What is HTTP Flood?
What is an HTTP flood attack?
HTTP floods are a type of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, in which an attacker exploits seemingly legitimate HTTP GET or POST requests to attack a web server or application.
HTTP flood attacks are attacks that often use a botnet zombie army, a group of computers connected to the Internet, each computer has been taken over, usually with the help of malware. like Trojan Horse.
As a sophisticated Layer 7 attack, HTTP floods do not use oddly formatted packets, spoofing or reflection techniques (require third-party mapping), and require less bandwidth than those that are known to be malicious. Another attack, to 'depose' the targeted website or server.
Therefore, they require a deeper understanding of the targeted website or application and each attack must be specifically designed to be effective. This makes HTTP flood attacks much harder to detect and prevent.
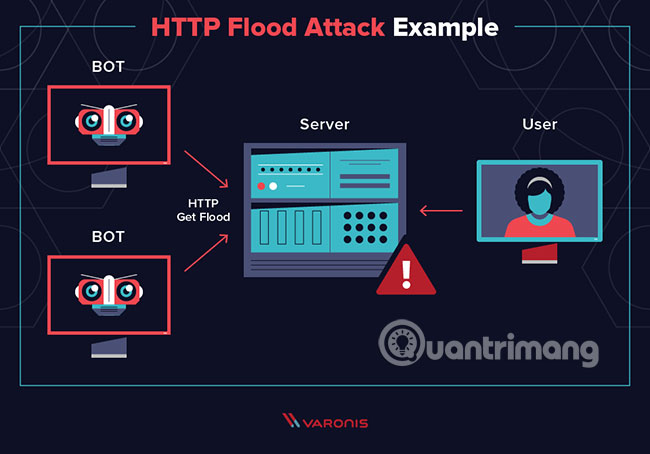
Describe the HTTP flood attack
When an HTTP client like the web browser 'communicates' with the application or server, it sends an HTTP request - usually one of two types of requests: GET or POST. The GET request is used to retrieve static, standard content such as images, while the POST request is used to access dynamically generated resources.
An attack is most effective when it forces the server or application to allocate maximum resources possible to meet each request. Therefore, hackers will generally aim to flood the server or application with lots of requests, the more each request uses the resources it can handle.
For this reason, HTTP flood attacks that use POST requests tend to be the most 'resource efficient' in the attacker's perspective; because POST requests may include complex server-side trigger triggers. On the other hand, HTTP GET-based attacks can be created more easily and effectively in botnet scenarios.
Methods to minimize HTTP flood attacks
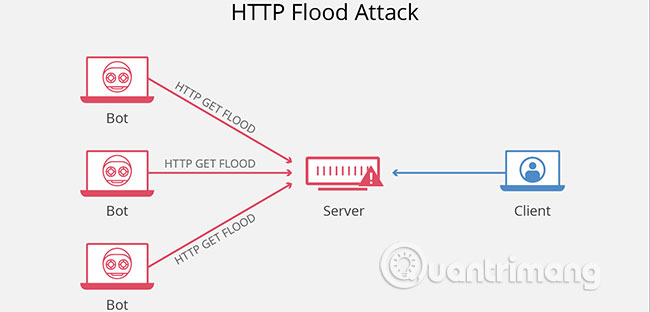
HTTP flood attacks are difficult to distinguish from valid traffic, because they use standard URL requests. This makes them one of the most advanced security challenges currently facing servers and applications. Traditional scale-based detection is ineffective in finding HTTP flood attacks, because the traffic in HTTP floods is often below the detection threshold.
The most effective mitigation mechanism is based on a combination of various methods of shaping traffic, including IP identification, abnormal activity tracking, and the use of advanced security methods (e.g., JavaScript parsing bridge).