Set up Wi-Fi authentication in Windows Server 2008 - Part 2
In this article, I will continue the discussion by configuring the RADIUS function in Windows Server 2008, introducing how to configure wireless access points and how to configure clients.
In Part 1 of this series, I explained why businesses should use Enterprise mode of Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA or WPA2) instead of using Personal mode (PSK). . We also know that 802.1X authentication in Enterprise mode requires a RADIUS server and this is a component available in Windows Server.
We have installed and configured the Certificate Services in Windows Server 2008. In this article, I will continue the discussion by installing and configuring the Network Policy and Access Services. It will then set up wireless controllers and access points with encryption and RADIUS settings. Next we will configure the clients and make the connection.
Install the Network Policy and Access Services Role
In previous versions of Windows Server, the RADIUS function was provided by the Internet Authenticate Service (IAS). However, starting with Windows Server 2008, it is provided by the Network Policy and Access Services. This component includes previous IAS services along with the new NAP feature.
In the Initial Configuration Tasks window, find and click Add roles . If you have closed or hidden that window, click Start> Server Manager, select Roles and click Add Roles.
Select Network Policy and Access Services (see Figure 1) and click Next .

Figure 1: Network Policy and Access Services role settings
Review the tutorial and click Next .
Select the items listed below (see Figure 2):
- Network Policy Server
- Routing and Remote Access Servers
- Remote Access Services
- Routing
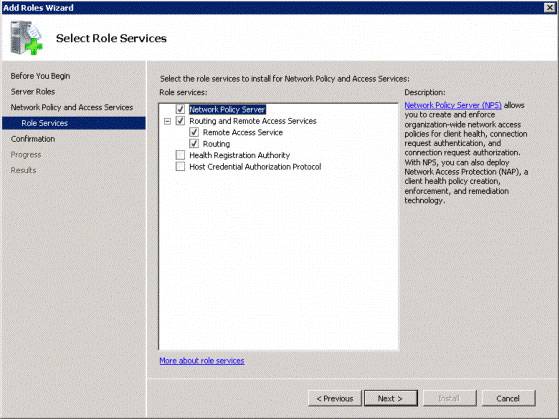
Figure 2: Choose to install the first four options
Click Next , and then click Install and wait for the installation process to complete and click Close .
Now you can start configuring NPS with the RADIUS function: click Start , type nps.msc and press Enter .
With the Standard Configuration option, select RADIUS server for 802.1X Wireless or Wired Connections (see Figure 3) from the drop-down menu.
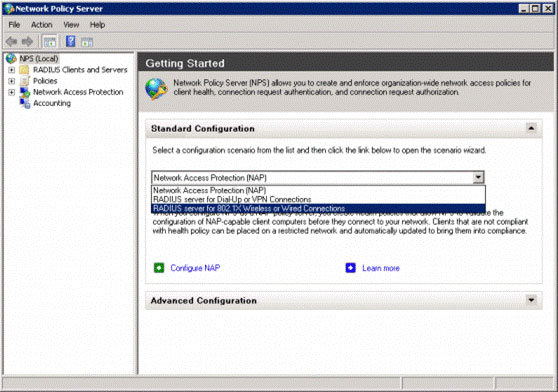
Figure 3: Select the RADIUS server for 802.1X
Click Configure 802.1X .
With Type of 802.1X connections, select Secure Wireless Connections (see Figure 4) and click Next .
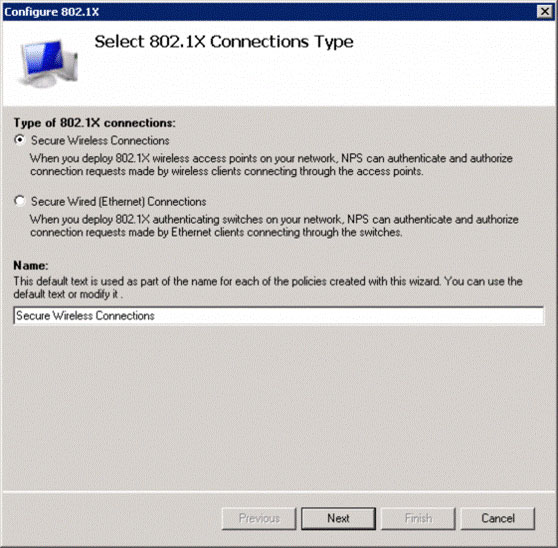
Figure 4: Choose to secure wireless connections
For each wireless controller or access point, click Add to create a new RADIUS client entry. But what is shown in Figure 5, you will have to specify the name, which is easy to distinguish, IP or DNS address and Shared Secret shared secret.
