What is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is an area in Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science to help computers have the ability to see and understand like humans.
Creating a machine that looks like the way people look is not simple, not only because it's hard to create such a machine, but even we don't really understand how the process looks.
No one thinks this is easy, perhaps except for the pioneer AI Marvin Minsky, in 1966 famous for guiding his students "to connect the camera to the computer and let it describe what it sees'.But that was 50 years ago and now research is still incomplete.
This human visual simulation gift is divided into 3 successive stages (similar to the way people look): eye simulation (acquisition - difficulty), simulating visual cortex (processing - very difficult) and Simulate the rest of the brain (analysis - most difficult).
Received
Eye simulation is the field where we achieve the most success.Over the past few decades, people have created sensors, microprocessors that look like (and to some extent better) the ability of the human eye to see.
Larger, optically perfect lenses and semiconductor sub-pixels that are as small as nano meters help today's cameras with incredible accuracy and sensitivity.The camera can capture thousands of images per second and remotely identify with high accuracy.
Despite the high fidelity, these devices were no more than cameras shot through the 19th century needle hole.They merely record how photons are distributed in the direction specified.The best camera sensor cannot recognize a ball, let alone catch them.
In other words, hardware is limited when there is no software - it is still the biggest problem.However, today's cameras are also quite flexible and serve as a good platform for research.
Describe
The brain is built from zero with images that gradually fill the mind, it does more vision-related tasks than any other job and this all comes down to the cellular level.Billions of cells combine to take samples, catch signals.
A group of neurons will tell another group when there is a difference along a straight line (at a certain angle, such as faster movement or in a different direction).High-level neural networks that synthesize these patterns form super-models: circles, moving upwards.Other information will gradually be added: white circle, that color line, increasing size . The image will appear when the information is added new.

The diagram describes the path, finding borders and other features in the image area of the brain
The first study on computer vision suggests that neural networks are so complex that they are incomprehensible when approaching from the top to the bottom: this book looks like this> so there will be this pattern> otherwise it will look like this .
For some subjects, this is also effective, but when describing each object, from many perspectives, variations in color, motion and many other things, imagine how difficult it is.Even a baby's level of awareness will need enormous amounts of data.
The bottom-up approach mimics how the brain works seems more promising.Computers can apply transformation sequences to images and find out the contours, the objects it refers to, the angle of view, the movement, etc. This process requires a lot of computational and statistical figures, but only by number of images. the picture he used to be taught - just like the human brain.
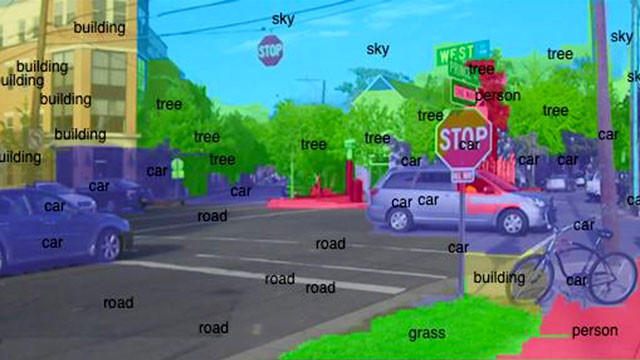
Awareness of computer images
The image above (from Purdue University's E-lab) shows a computer that displays (according to its calculations) the highlighted objects with looks and properties as other examples of that object, according to some degree of certainty about statistics.
Proponents of this approach can say 'I told you' until recent years, the creation and operation of artificial neural networks is very difficult because the calculation is too large.Progress in parallel calculations has reduced this difficulty.The past few years have seen the explosion of research and use of this system in mimicking the human brain.The process of pattern recognition is still accelerating and we are still making progress.
Understanding
Of course you can still build a system to identify an apple, from any angle, in any situation, whether standing or moving, whether bitten or intact, but still unable to receive an orange.
It also cannot tell you what an apple is, how much it is to eat, how big or small it is to use.This means that even good hardware and software cannot do anything without an operating system.
That's the rest of the brain: short / long-term memory, sensory data, attention, awareness, lessons when interacting with the world . written on the network of connected neurons more complicated than anything we've ever seen, in a way we can't understand.
That's where computer science and artificial intelligence meet.Between computer scientists, engineers, psychologists, neuroscience and philosophers, there is still no definition of how the brain works, let alone simulate.
Although new in the early days, computer vision was still very useful.It is present in your Face ID camera and smile.It helps self-driving cars identify signs and pedestrians.It is in robots in the factory, identifying products, transmitting to humans.
The path is still long until they look like people but on that road, the things they do are amazing.
See more:
- Instructions for new learners AI: networks of neural networks
- How does Al revolution help us answer the most fundamental problems of philosophy?(End)
- Train AI tools without knowing code with Google's new tool
You should read it
- ★ Nvidia's STEAL AI offers the ability to support inference for better computer vision models
- ★ Winnow uses computer vision to help cut waste in food processing
- ★ 4 eye protection tips for computer users all day
- ★ Google released a huge AI training data warehouse with over 5 million photos of 200,000 locations worldwide
- ★ Apple Vision Pro achieved impressive results in durability tests