How to identify phishing emails and unsafe websites
How to identify phishing emails
1. Check the domain name of email address
The first thing to keep in mind is that there aren't any companies that contact you from a public domain name like '@ gmail.com', '@ yahoo.com', or '@ outlook.com' ,. .
Most companies, corporations, or organizations have their own email domain and email addresses. For example, Google or its employees will never email you from addresses like 'xyz@gmail.com'. Instead, they will use their own domain name, for example '@ google.com'.
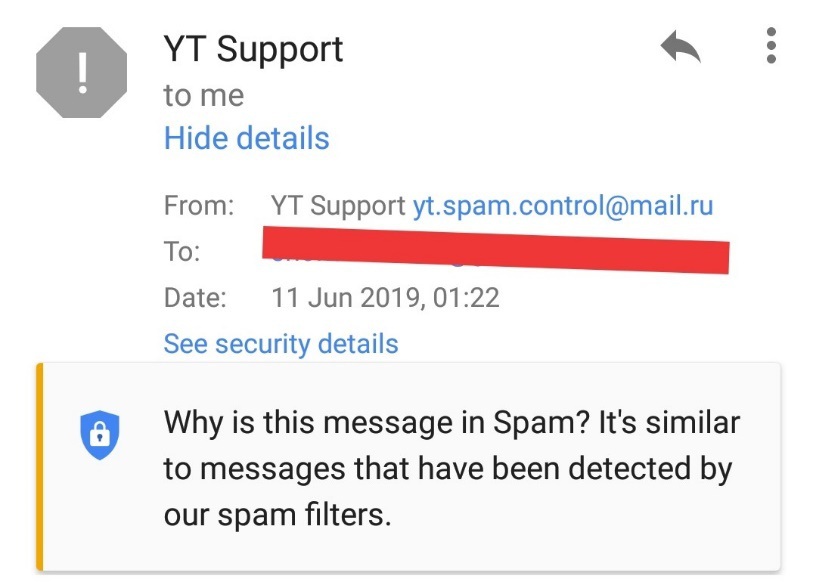
Therefore, if you see the domain name after the '@' character in an email address coincides with the domain name of the official website of a company, corporation, or organization, that email is an official email from public company, corporation, or organization and vice versa.
2. Check the Mailed-by, Signed-by, and Security items
Hackers can use fake servers to fake email addresses like 'xyz@google.com' or similar. However, they cannot forge other credential information such as mailed-by (sent by), signed-by (authenticated by), and security (confidential).
To check the authenticity of this information, click on the down arrow located below the sender's email address. You should now see details including mailed-by (sent by), signed-by (authenticated by), and security (confidential).
The items mailled-by and signed-by indicate that the email has been SPF verified , and has the corresponding DKIM signature .
According to Wikipedia: Sender Policy Framework (SPF), derived from spam prevention technology (spam), is a method to verify the sender's address (email address). This technique helps the recipient identify the sender's address is real or fake, thereby preventing the spread of spam or phishing online (phishing).
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is a method of detecting fake email addresses. It allows the recipient to check if an email originating from a particular domain is actually authorized by the owner of that domain.
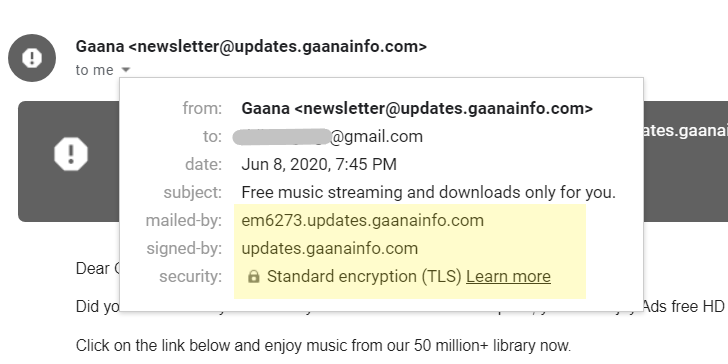
In addition, the security section indicates whether email is encrypted using TLS or SSL encryption during sending. These encryption standards ensure that no third party can eavesdrop or tamper with email during the sending process.
Emails from corporations, companies, organizations or banks will always have mailed-by , sign-by fields with official domain names, accompanied by encryption standards. Meanwhile, most phishing emails don't use secure connections, nor do they have any certificates or encryption methods. Even when this information is available, they are usually general information and are not relevant to the official domain name.
3. Identify links, phishing buttons in emails
Before clicking on any link or button in an email, you should hover the mouse pointer over it.
Immediately, you will see the actual link or click button at the bottom left of the browser. This will help you check whether these objects take you to a fake website, contain malicious code, or a website that is completely unrelated to the official website.

