How to Connect 2 Routers to Expand Your Network
Set up the first router

Connect the modem to the first router. Use an Ethernet cable to connect the router's WAN port to the high-speed modem's WAN/Internet port. For the purposes of this article, the router connected to the modem will be referred to as 'router 1'.
Some routers incorporate the function of a high-speed modem. If router 1 has this function, you just need to connect the device using a network cable.
The WAN port is also called 'Internet.'

Spike Baron
Network Engineer & Desktop Support
Spike Baron is the owner of Spike's Computer Repair. With over 25 years of experience in the technology industry, his business specializes in desktop and Mac repair, used computer sales, virus removal, data recovery, software upgrades, and Hardware. He holds CompTIA A+ certification and is a Microsoft solutions expert.

Spike Baron
Network Engineer & Desktop Support
Carriers often limit your internet speed. So connecting to a second router won't help. First, you should talk to your carrier to see if adding a second router will improve your internet speed or if they can increase your limit.

Connect router 1 to the computer. Use an Ethernet cable to connect one of router 1's LAN ports to your computer's Ethernet port.
You can also connect to the router without wires by entering the wi-fi name and password.

Turn on the modem and router 1. You need to wait while both devices boot up.

Open a web browser. You will need a web browser to connect to router 1's admin interface.

Enter the IP address of router 1 in the address bar. Type the IP address of router 1 into the address bar at the top of your web browser. The screen will display the router's administrator account login page. You'll need to check the user manual or the manufacturer's website to find the default IP address of router 1.
Here are a few default IP addresses of routers used by many people:
2Wire: 192.168.1.1, 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.254, 10.0.0.138
Apple: 10.0.0.1
Belkin: 192.168.1.1, 192.168.2.1, 10.0.0.2, 10.1.1.1
Dlink: 192.168.1.1, 192.168.0.1, 192.168.0.101, 192.168.0.30, 192.168.0.50, 192.168.15.1, 192.168.254.254, 192.168.1.254, 192 .168.0.10, 192.168.15.1, 10.0.0.1, 10.0.0.2, 10.1.1.1, 10.90.90.90,
Netgear: 192.168.0.1, 192.168.0.227

Sign in with your router's username and password 1. This opens the router's admin interface 1. Check your user manual or manufacturer's website to find your username and the default password for router 1.
Most routers choose "admin" as the username and password. You can also try entering "Password" or "12345678" in the password field. With some routers, the username or password is left blank.
If you enter the correct password but still can't connect, check the user manual or the manufacturer's website to learn how to reset the router's factory settings.
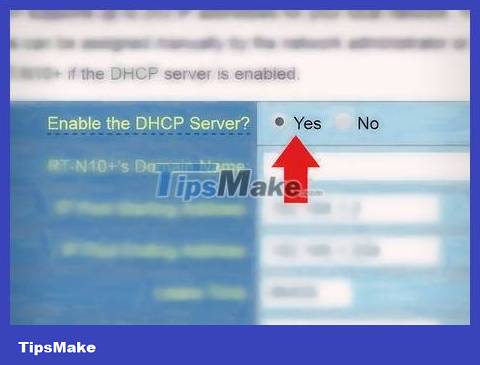
Enable DHCP on router 1. This will allow router 1 to assign all IP addresses on your network.
These settings are usually found under 'Network settings' or 'LAN settings'. The router's admin interface will vary by manufacturer and product line.
In most cases, the DHCP server is enabled by default.
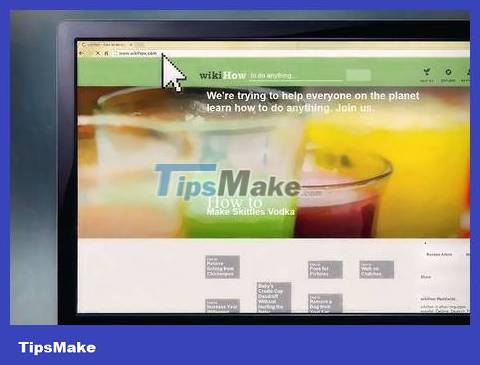
Check the network system and internet connection. Visit any website (such as https://www.wikihow.com) to see if you have an Internet connection. You need to make sure your network configuration still leaves room for an open LAN port on router 1.

