Theory - What is Ransomware?
Ransomware - you've probably heard of this name many times already. Ransomware, spyware, extortion software . are all 1. This is the common name for a type of malware - Malware, which has the "effect" of preventing users from accessing and using the system. Their computer system (mostly detected on Windows operating systems). Malware variants of this type often give messages to victims that they have to pay a decent amount of money to a hacker account if they want to retrieve personal data or information or simply access it. their calculation. Most Ransomware software takes over and encrypts the entire information of the victim it finds (often called Cryptolocker ), while some other Ransomware uses TOR to hide and hide the C&C packets on computer (another name is CTB Locker ).
The price that Ransomware offers to victims is also diverse, "gentle" is about $ 20 , "heavier" can reach thousands of dollars (but on average, it is $ 500-600 ), also case of accepting payment by Bitcoin.

Notice of the familiar ransom of a Ransomware form
However, you need to be aware that even if you pay for a hacker, the percentage of users who get back their data and personal information is not 100%.
Theory - What is Ransomware?
- 1. Ransomware - where are they from?
- 2. How does Ransomware work?
- 3. Ransomware's history of formation and development
- Early birth
- Reaching outside Russia
- Reveton's time or Police Ransomware
- 4. The era of CryptoLocker
- 5. The structure of an attack
- 6. Entropy of a file
- 7. Is there any difference between Ransomware and normal malware software?
- 8. Popular 'hidden' methods
- 9. Is Ransomware simple?
- 10. Tactics against ransomware
- Master File Table
- Desktop environment
- Blackmail message
- 11. Think carefully before paying
1. Ransomware - where are they from?
Like other malicious software, Ransomware can access users' computers when:
- Find and use crack software.
- Click on the ad.
- Access black web, depraved.
- Access to fake websites.
- Download and install unknown software.
- Attached via spam email.
- .
2. How does Ransomware work?
Once compromised and activated in a user's computer, Ransomware will simultaneously perform the following tasks:
- Lock the computer screen, display the message as shown in the example above.
- Encrypting any document file it finds, of course, will have a password protected.
If case 1 happens, the user will not be able to perform any operation on the computer (except turning on - off the screen). Also on the screen will also have detailed instructions and specific transfer, money to hackers to retrieve personal information. The second (usually worse) because Ransomware will encrypt all text files (usually Office files like * .doc, * .xls . email files and * .pdf files ), files This will be converted to certain formats, password protected, you cannot perform any operations such as copy, paste, rename, change the tail or delete.
Ransomware , or called Scareware has a similar way of working with fake security software - FakeAV (1 type of Malware)
3. Ransomware's history of formation and development
Early birth
For the first time, Ransomware was discovered between 2005 and 2006 in Russia. The first reports of TrendMicro were in 2006, with the variant TROJ_CRYZIP.A - a type of Trojan after infiltrating into a user's computer, which would immediately encrypt, compress system files with a password, copper Time to create * .txt files with content that requires victims to pay $ 300 to retrieve personal data.
Gradually growing over time, Ransomware attacks the text and system files such as * .DOC, * .XL, * .DLL, * .EXE .
And until 2011, another form of Ransomware was SMS Ransomware that was discovered. The method of SMS Ransomware is a little different, that is, users have to send a message or call a hacker phone number, until the procedure of transferring money to the hacker is done. This variation of Ransomware was discovered under the name TROJ_RANSOM.QOWA - will continuously display fake notifications on the computer screen.
Besides, there is another variant of Ransomware - much more dangerous with the goal of hackers to attack the OS Boot Record (MBR) of the operating system. And when attacked, the operating system - Windows will not be able to boot. More specifically, these malware will copy the original MBR part of the system and override the fake MBR. When completed, the process will automatically restart the computer, and the next time hacker notifications (in Russian) will appear on your screen.
Reaching outside Russia
Initially they operate in Russia, but based on the popularity, number of victims, targets . these Ransomware types gradually spread out, first in Europe. By early 2012, TrendMicro has recorded a lot of attacks happening throughout Europe (even in the US and Canada). Also quite similar to TROJ_RANSOM.BOV, another Ransomware variant has spread very strongly in two main areas, France and Japan, along with the way the original Ransomware works.
Reveton's time or Police Ransomware
Why is it called Police Ransomware? Quite simply, because these Ransomware types when entering a victim's computer, will display a message as a true legal unit (you can review Figure 1 above). With content like:
- "Hello, you have been arrested for violating the law of abc xyz, while violating the constitution of the USA . for participating in illegal activities online ." along with that is the image, the insignia of the law. All of these Ransomware are briefly called under the name - Reveton .
