Learn about Dynebolic: Portable operating system that can be carried with you anywhere
Dynebolic is a portable Linux distribution based on Devuan, providing a complete multimedia production system that can run on almost any computer. Today's article will show you what makes Dynebolic great, how it works with similar systems, and how to install and run Dynebolic on USB.
Why should you use Dynebolic as a portable system?
One of the biggest advantages of Dynebolic is that it can respond to any type of task instantly. For instance, the distribution comes with a drawing tool, a digital audio workstation, and a full-featured video editor. This makes Dynebolic an attractive choice if you are looking for a great media production environment.

Another advantage of Dynebolic is that it runs entirely on free and open source software. This means that every part of the system, from the kernel to the applications, is free of any proprietary code. As a result, Dynebolic is also attracting security-conscious users who want to ensure that their distribution is fully auditable.
Compare Dynebolic with Puppy Linux
Dynebolic is not the only Linux distribution on the portable operating system market. Puppy Linux, a popular lightweight system, also provides a complete desktop that can run from USB.
Although both systems aim to be portable, each system has its own strengths and weaknesses. For comparison, let's look at some of the features that make a good portable operating system.
Overall interface and resource consumption
Puppy Linux uses a custom JWM-based environment for releases. This gives the system headroom when running on lower spec machines. However, its biggest drawback is that it can be difficult and unfamiliar to new users.

In contrast, Dynebolic uses the standard KDE Plasma environment for its interface. This Windows-like desktop makes it accessible to both new Linux users as well as veteran Windows users. KDE Plasma can consume a lot of resources, so it is not suitable for slow computers.
Application availability
Puppy Linux only comes with basic applications like AbiWrite for writing text and Inkscape for editing graphics. While it is possible to install third-party apps, doing so requires manual downloading and configuration when installing Puppy. As a result, you may find this operating system a bit lacking if you don't tinker with it.
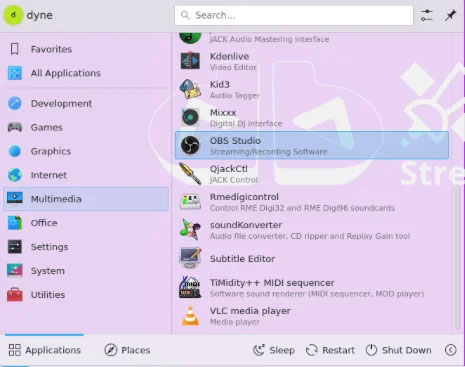
The Dynebolic, on the other hand, is designed to be a fully featured multimedia powerhouse. The developers have covered almost every popular productivity app like GIMP, Audacity, VLC, and OBS. Dynebolic does not require any configuration or manual downloading of files to be useful for media production.
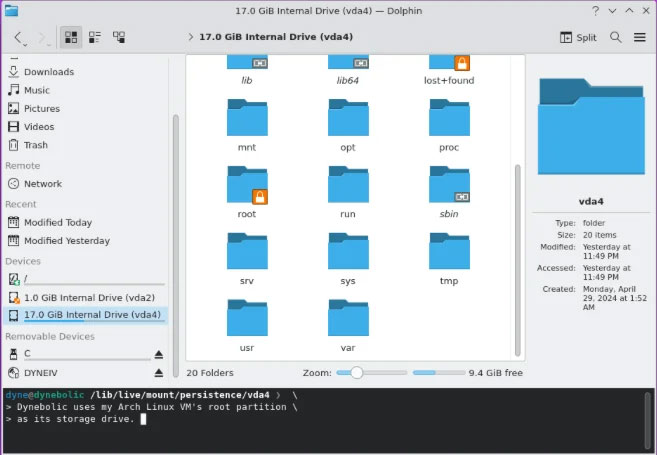
Permanent data
Puppy Linux uses the "save" feature to preserve any changes made in its system. These are small files located in a separate file system that the operating system records whenever the computer is turned off. This gives Puppy Linux the best of both worlds: Allowing files to be saved on a live distribution while keeping the distro portable.

