Find out what is HTTPS? Why should you use HTTPS instead of HTTP?
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol with Secure , a secure version of HTTP, allowing us to securely communicate with websites using encryption. To clearly see the difference between HTTPS and HTTP, you can follow the HTTPS and HTTP comparison article here

Instead of being left in plain text , all data will be encrypted before being sent to the website server. This helps prevent attackers (or even governments) from monitoring and viewing this data.
If you are using the HTTP standard, attackers can use tools to see what you are doing, reading or searching on the Internet. Even attackers can 'steal' your username, password, personal information and financial information.
However, when switching to HTTPS, all this information will be encrypted before being transmitted to the website or vice versa. Therefore, an attacker has no way to interrupt the process and view this data.
Of course, no one can be sure whether these encryptions will be broken in the future or not.
The risks of using the HTTP standard
The biggest risk is that when you access a website via the HTTP standard, your web browser will find the IP address that matches the requesting website with the help of the DNS server. It then connects to the IP address and pulls data to display the correct website, as well as send data needed to communicate with the website, such as logging in or making transactions, currently available Many different fast DNS help users choose to access services blocked by the network. You can find and use these fastest DNS on the internet or on TipsMake.
However, all data will be transmitted in plain text without encryption. So an attacker can use appropriate tools (or permissions like your Internet service provider or government intelligence agency) to easily see the website you are visiting. access, as well as the data you are sending and receiving.
But do you know what's the worst? There's no way to verify that you're on the right website. For example, if you visit a particular website with the domain name:
www.abcxyz.com
Via HTTP, and it will display the correct website as you normally see it. However, if you are using a public network, a hacker can create a fake website and redirect you to it.
Basically, this fake website is similar to the real website, but the main purpose of these websites is to steal your data, such as credit cards. The most common trick is to create fake online banking service sites, Paypal.com or Google Wallet , then hack the network (or create a fake wireless network for free) and redirect users to those sites. This fake website collects personal information, passwords and bank account information.
The problem is that users cannot recognize that these are fake websites because there are no warnings on browsers. Furthermore, when you enter details (such as username and password) on the fake website, it redirects you to the correct website, where you need to provide the details again. there again. At that time, you may think that the website has an error, but never think that it is a fake website.
With the HTTPS standard there is no way to create such fake websites. With the help of an SSL certificate , your browser will verify the URL, IP address and SSL certificate of each website to ensure it is a legitimate website. If it is a fake website, you will receive one of these warnings: Your connection is not private , This connection is untrusted , or Your connection is not secure, depending on the browser you are using .
Currently there are two types of SSL certificates: free and paid. For less experienced users, it is difficult to distinguish between these two types. If you are interested, you can refer to the free SSL certificate review here.
It is clear when learning what HTTPS is? Why should you use HTTPS instead of HTTP? You will find HTTPS much more secure than regular HTTP.
That is also why users are recommended to use HTTPS when making payments or placing orders.
In addition to protecting your sensitive information, HTTPS also protects your privacy when you perform normal tasks, such as searching for something on Google.com. With HTTPS, no one can know what you are searching or viewing on the Internet, not even your Internet service provider or government organizations.
In terms of online security, HTTPS is obviously quite safe as well.
How to tell if you're connecting to an HTTPS site
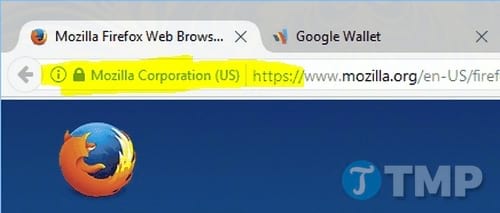
It is very simple to know that you are connecting to a website with HTTPS standards, if the URL in the browser address bar begins with https://. There is also a blue lock icon. Sometimes it also includes the name of a company or organization, depending on the type of SSL certificate the website uses. To view information about the website and its encryption, click on the green lock icon.
However, it will depend on the web browser you are using because each browser has a different way of displaying HTTPS.
For example:
This is how a website HTTPS looks in the Google Chrome browser
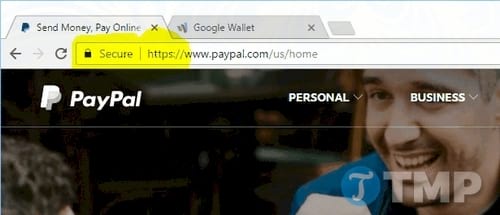
Or on Firefox browser
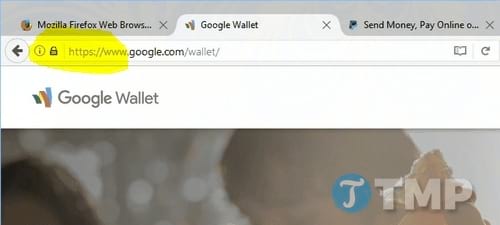
And Microsoft Edge browser

A few months ago, Google Chrome started classifying and marking HTTP and HTTPS websites with Not Secure and Secure tags in the address bar.
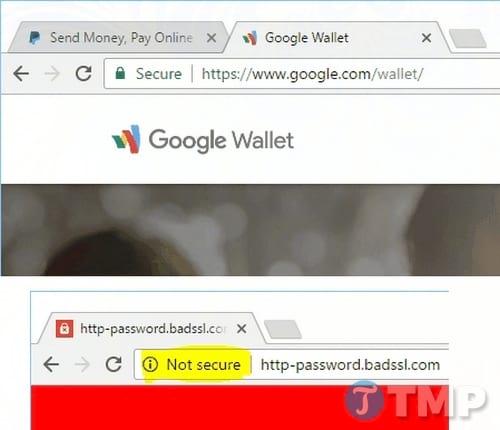
So if you log into your Paypal.com account, make a payment or place an order, it's best to use HTTPS instead of HTTP.
On the webmaster aspect, Google has recommended and rewarded websites that are using HTTPS with a change to get better positions in their search engine giant, which a lot of website owners are doing. try to get. But that doesn't mean that when you switch to HTTPS, your website will definitely have a higher position in the search engine results list. It's just one factor in addition to all the other ranking factors.
If you receive one of the warnings above, or can't find the HTTPS indicator when accessing the login site, the network you're connecting to may be attacked and compromised. So avoid entering any important information, such as passwords, bank accounts or credit cards.
In case you are worried that you forgot to use HTTPS, you can use a plugin called HTTPS Everywhere , which will force your browser to use HTTPS at all times, if the site is supported. Otherwise, it will redirect to HTTP. You can download and install this utility for your browser here: Download HTTPS Everywhere
However, at this time, the HTTPS Everywhere plugin is only available for Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome and Opera browsers.
However, don't just rely on the HTTPS lock icons on your browser without paying attention to the security issues on your computer or devices. Of course, you will have to proactively protect your computer as well as all your other devices from threats because hackers can find and use many different ways to exploit your data.
The above is all about what is HTTPS? Why should you use HTTPS instead of HTTP? that TipsMake wants to introduce to readers. Hopefully after this article you will have more knowledge about security to protect your important data, avoid threats and hacker attacks.