By now you will have questions:
- How do they - Hacker know exactly that the victim - the computer user is in the locality, the city . to give content that is threatening to them? The answer here is that hackers rely on the IP address detection feature. For example, for victims in the United States, they will show a notice accompanying the FBI image, while in France it will be Gendarmerie Nationale.
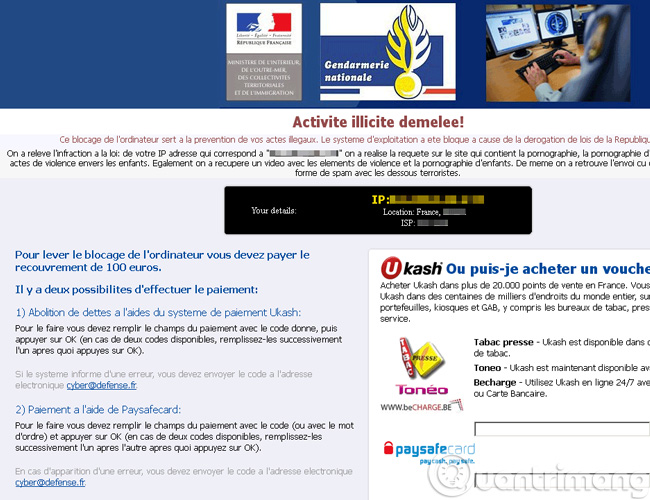
Fake notice of Ransomware in France, with the request of users to "pay a fine" of a fee of 100 Euro
Reventon variants use different accounts, payment methods to receive victims' money, usually systems like UKash, PaySafeCard, or MoneyPak . Hackers use these forms of payment because the system often blurs (not to display) the payee name, so they will be assured when making transactions via UKash, PaySafeCard, and MoneyPak .
By 2012, Reventon had developed new forms and tricks. That is they use the recording - Recording (using the voice of the local people) to convey information to the victim instead of the old way of notification.
4. The era of CryptoLocker
At the end of 2013, TrendMicro received the first reports on a completely new Ransomware category. These variants besides encrypting the entire data of the victim and locking their entire computer system. Based on Ransomware's actions that were named CryptoLocker - specifically if the malware was deleted, users still had to complete the transfer process, otherwise their entire data would be lost. .
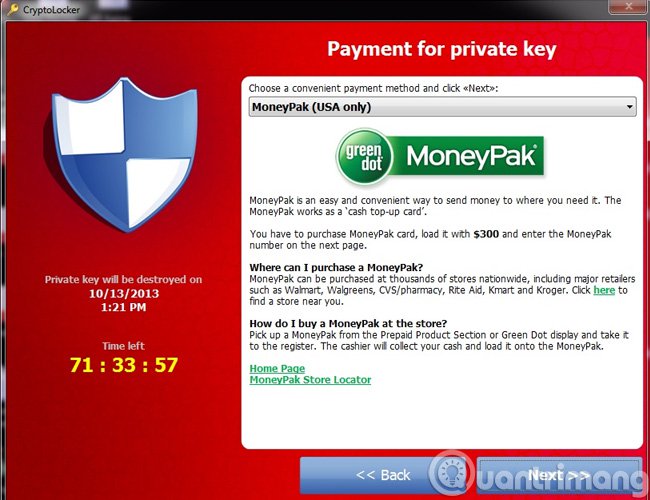
CryptoLocker familiar message
In addition, the hacker's "blatant" message indicates that user data has been encrypted using RSA-2048, but TrendMicro's report has shown that CryptoLocker 's encryption algorithm is AES + RSA ,
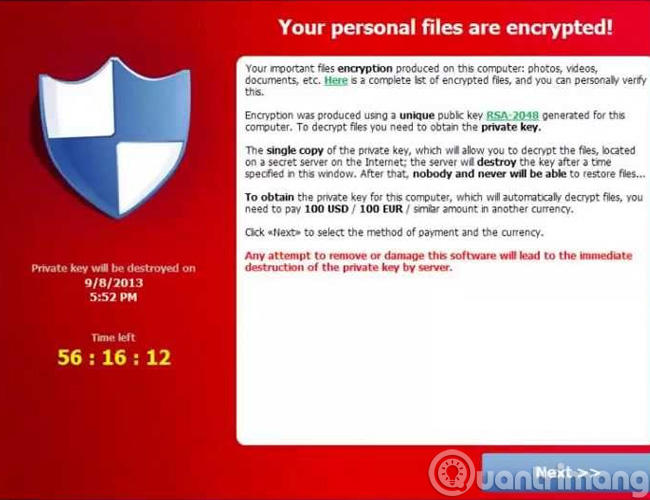
5. The structure of an attack
Unlike some popular malware variants, ransomware tries to hide itself for as long as possible. This is to create more time to allow ransomware to encrypt user files. Ransomware is designed to keep the maximum amount of system resources available to users, so there is usually no warning. Therefore, many users only detect infected ransomware after seeing the hacker message on the screen.
