What is HTTP
HTTP is an application-level protocol for distribution, collaboration, multimedia information systems, which is the foundation for data communication for WWW (eg Internet) since 1990. HTTP is a common protocol and stateless, which can be used for other purposes as well as the scaling of request methods, error codes and its Header.
Basically, HTTP is a TCP / IP-based communication protocol, which is used to distribute data (HTML files, image files, etc.) on WWW. The default port is TCP 80, other ports can also be used. It provides a standardized way for computers to communicate with each other. The HTTP specification determines how the client's requested data will be built and sent to the server, and how the server responds to these requests.
Basic features of HTTP
There are three basic features that make HTTP a simple yet powerful protocol:
HTTP is a connectionless protocol : HTTP client, for example: a browser initializes an HTTP request and then a request is created, the Client disconnects from the Server and waits for a response. feedback The server processes the request and resets the connection with the Client to send the response back.
HTTP is an independent medium : It means, any kind of data can be sent by HTTP as long as Server and Client know how to control the data content. It is required for the Client as well as the Server to determine the content type by using the appropriate MIME type.
HTTP is stateless : As mentioned above, HTTP is connectionless and it is a direct result that HTTP becomes a Stateless protocol. Server and Client know about each other in a current request. After that, both of them forgot all about each other. Due to the nature of the protocol, both the Client and the browser can retain information between different requests between sites.
Basic structure
The diagram below shows the very simple structure of a web application and describes the location of HTTP:
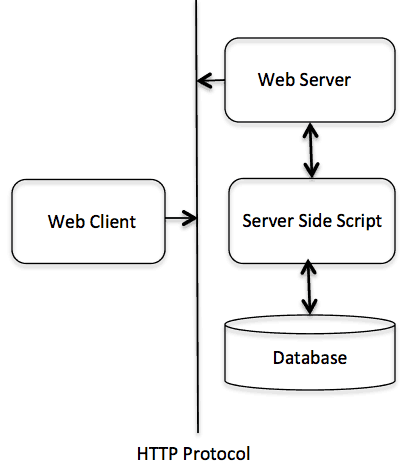
The HTTP protocol is a Request / Response protocol based on the Client / Server structure, where web browsers, devices search, etc. act as clients, and web servers act as servers.
Client
The client sends a request to the server in the form of a request method, URI, and protocol version, followed by an MIME message containing the required editors, Client information, and object content. via a TCP / IP connection.
Server
The server responds with a status line, including the protocol version of the message and a successful code or error, followed by an MIME message containing Server information, multimedia entity information and object content. may.
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: Browser compatibility in JavaScript
Next article: Parameters in HTTP