Optimize performance on Forefront TMG - Part 1
Network Administration - In this section we will show you some of the factors that affect the stability and performance of the TMG firewall.
The Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 firewall is an integrated security gateway capable of providing application layer security and advanced network layer services. It can perform low-level protocol inspections, application traffic inspections, user authentication, enable reputation-based control and HTTPS communications inspection. These advanced features consume a lot of resources and can interfere with throughput and slowdown if the system is configured incorrectly or not appropriately sized. In this article, we will introduce some common problems that can lead to poor performance and besides some ways to improve and optimize the solution.
Hardware configuration
Before starting any TMG firewall discussion and performance, it is important to note that the underlying hardware for TMG's support task is in the role it is deployed in. The best way is to use high quality server-class hardware or dedicated security devices. For best results, the hardware needs to be properly sized for its environment and has the appropriate load. TMG's application layer inspection and advanced network layer can significantly abuse system-dependent resources, so to get satisfactory processing power, memory, disk space and primary network It is of fundamental importance to the solution's high stability and performance.
Determining how much hardware is required for a particular implementation is extremely difficult, the reason being that each implementation is unique and has many dependent factors. To assist in determining hardware requirements, Microsoft introduced the Forefront TMG Capacity Planning Tool. This tool allows you to enter specific details about your environment and it will provide advice on hardware specifications by relying on the number of users expected and bandwidth. You have as well as protection features to be used. There should be a redundancy plan for CPU and memory to ensure the best performance, which is also a preventive measure in case of future expansion.
Infrastructure services
The TMG firewall relies heavily on supporting infrastructure services to perform its tasks. The overall performance of the solution depends on how well services such as Active Directory and DNS work. If there are problems with Active Directory or DNS, there is no way to control TMG to overcome the performance issue. While there are many things that can go wrong with Active Directory or DNS, we will not provide a comprehensive list of issues, but just mention some common issues that can significantly reduce TMG's performance. :
Network connection - Performance may be negatively affected if the TMG firewall does not have a reliable network connection with Active Directory or DNS. TMG needs to be well connected with these services; Ideal when they are located in the same physical location and have gigabit speed connection. Make sure all intermediate devices such as routers, switches, . work well and there are no error signs.
Active Directory site configuration - Sometimes poor performance may also be due to the TMG firewall performing domain controller authentication located in different geographical areas. This is caused by improperly configured Active Directory sites. Therefore, make sure that Active Directory IP subnets must be properly defined and that the Active Directory site is configured to contain domain controllers located with the TMG firewall.
Network connection
At the lowest level, TMG is a routing firewall that distributes data from one interface to another if the policy allows. Thus network configuration plays an important role in the performance of the system. Here are some key configuration settings and optimal throughput recommendations and network performance:
Port speed and duplex mode - Port speed error or duplex setting (duplex) will dramatically reduce network performance. To work properly, these settings must be the same as at the connections. That means that if you manually configure the settings on the TMG firewall's network interface, you must also do so on the switch to which it is connected. If the switch it connects to is a free switch, you must also set the settings of the TMG firewall network interface in auto-negotiate mode. You cannot configure one side manually and the other side is automatic. In any case, hubs should not be used in production environments.
DNS Configuration / Network Interface Link Order - This is one of the most common configuration errors and can cause poor name resolution performance as well as untrusted authentication. DNS servers need to be configured only on the internal network interface. In addition, basically the internal network interface on multiple firewalls needs to be pre-configured in the order list of network interfaces.
Quarantined network segments - A great idea when placing network interfaces of TMG firewalls in isolated network segments whenever possible. This way we can improve both performance and security issues, reducing the risk of ARP cache poisoning attacks and making the network harder to detect. If Network Load Balancing (NLB) is enabled, this is even more important. By default, NLB will broadcast synchronized information so that all hosts on the network segment can see it. TMG firewalls configured in isolated network segments will limit the broadcast, which will only advertise to hosts that require it.
Rear firewall configuration - TMG firewall is not an optimal configuration in terms of security and performance. Hosts exposed directly to the Internet are protected by scanners and inspectors. Configuring the TMG firewall as a back-end firewall for another firewall can reduce the amount of noise it must handle. For example, a Cisco ASA at the network edge is configured to allow only the protocols that TMG will handle to release a lot of resources to perform advanced application layer traffic authentication and inspection. Another benefit here is to reduce the ' pollution ' of the logs, making the log data clearer and easier to understand, recognizing unusual traffic.
Web Proxy Client - Configuring clients as Web Proxy clients brings a lot of performance benefits, although many administrators prefer to configure the SecureNAT client because it does not require changing client software. SecureNAT clients will essentially consume more resources on the TMG firewall than Web Proxy clients because the Web Proxy client will set up fewer TCP connections to the TMG firewall's web proxy listeners to Retrieve more web content. For example, when connecting to a popular website (in this example espn.com), the SecureNAT client has set up 31 TCP connections to display the main page.

While configuring a Web Proxy client, only 6 TCP connections are required to display the same page.
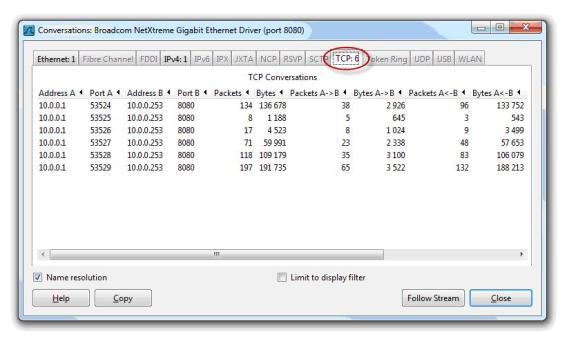
So if you have thousands of users, increasing the number of these TCP connections will greatly affect CPU performance.
Conclude
Indeed there are countless factors that can affect TMG firewall stability and performance. In this article, we have introduced you to the importance of having healthy infrastructure services such as Active Directory and DNS. We have set up the TMG firewall to be well connected to these services, and we need to configure the site and Active Directory IP subnet properly set up. We also consider configuring network connectivity and best practices to improve network throughput. Properly configured network settings such as port speed and duplex mode, DNS server configuration, network interface order, etc. are important issues in optimizing throughput. The installation of the firewall and client configuration also significantly affects the system's resource use and performance. In the next part of the series, I will continue the discussion by showing you some other ways to help optimize the TMG firewall.