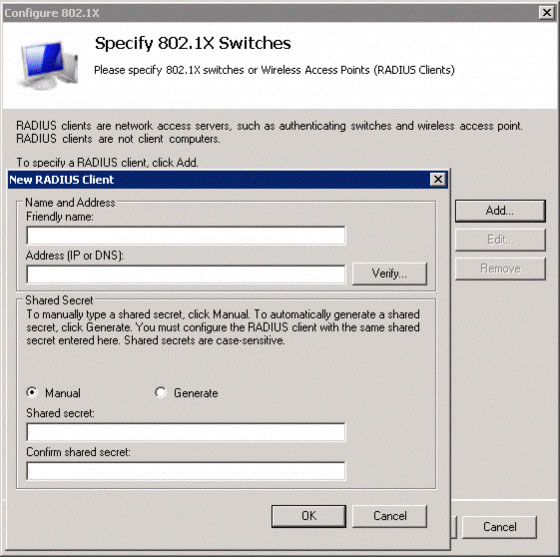
Figure 5: Enter details for your wireless controller or access point
These secrets are very important for authentication and encryption. Please enter complex details with a certain length, like a password. They need to be unique to each wireless controller or AP. You then need to enter such Shared Secret sharing secrets into the respective controllers or APs. Remember to keep them secret, save them somewhere safe.
Regarding the authentication method, Authentication Method, select Microsoft Protected EAP (PEAP) because we are using PEAP.
Click the Configure . button, select the certificate you created earlier, click OK .
In the Specify User Groups window (see Figure 6), click Add .
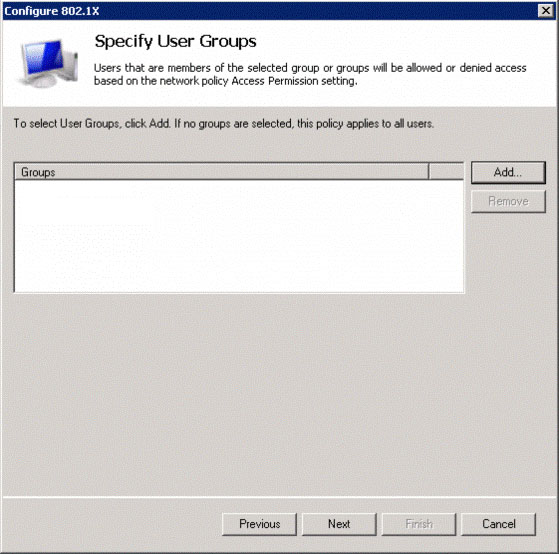
Figure 6: Add the user groups you want them to connect to
In the Select Group dialog boxes, enter groups, click Advanced to search for available groups. If you haven't created additional groups, select Domain Users to allow users and Domain Computers to authenticate the machine if your controllers or APs support it. If you receive an error message that the domain does not exist, restart the Active Directory Domain Services server and do it again.
Once you have added the desired groups, click Next to continue.
In the Configure a VLAN window (see Figure 7), if your network (switch and controllers or AP) supports VLANs and you have configured them, then click Configure . to set up VLAN functions.
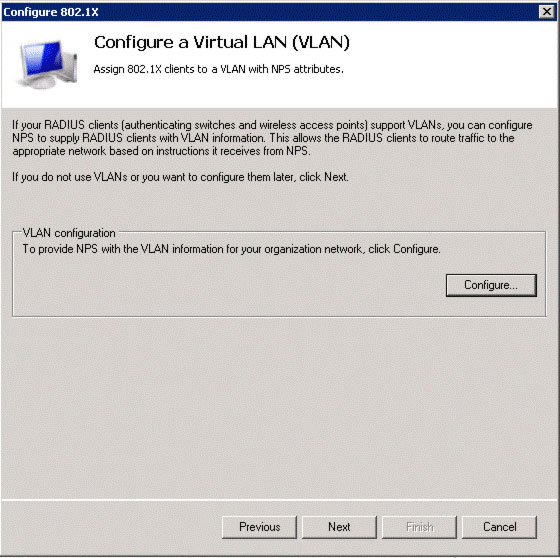
Figure 7: Click the Configure button to define VLAN settings
Now that you're done configuring VLANs, click Next .
