The terms you need to know when buying a motherboard
Motherboard is one of the most complicated computer components, so when you buy it, users often have difficulty understanding its parameters and terms. So this article will give you 20 terms to know when buying a motherboard.
The necessary terms when buying a motherboard
- 1. Form Factor
- 2. BIOS and UEFI BIOS
- 3. I / O Shield
- 4. MOSFET
- 5. PWM Fan Header (PWM fan plug)
- 6. Slot DIMM
- 7. PCI Express x16, x8, x4 and x1 slots
- 8. SLI and CrossFireX
- 9. USB plug
- 10. Front-panel plug (Front-Panel Header)
- 11. Chipset
- 12. AC '97 and HD Audio (Audio accessory connector on the front of the chassis - Audio Header Font)
- 13. Serial ATA
- 14. ATX 24 pin power supply plug
- 15. CPU power supply plug
- 16. CPU Socket
- 17. Acceleration processor (APU)
- 18. Capacitor
- 19. CMOS, CMOS battery
- 20. Debug LED
1. Form Factor
Form factor is a term that refers to the size and shape of a particular desktop motherboard. To ensure a motherboard fits into your PC computer case, you need to know how your computer can support the standard form factor board.

The three most common form factors
The most popular motherboard for those who self-plug their computers and upgrade their PCs is ATX, MicroATX and Mini-ITX. ATX is often referred to as "standard ATX" and ATX motherboards are 9.6 x 12 inches in size. This is the motherboard you usually see in mid tower computers or larger. Some boards use multiple CPUs, for servers and workstations, support larger 'standards' such as E-ATX and XL-ATX, but this is not what people build or upgrade themselves interest.
Flat computer enclosures, smaller towers and home theater PC (HTPC) cases tend to support microATX or smaller boards. MicroATX boards are 9.6 square inches (some smaller) and have fewer slots than the equivalent ATX board, but still enough to install a video card and one or two additional cards. Meanwhile, the standard 6.7-inch Mini-ITX standard for small-form-factor (SFF) cases (Small Form Factor is a case designed to be small in size, which can be bigger or equal to or smaller case HTPC.). With Mini-ITX, you usually have only one slot.
Note, most computer cases support motherboards with a certain form factor or smaller, but you should check the parameters before purchasing a new motherboard or case.
2. BIOS and UEFI BIOS
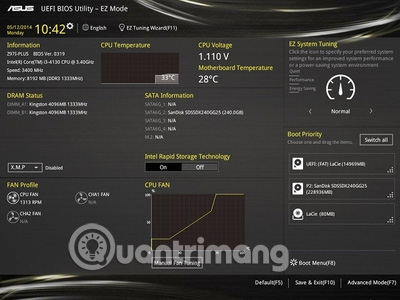
BIOS screen on Asus Z97 motherboard
See the following articles to understand the BIOS and UEFI concepts.
- BIOS - Basic information for beginners
- Concept of UEFI standard in computers
- Things to note when using UEFI instead of BIOS
3. I / O Shield
If you have ever assembled computer parts, you may have cut your hand by the I / O shield. I / O shield or also called FE piece, main block, main shield is a rectangular sheet of metal (usually with sharp edges), which is inserted into the gap on the back of the computer case. Each motherboard has a plate I / O shield. This shield has slots for specific ports on the motherboard and it is responsible for protecting the rest of the motherboard during use when plugging multiple cables into the port.

Plate I / O shield for EVGA motherboard
In general, plate I / O shield cannot be used for different models of motherboards. They have an overall size of about 1.75 x 6.5 inches, making sure they fit into regular computer enclosures. So, to be sure when buying an old motherboard, you should check the I / O shield plate in the box. Salespeople often lose this plate while upgrading and can trick you by replacing this board with older motherboards.
4. MOSFET
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect MOSFET The transistor, which is a type of field effect transistor, is used to regulate the voltage in computer motherboards.
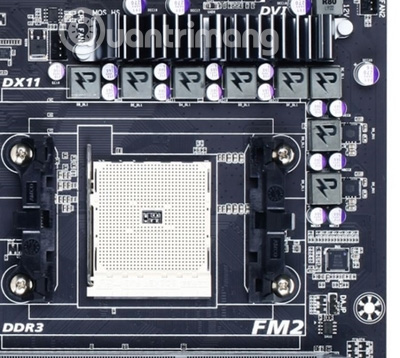
MOSFET surrounds processor socket on Gigabyte AMD FM2 motherboard
For non-technical buyers, they cannot distinguish MOSFETs from other components. Practically these components are hidden beneath the passive radiator to keep them cool during operation. The distinguishing feature of MOSFETs is their low strength design, sometimes denoted by RDS (on), which means less heat generated.
5. PWM Fan Header (PWM fan plug)
A four-pin jack is used to connect the computer fan. The motherboard usually comes with a fan and proportional plug, which means that the bigger the motherboard, the more fans are required. PWM connector (PWM stands for Pulse Width Modulation) that allows better fan speed control based on thermal instructions, placed at the system level. This plug sends a 12 volt current across one foot to power the fan, while the other one sends a signal to the fan telling it the current needed to adjust the speed.

