Some tricks in Windows Scripting
TipsMake.com - Whether you are a person working in the IT field, such as a web designer, or an office worker, even a student, needs Windows Scripting because it will provide give you a lot of utilities. For Mac users, they can use AppleScript as the top solution, but here we will show Windows users how to use Windows Scripting in their work, and read the following article to see if it has what ability
Windows Scripting itself (WSF) is a file that includes many code and is saved as .wsf. Windows will compile and run this file directly.
Windows Scripting is actually much more powerful than batch jobs that IT professionals often write and run for years. WSF provides users with the power of a Visual Basic-like language. By default, you can create a VBScript or JScript WSF file on Windows and they all work fine.
In this article, we will introduce you to three typical tools that people often use in a professional and home IT environment. These three tools include: receiving input data from text files; ping different devices on your network; and sending email through the script is available.
The power of Windows Scripting
From the small script components you can completely combine them into a large, integrated file to perform tasks in turn with a single click. For example, after this article you can: get an IP list from the text file input, ping those devices and finally send an email notification about any device.
Receive and read the input file
The first step of this process is to learn how to read and process information from a text file input. Here we create a file called IPlist.ini (in .txt format that runs normally but we are not sure about possible problems) in the same directory as the script. The content of this file contains a list of all IP addresses that need to be checked. To be able to read each line of this text file, we use the following script:
This code uses an object in the Windows file system to open the file, then read each line at a time until the end of the file.

In case you misplaced the Iplist.ini file, the result will be displayed:

Ping to a Host
After reading the IP addresses of the incoming files, we now proceed to Ping them with Windows Scripting.
The Ping process is more complicated than reading a text file, because you need to use Windows Management Instrumentation scripting (WMI). You enter the following code:
After running the above script, a pop-up window will appear indicating whether the result of that IP is Ping or not.
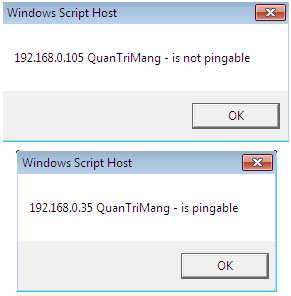
In this code, we only ping Ping to a single IP address, and what you need to do is embed the Ping command after each IP address is read from the text file, so you will Ping the entire address list.
Send an Email
Finally, when you have a script to check the IP address and a pop-up window will pop up if you encounter any errors. But if you have to run these scripts on a daily basis, it will not be interesting for most users. Instead, set up so that problems are automatically sent to the email.
To do this you need to know how to send emai via script. On the Internet there are many ways to do it, the most common is using the CDO method.
The above script allows you to send any text in the body of an email to any address using the Gmail service. You can modify the parameters to use for other SMTP mail servers.
Now proceed to put the above code together. As a result, the script will read the IP address, Ping to each address and then send a message string in the body section to the email:
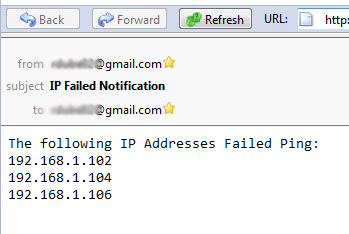
It is easier to automate your work in IT if you take advantage of the power of Windows Scripting. Any time these scripts will automatically check for you, especially if the system has a multitude of devices.
You should read it
- ★ Microsoft Windows PowerShell and SQL Server 2005 SMO - Part 1
- ★ How to Select Cells and Ranges in Excel Visual Basic
- ★ Detecting WhatsApp flaws allows an attacker to access files on the machine
- ★ Manage Windows networks using scripts - Part 4: Use Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration
- ★ Instructions on how to use PowerShell in Windows Server 2012