Review the settings and click Finish .
Configure the wireless controller or AP
Now is the time to configure the controllers or access points. First, invoke the web interface by entering their IP address into the browser. Then navigate to the wireless settings.
Select -Enterprise or WPA2-Enteprise . For encryption type, select TKIP if using WPA or AES if using WPA2 . Then enter the IP address for the RADIUS server, this is the Windows Sever machine you set up. Next, enter the shared secrets you created earlier for the controller and AP. Then save the settings.
Install the CA certificate of the client name
In Part 1, you created the server certificate and the Certificate Authority (CA) for yourself. So you need to install the CA on your clients. In this way, the client can validate the server before performing authentication.
If you are running a domain network using Active Directory, you need to deploy this certificate with Group Policy. However, it is possible to install it yourself, this is what we will discuss.
To view and manage certificates in Windows Server 2008, call the Certificate Manager. If you saved that MMC to your desktop in Part 1, open it. Otherwise, follow the steps below:
- Click Start , type MMC and press Enter .
- On the MMC window, click File > Add / Remove Snap-in .
- Select Certificates and click Add .
- Select Computer account and click Next .
- Select Local computer , click Finish , and then click OK .
Tip: You should save this MMC to your desktop for easy access later: click File > Save .
Expand Certificates (Local Computer Account) , open Personal , click Certificates .
As shown in Figure 8, right-click the certificate with the end of CA, then select All Tasks , Export . Then follow the wizard to export. When prompted, do not export the private key but use the DER format. You should export to the USB drive so you can bring it to other clients easily.
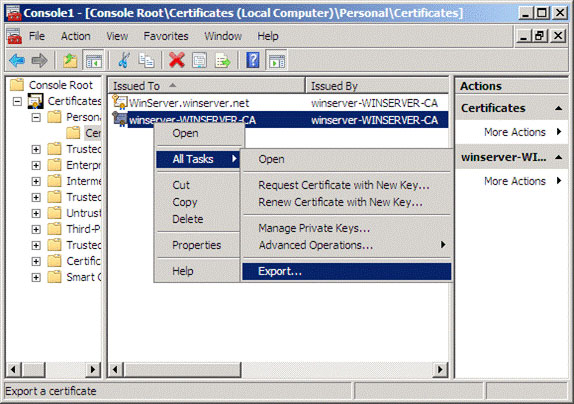
Figure 8: Export the CA certificate to install on the clients
Now on the client computers, double-click the certificate and click the Install Certificate button (Figure 9). Use the wizard to import it into the Trusted Root Certificate Authorities repository .
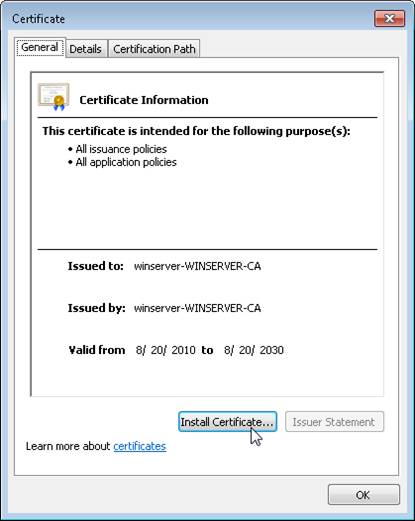
Figure 9: Installing the CA certificate on the client
Configure network settings on the client
You can configure network settings. Like installing certificates, you can push network settings for clients using Group Policy if you are running a domain network with Active Directory. However, you can still manually configure the clients, as discussed in Windows XP, Vista and 7 below.
First, create a preferred network profile or network entry. With Security Type choose WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enteprise . With Encryption Type , select TKIP if using WPA or AES if using WPA2 .
Open the network profile and select the Security tab (in Vista & 7) or the Authentication tab (in XP). In XP, check the Enable IEEE 802.1x authentication option for this network.