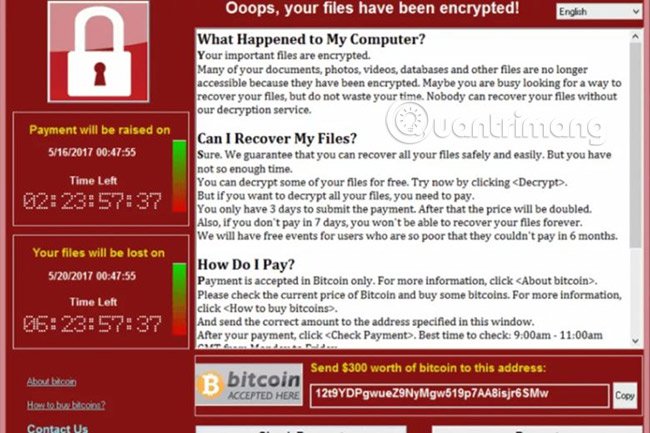
Compared to other malicious software, the process of ransomware infection is predictable. Users will download an infected file. This file contains the payload of ransomware. When the ransomware file is executed, nothing will happen immediately (depending on the type of ransomware). Users still don't know that ransomware has started encrypting their personal files.
Also, a ransomware attack has several forms as follows:
- Transfer data between host and control server in background.
- Entropy of files changes.
6. Entropy of a file
Entropy of a file can be used to identify encrypted files using ransomware. Rob VandenBrink briefly outlines entropy and ransomware files:
In the IT industry, an entropy of a file refers to a random unit, specifically called Shannon Entropy, named after Claude Shannon. This value is basically a measure of the predictability of any particular character in the file, based on the previous characters. In other words, it is a measure of the randomness of data in a file - measured in a scale of 1 to 8, in which normal text files will have low value and encrypted files or The compression will be of higher value.
7. Is there any difference between Ransomware and normal malware software?
Ransomware and malware have the same common goal: Always try to hide yourself. Users still have the opportunity to fight ransomware if they detect an early infection. The key point here is coding. Ransomware is 'notorious' for its ability to use encryption, although it has been used in malware for a very long time.
Encryption helps malware overcome the control of antivirus programs, by confusing signatures detection. Instead of seeing a sequence of familiar characters - which will warn anti-virus software to create a defensive barrier, the infection happens without attention. Although anti-virus software suites are becoming more "sensitive" to these strings - often referred to as hash - but malware developers are also actively dealing with these.
8. Popular 'hidden' methods

Here are some popular 'hidden' methods of ransomware:
- Detection - Many malware variants can detect whether they are being used in a virtualized environment. This allows malware to avoid the attention of security researchers by refusing to execute or extract. In return, this prevents the creation of an updated security signature.
- Timing - The best antivirus software suite that constantly warns, tests new threats. Unfortunately, antivirus programs in general cannot protect every aspect of the system at all times. For example, some malware will only deploy after restarting the system, escaping (and potentially disabling in the process) antivirus activities.
- Communication - Malware will get in touch with command and control servers (C&C server) to get instructions. This is not true for all malware. However, when malware does this, an antivirus program can detect specific IP addresses to host C&C servers and try to prevent communication. In this case, malware developers need only change the C&C server address, to avoid detection.
- False Operation - An ingenious counterfeit program is probably one of the most common signs of a computer being infected with malware. Users often assume that this is a regular part of the operating system (usually Windows) and completely follow the instructions on the screen. They are especially dangerous for PC users who do not have a lot of skills and, while operating as a user-friendly interface, it can allow a variety of malicious entities to access the system.
This list is not comprehensive. However, it includes some of the most common methods that malware uses to 'hide' on your PC.
9. Is Ransomware simple?

The word 'simple' may not be very accurate. Ransomware is very unusual. A ransomware variant uses more encryption than other ransomware, as well as in a different way. It is ransomware's action that makes it special and creates the fear of ransomware.
Ransomware uses slightly new features, such as:
- Encode large numbers of files.
- Deleting backups often allows users to restore from there.
- Create and store encryption keys on remote C&C servers.
- Request ransom, usually by Bitcoin.
While traditional malware, merely stealing user information and passwords, ransomware directly affects users themselves and upsets the computer environment immediately. In addition, its consequences are very noticeable.