Learn about USB PD
There are many different charging methods for phones and devices and USB PD is one of the fastest. In fact, existing Android phones use this technology for faster charging.
So what is USB PD and how does it help? Let's find out through the following article.
What is USB PD?
The USB in USB PD stands for 'Universal Serial Bus' . It's familiar to you because it's the same technology that allows you to plug a mouse, keyboard, and other peripherals into your computer. However, the new PD cluster represents 'Power Delivery'.
So what is Power Delivery and what role does it play? The goal of this technology is to charge devices faster than regular USB. It uses the USB-C format, which a lot of modern devices are using.

The USB PD charger can charge devices with up to 100 watts and power some powerful USB-C devices. Of course, if you plug a 100-watt cable into your phone, it's likely to do more harm than good! That's why the cable 'listens' to the needs of the devices and adjusts the power flow accordingly.
With the USB-C universal standard combined with a USB PD-compliant power output, you get a cable that can plug in and charge a wide range of devices.
Why is USB PD important?
USB PD must compete with Qualcomm's Quick Charge, Huawei's SuperCharge and Samsung's Adaptive Fast Charging technologies. So what makes USB PD really different?
Eliminate monopoly barriers and reduce waste
The problem with the above technologies is that they are privately owned by the companies. Manufacturers create them to charge their own devices. Things get more complicated if the Qualcomm-powered phone breaks and you replace it with a Samsung phone. At that point, the Qualcomm charger will no longer fit the new phone's specifications, so you'll have to use a Samsung fast charger instead.
As technologies come and go, people throw away old chargers and cables that no longer work, which adds to the amount of technological waste generated.
USB PD prevents this by introducing a new standard. You use a USB PD charger to charge your phone quickly, then use the same charger to power a phone made by another company or even something larger like a game console.
It doesn't matter whether the device is small or large, or who makes it, because the charger always adjusts its output to meet the device's needs.
USB PD uses two-way charging
Any USB PD device can receive or supply power. This handy feature means there's no need for different types of chargers.
This is why USB PD is so essential. It has the potential to change the world of fast charging technology and create a simple solution for consumers and manufacturers alike.
USB PD applies good ideas
The video above shows many examples of the evolution of USB PD over the years. When manufacturers began developing in-house fast charging technology, each followed a different path. Charger output (W, watts) is measured as voltage (V, volts) multiplied by current (A, amps).
Different fast charging standards use different techniques to increase output. For example, Qualcomm increased the voltage to achieve higher wattage (hence faster charging speeds), while BBK Electronics, maker of OnePlus, Oppo and Realme) used larger ampere values.
Each conduction standard has its pros and cons, but the best of both worlds is to combine incremental steps in current and voltage to achieve the optimal power supply for each scenario. That's what the group that defines USB specifications, the USB Consortium, did. It starts with USB PD 1.0, which supports 5, 12, or 20 volts at 1, 2, 3, or 5 amps.
USB PD specifications explained
USB PD has 4 different versions: 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 3.1. The first version, 1.0, released in 2012, was quite simple. It offers manufacturers five different configurations to use for the device. These configurations have a maximum output of 100W, as shown in this table during the USB PD 1.0 announcement presentation in July 2012.
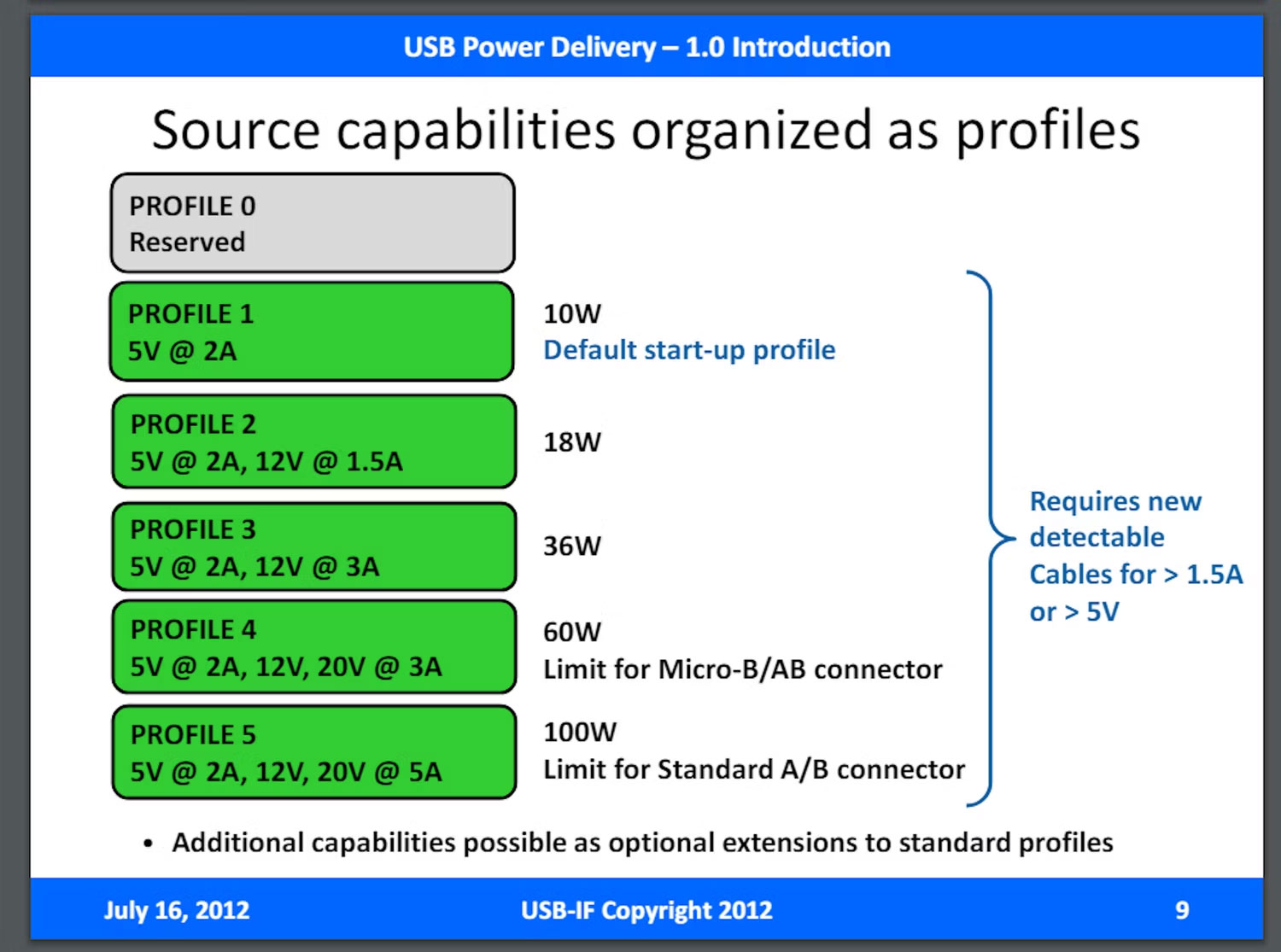
