11 uses of ps command in Linux
For system administrators, ps is a frequently used tool. The ps command in Linux is used to list the processes currently running on the system, with many available filtering and display modes via flags and arguments.
The syntax of ps may be strange. Normally we will follow the UNIX convention, using a single dash before each flag. So far, that syntax is most widely supported. However, the command can also be run with BSD syntax, remove the prefixed dash and use a separate flag name syntax. For example, flag aux replaces the more popular -ef flag. Make sure you know which one you're using.
How to use ps command in Linux
- 1. Show all processes
- 2. Filter by user
- 3. Filter by process name
- 4. Filter by process ID
- 5. Transfer the results to grep
- 6. Display specific columns
- 7. Arrange processes according to usage
- 8. Rename the column title
- 9. Display results according to hierarchical tree type
- 10. Display the thread inside the process
- 11. Show all root processes
1. Show all processes
ps -ef 
The ps command displays all running processes with complete data about each process. This data includes columns showing PID, terminal type (TTY), runtime and command name.
2. Filter by user
ps -e -u userName The ps command filters the results and displays only the processes owned by the specified username. This command can also be used without a prefix.
3. Filter by process name
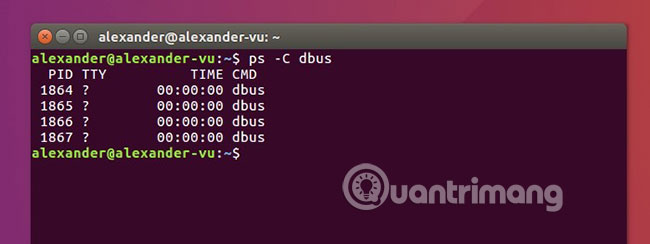
ps -C name The ps command on the filter results according to the process name. Search is not case sensitive, but all process names are in lowercase after filtering. The command will search through all processes without prefixes -e.
4. Filter by process ID
ps -ef -p 1234,5678,9012 If you know the ID of the running process you want to display, you can filter it specifically with the -p flag . This command can take multiple PIDs as arguments, separated by a comma and no spaces.
5. Transfer the results to grep
ps -ef | grep worker 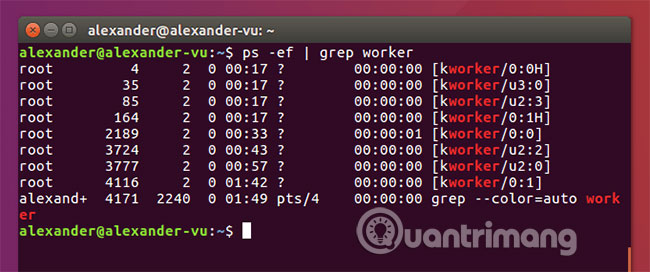
If you want more flexibility when looking for results from ps, you can convert the results to grep. Although this is a combination of many commands, not just a pure ps command, it is a normal part of any administrator tool. With grep, you can search using regular expressions to find results that match the pattern and more.
6. Display specific columns
ps -e -o pid,uname,pcpu,pmem,comm 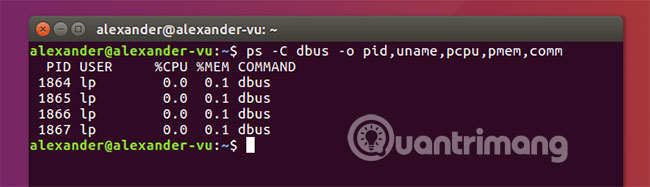
Flag -o sets the options for displaying specific output for the results of the ps command . See the full list of standard display options for ps command at https://linux.die.net/man/1/ps.
7. Arrange processes according to usage
ps -e --sort=-pcpu -o pid,pcpu,comm The above syntax arranges commands according to the listed columns. The prefix minus (-) arranges the feature in descending order, while the plus (+) prefix is sorted in ascending order. This command also uses the -o flag to display specific columns, not necessarily arranged.
8. Rename the column title
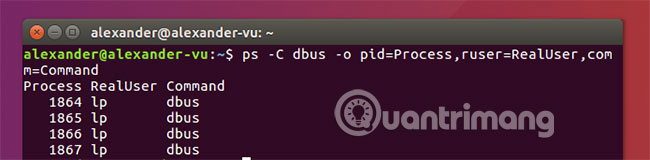
ps -o pid=Process,ruser=RealUser,comm=Command When using the -o flag to create user-specified output interfaces, columns can be renamed. Add an equal sign (=) and enter the desired new name, using the -o flag for each renamed title. Titles can also be hidden in specific columns by leaving the name section blank after the equals sign. You can mix and match with name columns that are renamed and by default. Just make sure to use the -o flag for each column to be renamed as follows:
ps -e -o pid,pcpu=CPU -o pmem=RAM,comm 9. Display results according to hierarchical tree type
ps -e --forest Use ASCII to create tree-style structures, displaying processes. The command displays the child processes of major processes and organizes the results accordingly. To hide sub-branches, use -H instead of --forest.
10. Display the thread inside the process
ps -p 4041 -L 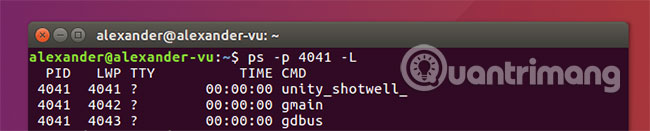
Flag -L switch the display for every function of ps on the screen. This command is most useful when tracking threads of a particular process.
11. Show all root processes
ps -f -U root -u root 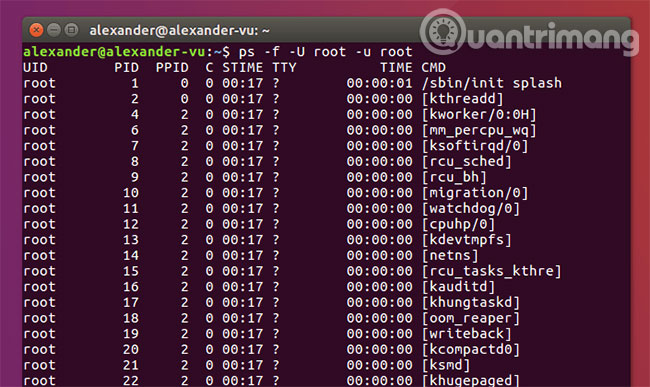
The ps command performs a search for all root processes running efficiently. This command shows them in full format thanks to the -f flag . You can combine it with the -o flag to customize the output.
Although many UNIX-style flags are more suitable for other terminal commands, BSD commands can display information in many different and sometimes more useful formats. If you are interested in learning about BSD style flags, see the following man page: https://linux.die.net/man/1/ps.
Hope you are succesful.