4. Check for spelling and grammar errors in emails
It sounds humorous, but it is an effective way to prevent phishing emails.
Phishing emails often have sloppy and ugly presentations, as well as often make silly spelling mistakes. Therefore, please check the email content to see if it contains any spelling, grammar errors. Also, you need to check if the email uses the keywords you often see in the junk email you've received before. If you make one or all of the errors mentioned above, it is definitely a fake email.
5. Check the attached file
Do not open attachments from senders you do not know unless you are sure it is safe. In many cases, the attachment is often a malicious file, and it can infect a computer or network when a user clicks on it.
Therefore, if an email has an attachment, check it for any unusual signs. In addition, always equip anti-virus software for personal or corporate computers.
How to identify unsafe websites
Links, buttons in emails or on social networks can redirect you to a fake website that looks exactly like the official website. Therefore, before entering any personal information, or paying for anything, it is essential to check that the website you are about to visit is safe.
1. Check the URL
As noted above, the URL can help determine the validity of a website. When you visit a website, always check that it is the official website of a company, organization, or corporation. For example, flipart.com is the official physical address, so if you see any other domain names than this one, for example flipart.offer24.com, it is definitely a fake domain.

2. Check if the website is encrypted
The next thing you need to do is check to see if the website you visit uses any coding standards. If you see a padlock icon next to the website's URL, the site uses SSL or TLS encryption . If you do not know, websites using HTTPS (HTTP + TLS) are usually more secure than websites that use HTTP .

Encryption standard SSL to ensure your information is transmitted safely and without any third party can eavesdrop or interfere with the data. Without SSL , the risk of data being eavesdropped or stolen will be very high.
Therefore, if you see a website using HTTP or FTP and do not have a padlock icon next to the domain name, do not enter sensitive information such as credit card information, home address, information. finance,.
3. Identify phishing websites based on domain names
Not all sites with SSL or HTTPS encryption are official and secure sites. Hackers can trick you with subdomains similar to the main domain.

For example, the official PayPal website has the domain name paypal.com. Therefore, if you see any other domain name, such as the domain name in the image below, it is a fake address. In this case, the hacker created the domain 'paypal.com.confirm-manager-security.com' to deceive the victim's vision. If not observed carefully, victims may think this is the PayPal website because the phrase 'paypal.com' in the URL.
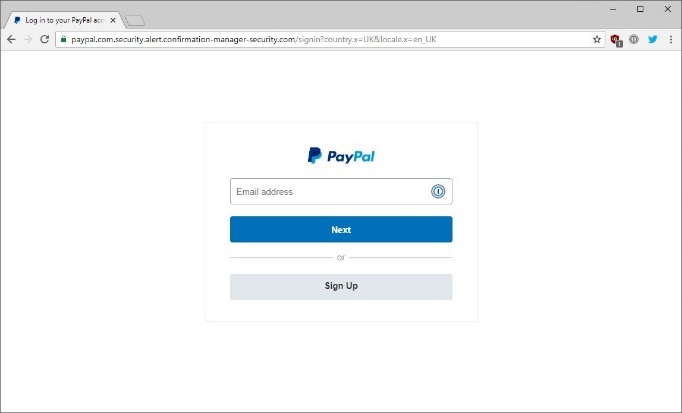
You should note that the real domain name is the part before the '.com' section. For example, in the address 'paypal.com', the section 'paypal' is the domain part. Similarly, in 'paypal.com.xyz.com', the section 'paypal.com.xyz' is the domain name.
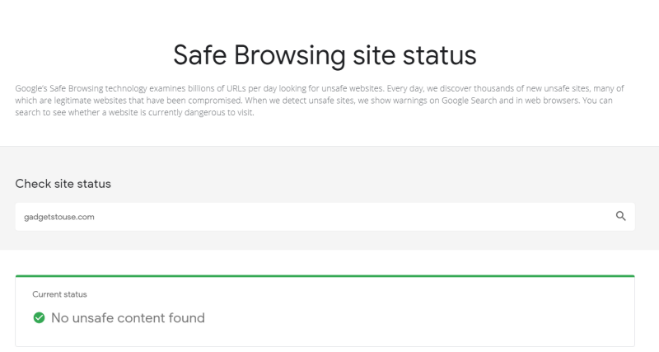
4. Check the website domain name using Google's Safe Browsing service
Google's Safe Browsing tool allows users to check if a website is fake.
To use this tool, go to the following address, then enter the website address you suspect and wait a moment for it to analyze and display the results in the Current status section .