GIBON extortion code spread through spam
A new ransomware called GIBON, once again malspam (malware spread via email) attaches a malicious file and contains the download macro, installs the malicious code to blackmail the victim's computer.
Although there is not much information about this malspam, at least you know how to operate it and fortunately it can be decoded. So if you are a victim of this ransomware, download the file decryption tool here. https://download.bleepingcomputer.com/demonslay335/GibonDecrypter.zip
Why is it called GIBON ransomware?
When a new malicious code appears, researchers often name the string found in the executable file or malware itself, suggesting a naming scheme.

Gibon Ransomware communicates with C2 server
GIBON's name comes from 2 locations. The first is the identification string (user agent) of GIBON used when communicating with C&C server. The second is the Admin panel. In the image below, you also see it calling itself 'GIBON coding machine'.

Admin control panel of GIBON
See also: 10 typical malware types
How does GIBON encrypt computers?
Although detailed information on how to invade GIBON is not available, this is how it encrypts victim computer data. On startup, GIBON connects to the C&C server and registers the new victim by sending base64 encoded string containing timestamp, Windows version and 'register' string. It will tell C2 that this is a new victim.
C2 then sends a response containing the base64 encoded string used for extortion notice. Using the C2 server to create a blackmail notification instead of being made available to the executable file, the attacker can update it easily without having to run a new executable file.
When registering with C2, there will be a key code that encodes XOR sent to C2 based on base64 string, which is used to encrypt all files on the computer. The extension extension is .encrypt. In the process, GIBON periodically sends a ping to C2 to indicate that it is still encrypted.
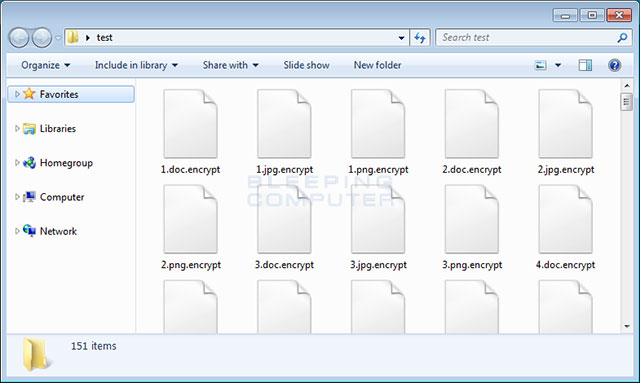
Encrypted files have additional .encrypt extensions
Each encrypted folder will also have a separate extortion notice READ_ME_NOW.txt that provides paid information and instructions.
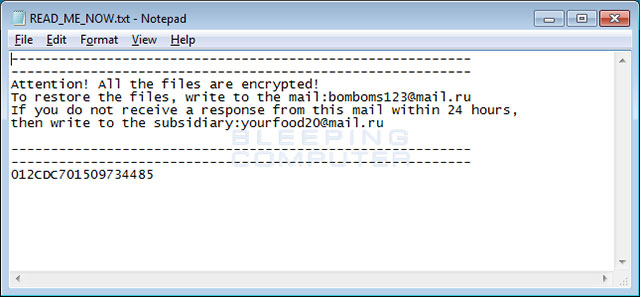
GIBON extortion notice
When completed, ransomware sends a message to C2 with a 'finish' string with a timestamp, a Windows version, and the number of encrypted files.
See also: Enable ransomware Controlled Folder Access on Windows 10
IOC information about GIBON Ransomware
Hash
SHA256: 30b5c4609eadafc1b4f97b906a4928a47231b525d6d5c9028c873c4421bf6f98
Related files
READ_ME_NOW.txt
Email related
bomboms123@mail.ru
subsidiary: yourfood20@mail.ru
Notice of extortion
Attention! Đã có tập tin được tập tin đã được xác thực!
Để phục hồi tập tin, ghi vào thư: bomboms123@mail.ru
Nếu bạn không nhận ra câu trả lời từ thư này trong 24 giờ,
rồi ghi vào tên chính của: bạnfood20@mail.ru
You should read it
- ★ Lukitus Guide to preventing extortion malicious code
- ★ Ako ransomware is raging all over the world, what do you know about this ransomware?
- ★ Ryuk Ransomware has added 'selective' encryption capabilities.
- ★ How to remove Moba ransomware from the operating system
- ★ Top 20 best encryption software for Windows