Disconnect router 1 from the computer. You just need to remove the Ethernet cable connecting router 1 to the computer and leave the remaining connections intact.
Set up the second router

Connect and start the second router. Make sure you have enough electrical outlets and a computer near where you want to install the second router. Now you just need to connect and start the device. This is the device named "router 2" in the scope of this article.

Connect the computer to router 2. First, use an Ethernet cable to connect to the LAN port on router 2. The next step is to connect to the Ethernet port on the computer.

Enter Router 2's IP address in the address bar of your web browser. The screen will display the router 2 administrator account login page.
For most routers, the IP address will be 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1 or 10.0.0.1.

Log in with router 2's username and password. Use the default username and password to log in to router 2's admin interface, the same way you did with router 2. Route 1. You need to check the user manual or the manufacturer's website to find the default username and password.
With most routers, the username and password are usually "admin".
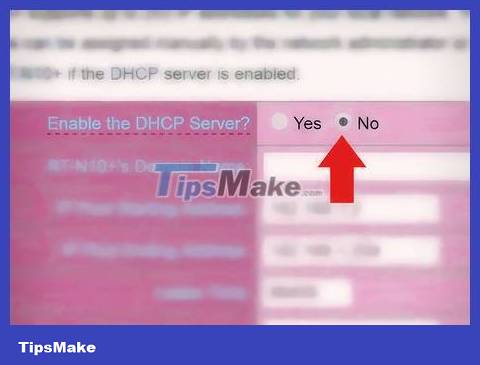
Disconnect the DHCP connection on Router 2. Since DHCP is enabled on router 1, you need to disable it on router 2 to avoid IP conflicts. Just find the DHCP settings in the admin interface and push the DHCP server slider to 'Off'.
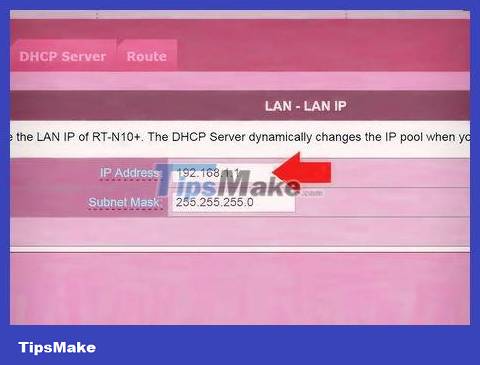
Assign a new IP address to router 2. From now on, the IP addresses of routers 1 and 2 will probably be the same. To avoid IP conflicts, router 2 needs to have a different IP address than router 1.
Look for the 'LAN' or 'Local Network' option on the admin interface. You will see a box containing the current IP address.
Replace the current IP address with a new IP address. The new IP address on router 2 must be in the same subnet as router 1. That means the first three groups of numbers in the IP addresses of both routers must be the same. You only change the number after the fourth dot of the new IP address so that it is different from router 1. This IP address must be different from the IP address currently assigned to the other device.

Set up a Wi-Fi name and password for router 2. This information will be the same as that for Router 1.
You'll find these settings under a menu called 'Wireless', 'Wi-Fi setup' or something similar.
If you're not sure about router 1's SSID and password, try looking it up on the device.
If router 2 is not a wireless router, skip this step.
Connect to the internet for your system

Turn off the power to router 2. Once router 2 is set up, it's a good idea to reboot the device - however, this time you should keep turning off the power instead of starting it up right away.

Connect the first router to the second router. First, use an Ethernet cable to connect to the LAN port on router 1. Next, connect to the first LAN port on router 2.
Make sure you do not attach the connection to the WAN port because the two ports look the same.

Connect router 2 to the power source and start the device. Router 2, after booting up, will have the IP address you have set up. When router 1 has an Internet connection, router 2 will also have a network.
Restart the computer connected to the router 2. Every time you connect the computer to a new network device, it is better to restart the computer.

Connect to other computers and devices. This can be a wireless connection or a connection via an Ethernet cable to an empty LAN port on the router. Router 1's DHCP server automatically assigns IP addresses to each device in the same subnet. Now is your time to experience the expanded network!