Red warnings to watch out for on insecure websites
In fact, web hosting can be risky if you are not careful. Studies show that up to 18.5 million websites are infected with malware.
Red Warning # 1: No SSL certificate
When visiting a website, the first thing you need to notice is a SSL (Secure Sockets Layers) certificate. It's really easy to check if a website has a valid SSL certificate, and there are two methods to determine it. The first method is to find the padlock icon on the left side of the URL at the top of the browser. And the second method is to consider the actual domain name itself.
If a website is already secured with an SSL certificate, you will notice that the domain name begins with 'https' instead of 'http'.
 The page that starts with https is the one with an SSL certificate
The page that starts with https is the one with an SSL certificate
The job of an SSL certificate is to protect sensitive information, such as credit and debit card details, from server to website (or vice versa). Without an SSL certificate, sensitive information is at risk of being exposed and accessed by cybercriminals.
Red Warning # 2: Poor customer reviews
If you want to know about the reputation of a website, the online community can give you something. Online review sites such as G2 Crowd and TrustPilot can help you see the opinion of the online community and evaluate specific websites and software.
The advent of social networking platforms has encouraged people to write about their personal experiences online. If the customer has had a good experience, they will leave a positive review and vice versa.
If you find that a brand, website, or software has many positive reviews, it's a good sign that you can trust their site and the sites associated with that brand.
Red Warning # 3: Lack of GDPR compliance policies and forms
Since the inception of the European Union's GDPR regulations, many websites have begun to request consent from users in exchange for access to and processing of their personal data. Consent is usually requested in a pop-up form.
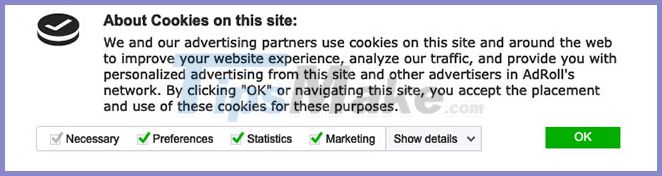 Read carefully before pressing the agree button!
Read carefully before pressing the agree button!
Most consent forms, like the example above, should clearly state how your data is collected and protected by the site.
Note : Make sure you read it carefully before confirming the consent.
The advent of this regulation marked a big step forward in data security.
Red Warning # 4: Lack of trust seal
Legitimate websites will have an authentication certificate, or trust seal, on the header and footer throughout the site. If it's an e-commerce site, then you will most likely see the trust seal on the checkout pages. Trust seal will come from recognized Internet security agencies such as Norton, McAfee and Trustwave.
 Trust seal will come from recognized Internet security agencies
Trust seal will come from recognized Internet security agencies
According to Sitelock, 79% of consumers expect to see a trust seal. Be wary, however, that there are some phishing sites that will try to deceive users with a similar look on their website. If you are unsure, try clicking on the trust seal. If they are authentic, you will be taken to another website explaining the accreditation.
Red alert # 5: Vague contact information
According to a survey by KoMarketing, 44% of respondents say that if they don't see any type of contact information, they will leave the website to look elsewhere. In addition, 54% say that the lack of adequate contact information reduces trust with suppliers.
A website must have contact information clearly visible on every page, such as an email address, phone number, physical address, and social media account. This gives consumers more peace of mind so they can contact someone if they need assistance.
Red Warning # 6: Presence of common malware indicators
Even if a website has the necessary SSL certificate, privacy policy, contact information or trust seal, it can still be unsafe if infected with malware.
Here is a list of all the common malware attacks:
1. SEO spam : You can see SEO spam in the comments section of the website. These often include misleading statements or a link to a website that contains external malware.
2. Phishing kit : They mimic websites that users often visit, such as banking websites and e-commerce stores, to trick visitors into disclosing sensitive information. These may include login information and related financial details.
In most cases, they look legitimate, but there will be grammar and spelling errors. Another Phishing kit is a malicious redirect - this is where you enter a URL and are redirected to another website that looks similar but suspicious. Again, pay attention to spelling and grammar errors.
3. Deface Attack : A recognizable attack pattern. This is where cybercriminals replace the content of a website with a different name, logo, and image.
4. Suspicious pop-ups : Be wary of any pop-ups that give out some extravagant and unrealistic claims. These pop-ups are trying to lure you into clicking CTA (Call-to-Action, a call-to-action button) to install malware on your system without your knowledge.
You should read it
- ★ Google Chrome will remove the Secure (Secure) label on the HTTPS website from September
- ★ Guidance on National Flagging on Facebook profile picture
- ★ Don't ignore these 10 security tips when creating a new website
- ★ What kind of SSL certificate does your website need?
- ★ The hacker 'World Cup' season