When USB 2.0 arrived, it introduced more configurations for manufacturers to use, and the power flow varied to suit the needs of the device. It stays limited to 100W, which is enough for most use cases. The Environmental Coalition on Standards (ECOS) has listed a table of different levels of USB PD 2.0 and above chargers in its "One Charger to Fit Them All" report:
| USB PD power strip | Fixed voltage | Current range | Device example |
| 0.5 - 15W | 5V | 0.1 - 3.0A | Headphones, small USB accessories |
| 15 - 27W | 9V | 1.67 - 3.0A | Smartphones, cameras, drones |
| 27 - 45W | 15V | 1.8 - 3.0A | Tablets, small laptops |
| 45 - 100W | 20V | 2.25 - 3.0A 3.0 - 5.0A with rated cable only | Large screen, laptop |
USB 3.0 uses the same power configuration as 2.0 but has some key differences. The ports you will notice when using the cable are the ports they are compatible with. USB PD 2.0 works with USB Type AC ports, while 3.0 is Type C only. However, the other benefits of USB PD 3.0 are aimed more at developers as they provide superior data reporting 2.0. Manufacturers can receive detailed information such as battery charging speed and device temperature through the 3.0 cable.
Then, in 2021, the USB Implementers Forum introduced USB PD 3.1. As stated on its website:
.USB PD Revision 3.1 specification is a major update that enables up to 240W of power delivery via a full-featured USB Type-C cable and connector. Before this update, USB PD was limited to 100W when using a 20V-based solution using a USB Type-C cable rated at 5A. The USB Type-C specification has also been updated to version 2.1 to specify 240W cable requirements. With the updated USB PD protocol and power definition, this expands the application possibilities of USB power to a large number of applications where 100W is not available.
Before running out to grab a USB PD 3.1 cable, it's worth noting that many of your home chargers won't reach this 240W output. For example, a phone charger won't require anything above 100W, even for fast charging. As such, getting a USB PD 3.1 cable will not 'unlock' faster charging speeds on the phone. If tried, the cable should fit whatever the phone requires.
How to use USB PD?
So how to get started if you want to use this technology? To get USB PD recharging speeds, a charger, USB-C cable, and device that supports this standard is required. So you have to double check that everything can use USB PD when shopping.
Check the user manual and specifications for your device to see if it supports USB PD. You should research your device's compatibility as some devices will support USB PD but are not compliant with the USB-C standard.
As for the charger, you may already own a USB PD compatible charger. If you own a USB hub and wonder what the "PD" charging ports are for, those are the only ports that fit the USB PD specifications. You can use these ports to charge your USB PD device faster.
What happens if the wrong cable is used?
With all the talk about proprietary chargers and different power levels, you might be worried about mixing and matching USB charging cables. If I accidentally plug the OnePlus fast charger into a phone that doesn't recognize it, will it damage the electronics?
Luckily, as ThioJoe's video above explains, there's very little chance that using the wrong cable will cause your device to explode. There are countermeasures to prevent 100W of current flowing into a pair of headphones and overloading them.
However, if you don't want to take any risks, it's best to use a charger specifically designed for your device. As long as you are using both the cable and plug that came with your product or purchasing them from the official store, there is nothing to worry about. Additionally, you can choose the safest USB-C chargers to avoid unfortunate incidents.
USB PD may seem confusing and even unnecessary at first. However, since manufacturers have adopted this standard on their devices, we now have USB fast charging that works on most devices and can charge both ways.