With Network Authentication method (in Vista & 7, as shown in Figure 10) or EAP Type (in XP), select Protected EAP (PEAP) . In XP, also cancel select both checkboxes at the bottom of the window.
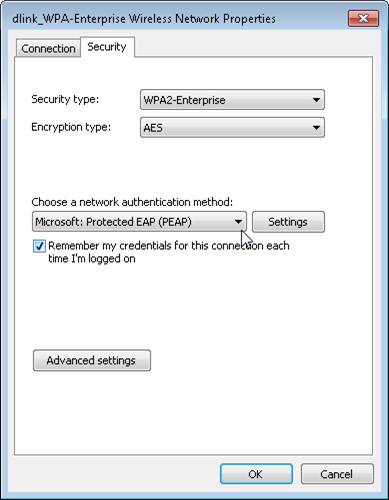
Figure 10: Select PEAP as the authentication method
Only in Windows 7, click the Advanced Settings button in the Security tab. Then on the Advanced Settings window, check the Specify authentication mode option, select User Authentication , and click OK to return to the Security tab.
Click Settings (in Vista & 7) or the Properties button (in XP).
Then in the Protected EAP Properties dialog box, follow these steps (Figure 11 shows an example):
- Check the first box, Validate server certificate.
- Check the second box, Connect to these servers , and enter the full name of the server. If necessary, find it on Windows Server by clicking Start> Server Manager.
- In the Trusted Root Certification Authorities list box, select the CA certificate you just entered.
- Choose Secured password (EAP-MSCHAP v2) as the authentication method.
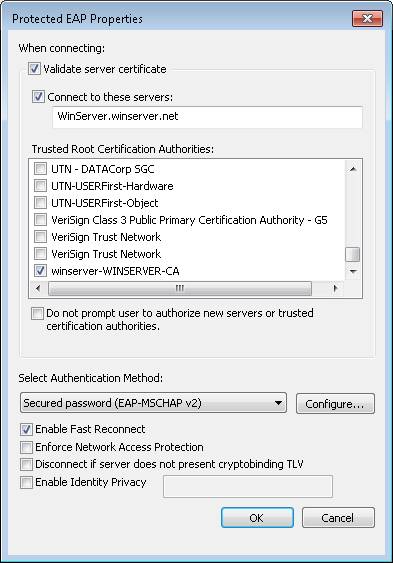
Figure 11: Configuring PEAP properties
- Click the Configure button. If you run a domain network using Active Directory, check this option. Otherwise, deselect it so users can enter their username and password and then connect to the network.
Finally, click OK on the windows to save the settings.
Connect and login!
Now you have configured the server, the AP and can make the connection.
On the client computer, select the network from the list of available wireless networks. Unless you have enabled client mode to automatically use its Windows login, you will be prompted to enter the login credentials, as shown in Figure 12. Use the account on the Windows Server in the group already Previous configuration in the Network Policy and Access Services section. If you select the Domain Users group, the Administrator account needs to be enabled by default.
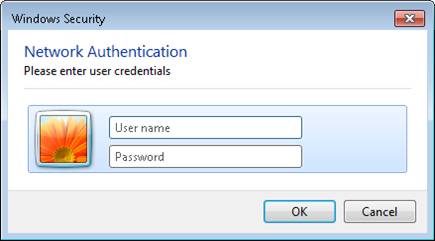
Figure 12: Login window
Conclude
You now have an Enterprise-encrypted network and 802.1X authentication, to do that, we really need to thank Windows Server 2008 for its built-in RADIUS functionality. In this article, I have shown you how to set up servers, APs, and clients for PEAP authentication. Users can now log in with their accounts.
To manage RADIUS server settings, such as adding or removing APs, use the Network Policy Server utility: click Start > All Programs > Administrative Tools > Network Policy Server .
You should read it
- ★ Overview of Windows Server 2008 Firewall with advanced security features (continued part 3)
- ★ Microsoft rushed to release security updates for Windows XP, Server 2003
- ★ Secure FTP Server with Windows Server 2008
- ★ Switch to WPA / WPA2-Enterprise encryption
- ★ What is WPA2 (WiFi Protected Access 2)?