Meanwhile, Dynebolic addresses data persistence by 'nesting' into the host operating system's existing file system. This is the process in which the operating system stores mutable system files on the existing file system instead of the computer's volatile RAM. During nesting, the operating system behaves very much like a regular distribution. However, doing so will prevent Dynebolic from becoming a portable Linux system.
Updates and developer support
One quirk of live Linux distributions is that they do not receive constant system updates from developers. This is because, by design, most systems run in 'read-only mode'.
Puppy Linux follows this trend by not providing a mechanism to update the system from within the operating system. Therefore, updating a Puppy Linux installation to a new version requires burning a new ISO to USB.
Just like Puppy, Dynebolic also does not provide any internal tools for updating the operating system. However, the developers have confirmed that they are working on a solution to this problem, which could make maintaining the operating system easier in the long run.
Download and install Dynebolic
The first step to get Dynebolic is to download the latest ISO file from the developer's website.
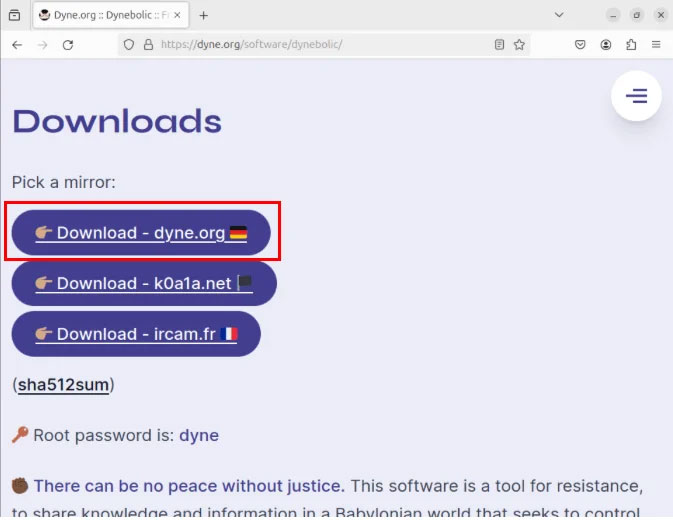
Burn ISO file to USB using BalenaEtcher or dd.
Turn off the computer you want to run Dynebolic, then plug the USB into the computer's USB port.
Turn on the device, then go to Boot Menu. The author was able to access this on his Lenovo ThinkPad by pressing F12.
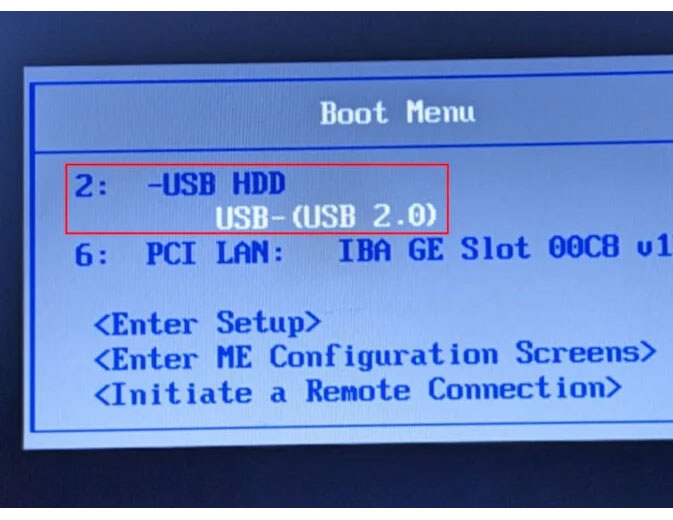
Select your USB, then wait for Dynebolic to load the bootloader screen.
Highlight 'dyne:bolic – no NEST', then press Enter to boot into the system.
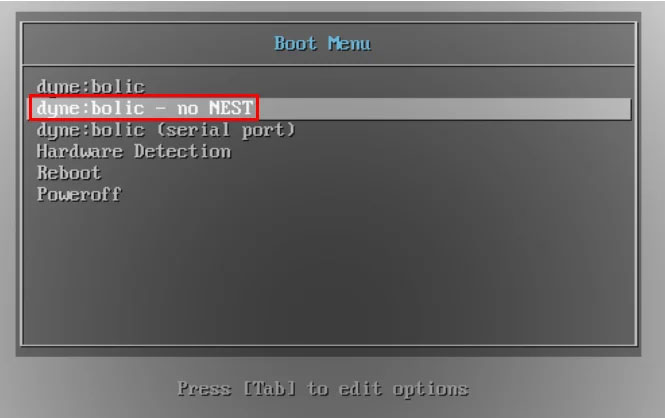
This will load the KDE Plasma screen and kernel into your computer's RAM.

 How to use jq command to process JSON in Linux
How to use jq command to process JSON in Linux How to use ifconfig command in Linux
How to use ifconfig command in Linux How to install Fossil version control system in Linux
How to install Fossil version control system in Linux 7 best Linux server distributions
7 best Linux server distributions How to install OnTrack software on Linux
How to install OnTrack software on Linux 6 best Linux desktop environments in 2024
6 best Linux desktop environments in 2024