How to Print Double Quotes in Java
Method 1 of 2:
Using Backslash as an Escape Character
-
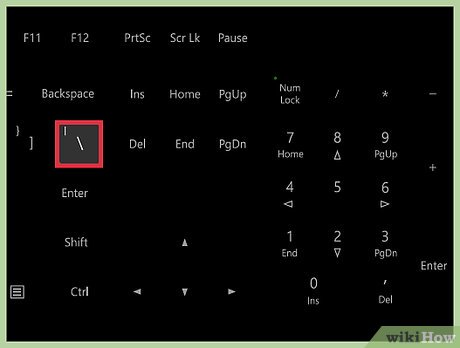
 Type the escape character . As you know, the double quote symbol " has special meaning in Java (displaying text). Whenever you want to ignore one of these meanings, use the escape character (backlash). This character tells the compiler that the next character is part of an alternate instruction.
Type the escape character . As you know, the double quote symbol " has special meaning in Java (displaying text). Whenever you want to ignore one of these meanings, use the escape character (backlash). This character tells the compiler that the next character is part of an alternate instruction.- Make sure you are hitting the backslash key, not the forward slash. The backslash key is next to the } key on most English keyboards.
-
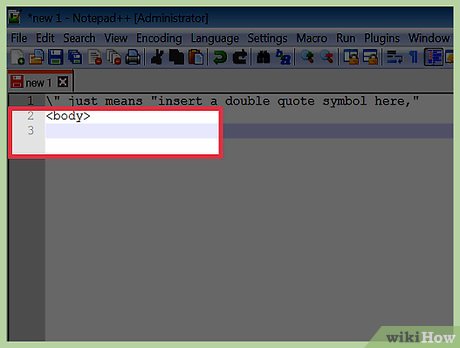
 Type " to display the double quote. These two characters together are called an escape sequence. Each escape sequence has a special meaning. In this case, " just means "insert a double quote symbol here,", without interpreting it as the beginning or end of text.
Type " to display the double quote. These two characters together are called an escape sequence. Each escape sequence has a special meaning. In this case, " just means "insert a double quote symbol here,", without interpreting it as the beginning or end of text.- You will need to use this sequence for each individual double quote you want to display.
-
 Continue your code as usual. The escape sequence does not affect the rest of your code. There is no need to type anything else to return to normal programming.
Continue your code as usual. The escape sequence does not affect the rest of your code. There is no need to type anything else to return to normal programming. -
 Remember to insert ordinary Java quotes as needed. One common mistake is to leave out the plain old " mark in your program. Remember that " is just for display, and does not remove the need to encase your display text in quotation marks. Here's an example:
Remember to insert ordinary Java quotes as needed. One common mistake is to leave out the plain old " mark in your program. Remember that " is just for display, and does not remove the need to encase your display text in quotation marks. Here's an example:- 1. The string for displaying "Hello" is "Hello"
- 2. To instruct the compiler to print this text, we wrap it in quotes: ""Hello"".
- 3. Here's what this looks like in a complete line of code:
System.out.println(""Hello"");
Method 2 of 2:
Using the ASCII Code
-
 Use char(34) to represent double quotes. Java can easily represent ASCII symbols using the char type. 34 is the ASCII code for the " symbol, so write char(34) to display " without using its special meaning.
Use char(34) to represent double quotes. Java can easily represent ASCII symbols using the char type. 34 is the ASCII code for the " symbol, so write char(34) to display " without using its special meaning.- You can look up a symbol's ASCII code by searching for an ASCII code table online.
-
 Place this code outside of the print string. If you make the mistake of putting this code inside the string, your program will print it exactly as it appears in your program: char(34). Here's the proper method of displaying "Hello" (with the quotation marks) using this method:
Place this code outside of the print string. If you make the mistake of putting this code inside the string, your program will print it exactly as it appears in your program: char(34). Here's the proper method of displaying "Hello" (with the quotation marks) using this method:System.out.println((char)34+"Hello"+(char)34);
Share by
Isabella Humphrey
Update 05 March 2020