX) and other components included. The figure below describes some dimensions of this ATX line:
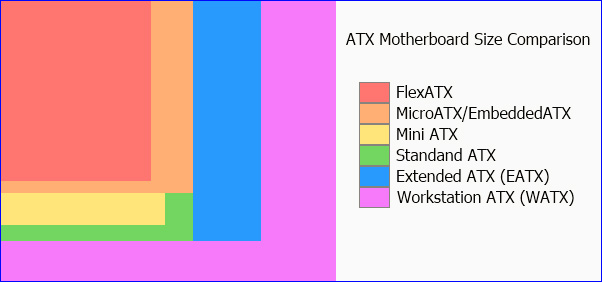
The size of the motherboard
Technically, this parameter of the mainboard not only shows the exact size, but also the location of the points for mounting screws on the case, as well as other important parts. If you look carefully, you will see that on most motherboards, CPU, RAM and external communication ports are quite close together. Simply, it is due to common standards. Those parts must be fixed in each individual position, otherwise the case and other source manufacturers will not know how to respond accordingly.
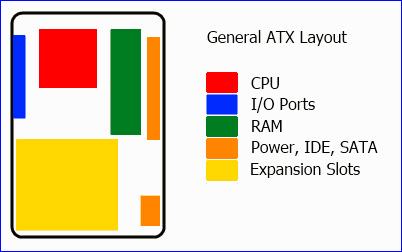
Mainboard model of ATX together with other components
Intel's next standardized motherboard effort is Balanced Technology Extended (BTX) . Intel's main goal this time is to limit the flow of gas in the case and break some of the limitations of the previous ATX device. Although BTX is said to have inherited quite well what the ATX left, it seems that it is not enough to create a "leap" in the consumer market. Some other giant manufacturers such as HP, Dell, and Apple are still using this BTX model.
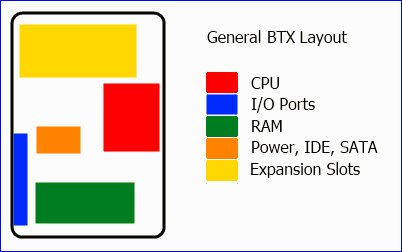
Model layout of BTX mainboard
In fact, this BTX model was killed by Intel in 2007, so users only need to focus on ATX motherboard with the size suitable for the case. The main difference between a large and small ATX type is the ability to support CPU standards and expansion slots.
In addition, there are a number of other motherboard sizes as follows:
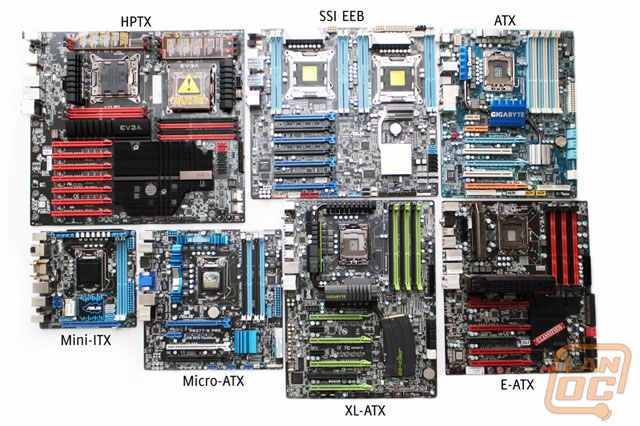
The motherboard in the picture (starting from the top left, Z format)
- HPTX - EVGA SR-X
- SSI EEB - Asus Z9P8-D8 WS
- ATX - Gigabyte GA-EX58-UD4P
- Mini ITX - Asus P8Z77-I Deluxe
- Micro ATX - Asus P8Z77-MPro
- XL-ATX - Gigabyte Assassin
- E-ATX - EVGA X58 Classified
Below is an analysis of the motherboards shown in the picture. These motherboards are measured when in vertical position.
Size
Width
Height
Official standard
Mini ITX
6.7 inches
6.7 inches
Have
Micro ATX
9.6 inches
9.6 inches
Have
ATX
9.6 inches
12 inches
Have
E-ATX
13 inches
12 inches
Have
SSI EEB
13 inches
12 inches
Have
XL-ATX
10.3 inches
13.5 inches
Is not
HPTX
15 inches
13.6 inches
Is not
There are a few things that can be noticed from the image and table above. First, SSI EEB and E-ATX have the same size but in pictures they have different sizes. EVGA X580 Classified used above is E-ATX but it does not show maximum size.
