How to manage and restore Tmux sessions in Linux
Tmux is a multiplexer terminal (a tool that allows to use multiple terminals in a window) that integrates many useful features and is supported by a large number of community-created plugins.
Terminal multiplexers like tmux and Screen give the terminal window super-power, allowing you to open multiple sessions in tabs and split screens.
Combined with numerous terminal tools and session saving features, you can also restore Tmux sessions after a hard reboot.
How to manage and restore Tmux sessions in Linux?
- Install tmux
- Create Windows and Pane
- Install the plugin
- Plugin manager
- Resurrect
Install tmux
Running tmux on a system is relatively simple if you are using a Linux distribution.
For Ubuntu, this means 'summoning' apt from the terminal and installing the package from the distribution's official repository. For other distributions, use the bundled package manager to handle installation (tmux is available on most distributions.)
sudo apt-get install tmux 
Create Windows and Pane
In tmux, there are two terms used to describe the main types of layout configurations that a user can create.'Window' is the term in tmux for tabs. Creating a new window will create a tab that you can switch to with a simple command.
On the other hand, 'Pane' is the separated part in the current tab or 'Window', which can also be switched using the command.
Before starting to create these things, it's important to note that tmux is a method in the function. This means that the interaction with the terminal session and tmux occurs in separate 'modes'. This is useful, since you can use each individual terminal session normally open, without accidentally triggering the tmux command.
To get access to tmux and start issuing commands, first start a new tmux session and name it:
tmux new -s babytmux 
Feel free to change your name (like 'babytmux' for example)!
Tmux will open immediately and a new shell session will start. But we want to open more sessions, remember?
To enter tmux's command mode, you need to use the prefix, usually press Ctrl and b simultaneously. You won't see anything change after pressing the prefix, but you can type the commands by typing : right after. To exit command mode, complete the command by pressing Enter or pressing the ESC key to exit without making changes.
We will use a shortcut to create horizontal division: Press Ctrl and b , then " .

Now you can navigate between the two sessions with the following keys: Ctrl and b , then o .
Each session is independent of each other, so you can open separate programs within each session. Divide the screen into 4 parts as follows: Ctrl and b , then press % .
Open whatever you want in each pane and it will keep running while you access other sessions.

To create a window, do the following: Press Ctrl and b , then c .
You can switch to the previous window or transition to another window with: Ctrl and b , then press p or Ctrl and b , then press n .

The status bar at the bottom of the screen shows you which process is running in each window and which window you're currently in.
To leave this tmux session, use: Ctrl and b , then type :detach-client .
The session will not stop running unless the machine is rebooted or you manually cancel it. To access it again, use the following command:
tmux a -t babytmux To make tmux sessions truly 'invincible' that you can come back after rebooting, you need to install one or two plugins.
Install the plugin
Using the plugin in tmux is relatively simple. However, there is a plugin manager you can use to make installing the next plugin easier.
Plugin manager
To install Tmux Plugin Manager, we will copy its files from Github with the following code:
# List of plugins set -g @plugin 'tmux-plugins/tpm' set -g @plugin 'tmux-plugins/tmux-sensible' # Other examples: # set -g @plugin 'github_username/plugin_name' # set -g @plugin 'git@github.com/user/plugin' # set -g @plugin 'git@bitbucket.com/user/plugin' # Initialize TMUX plugin manager (keep this line at the very bottom of tmux.conf) run -b '~/.tmux/plugins/tpm/tpm' 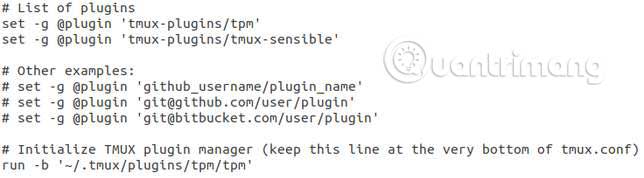
As you can see above, it is necessary to add the github username and plugin name (found in the plugin's github URL) for each plugin that you want to install from now on. The plugin manager will handle the rest. Use this code to make the plugin manager work:
tmux source ~/.tmux.conf Now, for plugins that need to recover a session after rebooting, continue reading the back of the article.
Resurrect
Tmux Resurrect does exactly what its name implies and returns the saved session using a simple command.
This plugin can be installed by adding the following to the .tmux.conf file :
set -g @plugin 'tmux-plugins/tmux-resurrect' 
Now let Tmux Plugin Manager install it using the following command in tmux: Ctrl and b , then press I (This is an uppercase 'i').
Once installed, you can start a session and save it with the following commands: Ctrl and b , then press Ctrl + s .
To restore a session, you can use Ctrl and b , then press Ctrl + r .

Using the above method, you can maintain an 'immortal' tmux session with all your favorite tools and processes, even after rebooting. Try and explore more features of tmux to make the most of the terminal.
Hope you are succesful.