Four-pin fan plug
When choosing a motherboard you need to make sure you have enough plugs for the fan in the computer case. Some computer fans have only three pins but you still use the four-pin plug but can't control the speed.
- Control computer fan speed
6. Slot DIMM
Dual In-line DIMM Memory Module is the type that has twice as many mainboard data lines as SIMM, these are the slots on the motherboard (usually two or four) accepting the system's RAM system. Sliders on one or both sides, lock memory into place.
In modern motherboards, this will be dual DDR3 or DDR4 data rate memory. In general, if you see the "DDR" label you will see fast performance when the RAM is used in identical pairs and plugged into the specified "paired" slots on the motherboard. Most, but not all, current motherboards support dual channel. Quad channel memory (using four or eight bars per set) is supported by several high-end platforms like Intel's X99 and X299. It works according to general principles like dual channel.
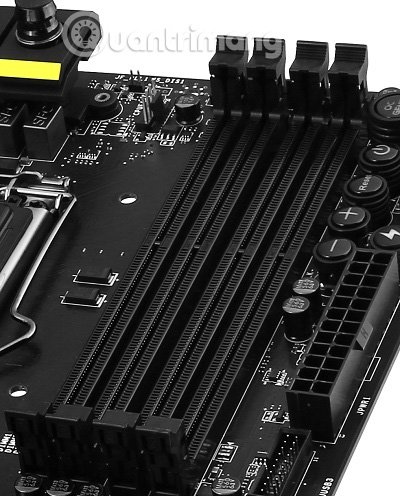

Four DIMM slots are capable of dual channel usage
The motherboard slots, if available, will sometimes be color coded. With paired memory, you must place two modules (dual channel) or four (quad channels) into the matching color slot or follow the motherboard manual. When buying RAM, if you know that two additional DDR memory sticks for a certain capacity can yield better performance than a bar with the same capacity thanks to dual channel capacity.
7. PCI Express x16, x8, x4 and x1 slots
PCIe slots are expansion slots on the motherboard that accept video cards, TV tune and other components based on the motherboard. The "x" represents two things, one is the physical size of the slot, and the other is the bandwidth of the slot itself. And they vary depending on a certain slot.
In terms of slot size, the higher the "x" number, the longer the slot. Ideally, you should choose a card with the same type as the slot. Cards with lower 'x' numbers can be used in a slot with a higher number but cannot do this otherwise. That is, you cannot use a card with a high x number for a slot with a low number. For example, you can install a PCle card x1 in a PCle x16 slot but can't do the opposite.

PCI Express x1 and x16 slots on MSI motherboards
The PCI slot bandwidth is more complicated although it is only relevant when installing the graphics card. All modern video cards can plug into the PCI Express x16 slot and the motherboard can have a few such slots. However, not all x16 slots or just one of them support PCI Express x16 bandwidth, although it is capable of fit x16 long cards. If you only install one video card, it is important to place it in the x16 slot that supports full x16 bandwidth, should not be installed in x8 or x4 lanes (lane is a form of bandwidth). Simply put, these lanes are power paths that allow better movement.
Motherboards that support Nvidia SLI and / or AMD CrossFireX multi-monitor card installation will also have different bandwidth / lane configurations that users should know if they intend to install multiple video cards. Using a card in a slot can give you x16 bandwidth with that card, but adding a second card can reduce both cards to x8 or maybe one card running with x16 bandwidth and the other card run with x8 or x4. Check bandwidth before buying if you plan to use it to play games to ensure the best performance.
- 10 'tricks' improve gaming performance on laptops
8. SLI and CrossFireX
SLI and CrossFireX refer to the ability of a motherboard to use more than one graphics card and operate smoothly to increase graphics performance. SLI stands for Scalable Link Interface which is the standard that works with Nvidia GeForce graphics cards, while CrossFireX works with AMD's Radeon cards. In general, these cards need to use the same graphics processor. With older cards, there needs to be a physical connection between the cards, usually with motherboards compatible with SLI or CrossFire, to have the proper bandwidth to communicate between the cards.
With SLI, a motherboard can support two-way, three-dimensional, or four-way SLI, showing the maximum number of supported cards, but with the Nvidia Pascal graphics card, the GTX 1000 limit is only supported. Official two cards. CrossFireX can support 2 to 4 cards; Check the motherboard specifications for the supported card numbers. Also, on some AMD-based boards for APU, don't confuse SLI or CrossFireX with "AMD Dual Graphics"; With Dual Graphics, you can combine some AMD Radeon cards with APU's onboard graphics to increase performance like CrossFire.
9. USB plug
One type of pin connector on the motherboard is USB Header, it consists of two types: USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. These connections are used to connect wires in the computer case, so that the front of the chassis (font pannel) USB connector can be plugged.
- Differentiate USB 2.0 and USB 3.0

