How to Check Null in Java
Part 1 of 2:
Checking Null in Java
-
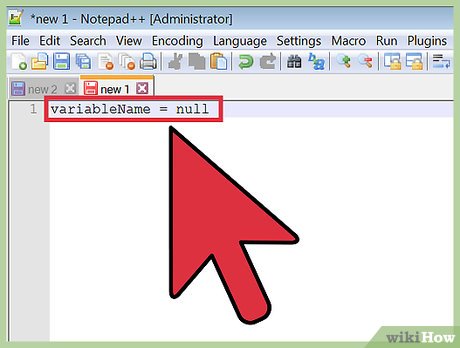
 Use '=' to define a variable. A single '=' is used to declare a variable and assign a value to it. You can use this to set a variable to null.
Use '=' to define a variable. A single '=' is used to declare a variable and assign a value to it. You can use this to set a variable to null.- A value of '0' and null are not the same and will behave differently.
variableName = null;
-
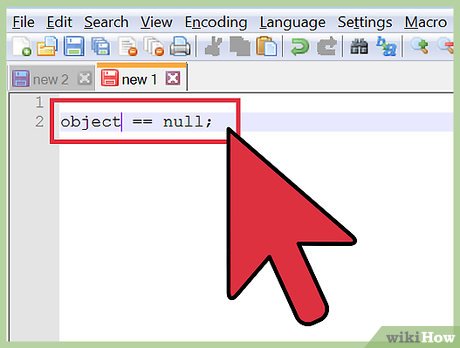
 Use '==' to check a variable's value. A '==' is used to check that the two values on either side are equal. If you set a variable to null with '=' then checking that the variable is equal to null would return true.
Use '==' to check a variable's value. A '==' is used to check that the two values on either side are equal. If you set a variable to null with '=' then checking that the variable is equal to null would return true.variableName == null;- You can also use '!=' to check that a value is NOT equal.
-
 Use an 'if' statement to create a condition for the null. The result of the expression will be a boolean (true or false) value. You can use the boolean value as a condition for what the statement does next.
Use an 'if' statement to create a condition for the null. The result of the expression will be a boolean (true or false) value. You can use the boolean value as a condition for what the statement does next.- For example, if the value is null, then print text 'object is null'. If '==' does not find the variable to be null, then it will skip the condition or can take a different path.
Object object = null ; if ( object == null ) { System.out.print ( "object is null "); } Part 2 of 2:
Using a Null Check
-
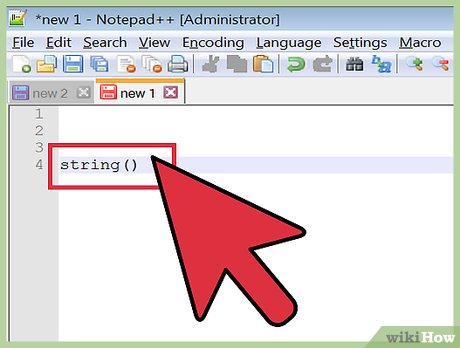
 Use null as an unknown value. It is common to use null as a default in lieu of any assigned value.
Use null as an unknown value. It is common to use null as a default in lieu of any assigned value.string()means the value is null until it is actually used.
-
 Use null as a condition for ending a process. Returning a null value can be used to trigger the end of a loop or break a process. This is more commonly used to throw an error or exception when something has gone wrong or an undesired condition has been hit.
Use null as a condition for ending a process. Returning a null value can be used to trigger the end of a loop or break a process. This is more commonly used to throw an error or exception when something has gone wrong or an undesired condition has been hit. -
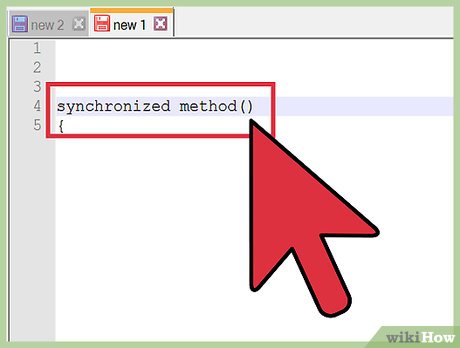
 Use null to indicate an uninitiated state. Similarly, null can be used as flag to show that a process has not yet started or as a condition to mark to be beginning of a process.
Use null to indicate an uninitiated state. Similarly, null can be used as flag to show that a process has not yet started or as a condition to mark to be beginning of a process.- For example: do something while object is null or do nothing until an object is NOT null.
synchronized method() { while (method()==null); method().nowCanDoStuff(); }
Share by
Lesley Montoya
Update 05 March 2020