Secondly, you might wonder why there are two standards here but have the same measurement. This is due to different standards for multiple CPU and single CPU motherboards. Specifically, SSI EEB has been defined by the Server System Infrastructure (SSI) forum for servers and workstations. They even continue to determine the location of each CPU to standardize cooling solutions. The real difference between SSI EEB and E-ATX is standoff. These motherboards use a lot of similar standoffs but there are three standoff points in the middle, they don't line up. Some minor modifications and you can make these new SSI EEB dual CPU boards fit into the standard chassis.
These sizes are official standard sizes. However, XL-ATX and HPTX are not really standard sizes, as it is difficult to find chassis that fits on these motherboards. XL-ATX motherboards can be found as Gigabyte and EVGA.
Note about Processor sockets - processors:
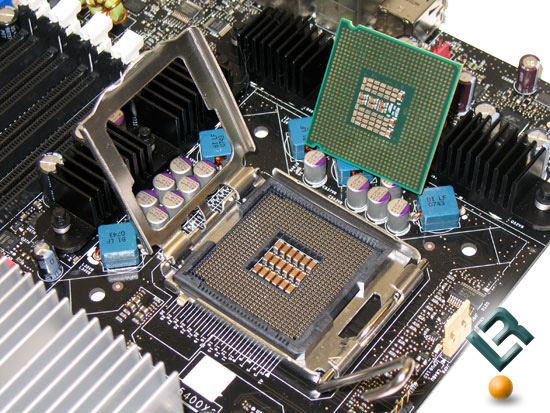
The next factor to consider is socket support for certain CPU lines. If the socket parameters on the mainboard and CPU are different, you will not be able to use it. Currently, the world's two largest CPU makers, Intel and AMD, all have processor and standard processor models that are suitable for their products. Therefore, please choose the CPU first and the other components later.
This is a list of all CPU sockets
Intel's socket standards often have a rather 'friendly' name, such as Socket H, and some 'technical' names like LGA 1156, in which LGA stands for Land Grid Array and 1156 is the total number of pins. When you want to find out information about the socket of the CPU and mainboard, the best way is to directly access the official website of the manufacturer.
Another point about Intel's product lines is its low power consumption, for example, socket 441 for Atom processors with normal consumption, with H-socket for Celeron, Core i3, Core i5 , and Core i7 800 is higher, similar to socket B for Core i7 900.
As for AMD, it doesn't change as often as Intel, in the past five years it has launched only three main models. Socket AM2, AM2 +, and AM3 support most of AMD's current processors. Specifically, AM2 and AM2 + can be used interchangeably, while AM3 with powerful DDR3 memory support.
Note about chipset:
Select the motherboard with the chipset criteria
Technically, we can understand that the chipset is a type of 'communication' between components such as CPU, RAM, VGA and some other peripheral devices, as well as a combination of north bridge chipset - Northbridge and southbridge chipset - Southbridge .
More specifically, Northbridge undertakes communication tasks between CPU, RAM, and VGA . This is also where you use features like SLI / CrossFire and DDR3. On most current CPUs from Intel and AMD, all Northbridge functions are focused on microprocessors. This also means that fewer complex operations for the motherboard and less processor latency when accessing high-speed devices such as RAM.
Compatibility and integration of many new technologies, as well as performance, and limited choices are also narrowed. For example, when AMD owns ATI, it is possible for them to "lock" the gaming VGA streams in certain features, if you are using an AMD processor. But this also caused some manufacturers like Nvidia to be kicked out of the Northbridge chipset market, which was once the big name for the Northbridge development for Pentium processors four days ago.
The Southbridge chipset will support users of the latest technology standards today such as PCI - E, SATA, USB 3.0 . It is also necessary to know the options you need, because because some Southbridge chipsets do not support multiple communication standards such as RAID and surround sound. And in fact, many manufacturers are ready to clearly specify all the features available on their products without focusing too much attention on the Southbridge chipset.
Therefore, the combination of features, interoperability and compatibility, microprocessor streams . constantly appearing with many options in a short period of time, we cannot paralyze Detailed and specific statistics on this information here. Instead, you just need to pay close attention to the specifications on the mainboard, and then the specific features of the chipset.
Additional options:
Select mainboard with other criteria such as number of expansion slots
Many manufacturers now try to give users more choices about the number of peripheral ports, the number of expansion slots, the level of stability and the warranty rate of each product. . But you do not pay too much attention to such numbers, we only need to rely on the need to use and the ability to exploit the maximum performance of the main board only. For example, it is completely different to choose a motherboard when using for gaming or office work purposes. Sometimes, the genuine information of the manufacturer on their home page is not really complete, and the best way to find out about a mainboard is to refer to the sales website, product review, forum or wiki. Besides, you also forgot to read the description material - Document Specification (usually in PDF format) that comes with each specific motherboard model.
Hopefully the above information can help you gain more knowledge and experience when choosing to buy a set of computers, especially motherboards. I wish you a good choice for your "wife"!