USB 2.0 connector on Gigabyte Z97 motherboard
A USB 2.0 plug will have two rows with five pins on each side, with one leg missing from the 10 pins considered 'key' for proper connection orientation. The cable connector on the computer case will have 10 holes (power supply for two ports) or 5 holes (power supply for one port). A simpler USB 3.0 plug, they are a rectangular grid of 20 feet, accepting power cables for one or two USB 3.0 ports. You need to make sure that the motherboard you buy has ports that match the computer case and vice versa. With new motherboards in 2017 there may be a USB 3.1 Gen 2 connector, which means the USB ports will be new and faster. However, there are only a few computer boxes with cables that work with this plug.
10. Front-panel plug (Front-Panel Header)
The front end of the chassis is a network of pins on the motherboard, some pins will be color coded or labeled, it accepts wires from the computer case. With this set of pins, you can connect with small cables for reset switches and the power of the computer case as well as the hard drive and power LED operation or onboard speakers on some designs. Most of these pins come in pairs, knowing the polarity of the pairs is not useful when switching cables but important for LEDs. The motherboard manual will have a circuit diagram showing the locations of these connectors.
- How to manually turn off the power light and hard drive light on the desktop
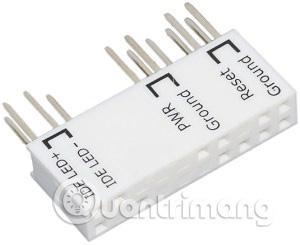
Asus Q-Connector for the chassis outside
Some motherboard manufacturers, pioneered as Asus with "Q-Connector", provide a small block plugged into the top of the chassis front pins with an identical footer on top. This allows you to plug the appropriate wires outside the computer case, then plug in the connector.
11. Chipset
"Chipset" is a term that includes motherboard silicon on the motherboard providing paths between (and the controller for) different subsystems in a computer. People who buy motherboard motherboards, come from Intel or AMD, identify the motherboard line and many features it supports. A motherboard manufacturer usually provides different number of motherboard form factors and features based on unique chipsets. However, a chipset can support certain features, in fact implementing these features depends (or does not depend on) the decision of individual motherboard manufacturers.
12. AC '97 and HD Audio (Audio accessory connector on the front of the chassis - Audio Header Font)
Most computer enclosures have a headphone and microphone jack, connecting the inside of the case in a cable with a 10-pin plug connector. This connector is plugged into a battery on the motherboard that is now called an 'HD audio' plug. In summary HD Audio has the function of automatically detecting ports, allowing the system to sense the presence of plugged and ported devices and operate accordingly.

HD Audio plug on Asus motherboard
Previously, this connector on the motherboard was a 'AC' 97 'connector and during the switching between these two connectors, some motherboards provided the selector in the BIOS, allowing silicon switch operation. The sound of the motherboard between AC'97 and HD Audio modes is often the same. For some older PC cases, you must have a forked cable with connectors for both HD Audio and AC '97. With the new motherboard, you can use the old connector because HD Audio is the modern standard.
13. Serial ATA

SATA 6Gbps ports on AMD MSI-based motherboards
See the article What to know about Serial ATA (SATA) for this term.
14. ATX 24 pin power supply plug
If you've ever built your computer or upgraded your motherboard, you've probably plugged a large power supply cable into this connector. A white socket has two rows, each of which is a main power source for the system, withstand the largest power cable from a PC's power source.

ATX 24 pin power connector on MSI board
ATX 24 pin is a motherboard connector. At the time of the mid-2000 transition, ATX power connectors were divided into 20 batteries and 4 batteries. That's because older motherboards require a 20 pin connector, and 4 additional batteries to add current at different voltage levels.
15. CPU power supply plug
On a modern motherboard, the CPU power connector is a 4-pin connector (divided into 2 and 2) and 8 batteries (divided into 2 and 4), connecting a Molex-type power supply, usually placed in the position near actual CPU socket. The cables from the recent PC model power supply fit into the CPU power plug, usually labeled with 'CPU power' labeled.
This plug provides a separate power supply from the main 24 pin connector and is sometimes called the '+ 12V' connection. Buyers rarely care about the 24-pin CPU and ATX power supply plugs in the motherboard, but if you plan to re-use the old power supply (produced from mid-2000 or longer), you should carefully consider the first two types. this plug.
16. CPU Socket
CPU Socket is the base of the CPU, has a square shape on the motherboard. Specific processor socket types need to be compatible with each other. In other words, not all Intel chips work on all Intel motherboards. Nearly full, the Intel processor uses a design with an interface pin that is part of the socket, in contact with the processor chip bottom. Meanwhile, AMD's chips still use old sockets with holes for chip batteries.

Intel LGA 1150 socket on Gigabyte motherboard
Here are some of the most popular sockets:
• Socket 2011 and Socket 2066 , these are the sockets used in Intel's most advanced processors, such as the Intel Core i7-6950X Extreme Edition and Core i9-7700X. The second type uses Socket 2066, new to Intel's Core X CPU line in 2017.
• Socket 1151. Socket 1151 is currently used with Intel's Core processors, the 1151 socket is equipped with Intel 6th generation chips ("Skylake") and also works with 3rd generation chips. 7 ("Kaby Lake"). It is a Socket 1150 connector.
• AMD FM2 and FM2 + , these sockets are used with APU accelerated processors, which is AMD's term for CPU-accelerated video chips. The FM2 + dock appears at the end of 2013 to be used with the 2014 'Kaveri' APU "Kaveri" series, but the older APU compatible with FM2 will work on FM2 + motherboards.
• AMD AM3 + , this socket is used with the latest AMD FX-series processors, only for CPUs, without integrated graphics.
• AMD AM4 is used by AMD's latest APU chips and Ryzen's main product line, AM4 is a new, dedicated socket for AMD consumer CPUs.
17. Acceleration processor (APU)
This is AMD's term for the A and E-Series processors that feature graphics acceleration. It stands for Accelerated Processing Init, and these chips use AM4, FM2 and FM2 + sockets, depending on when they are created. The first APUs that use the FM1 socket have stopped working. Intel's Core chips with Intel's HD graphics graphics card are also APU; However, the term is only used by AMD.
18. Capacitor
You will see these electronic components scattered on a typical motherboard that operates in many different subsystems, but their basic functions act as "containers" for charging. Depending on where they are used, they may take different shapes (small drums, small blocks), different sizes and colors.
Normal capacitors are electrolytic, containing a small amount of liquid immersion material. Depending on the quality of production and expected life, these types of capacitors may leak over time, resulting in motherboard failure. Users often prefer Japanese-made capacitors to ensure longevity and motherboard manufacturers often advertise 'Japanese capacitors' if they use it. Solid state capacitors are often used more because they do not leak when used over time.
19. CMOS, CMOS battery
CMOS stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, it is a memory array on the system board containing its BIOS and settings and maintaining system clock settings.
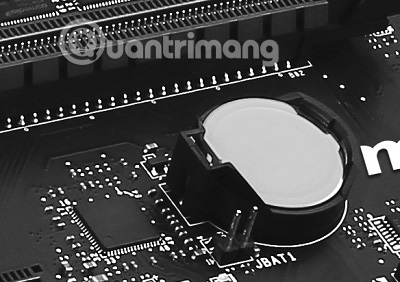
CMOS batteries are installed on MSI motherboards
In order to maintain its settings with the system turned off or not plugged in for a long time, a battery on the CMOS holder board increases. In modern motherboards, this battery is almost always a copper battery x CR2032.
20. Debug LED
An increasingly popular feature on high-end motherboards, Debug LED (Debug LED) is a particularly handy feature for people who build their personal computers. An indicator screen (usually two digits) displays an error code if the PC does not start. The codes, outlined in the motherboard manual, can help you determine the cause of the computer not booting such as unregistered RAM or video card error.
- Things to know when choosing to buy mainboard
- Learn computer components and decode signals for basic errors
- Clean the motherboard, increase computer life