Routing and filtering network traffic - Part 2: Windows Firewall
 Routing and filtering network traffic - Part 1
Routing and filtering network traffic - Part 1
Windows Firewall
Windows Firewall is a packet filtering and stateful firewall ( Stateful firewall ) that allows or blocks network traffic according to the configuration. The data filter protects the computer by using an access control list (ACL - Access Control List), which lists which packets are allowed to pass through the firewall based on the IP address and the assigned address. awake (especially port number). The stateful firewall checks the status of active connections and uses this information to determine which packets are allowed to pass through the firewall. Basically, if a user starts communicating with a computer located outside the firewall, the firewall remembers the conversation and allows the appropriate packets to be sent back. If an external computer tries to communicate with a computer protected by a stateful firewall, these packets will be blocked automatically unless access is allowed by the ACL.
Note:
Windows Firewall is enabled by default. Any program or service that needs to be communicated on a network must be opened in a firewall, including file sharing, pinging the server, providing basic services such as DSN and DHCP.
Compared to Windows Firewall included in Windows XP SP2, the Windows Firewall used in Windows Server 2008 has a lot of improvements, including these:
- Windows Firewall supports filtering of IPv6 connections
- By using outbound packet filtering, you can protect your computer against spyware and viruses that want to communicate with your computer from outside.
- With advanced packet filters, rules can also be assigned to source and destination IP addresses and port ranges.
- Rules can be configured for services because the service name is selected from the list, without specifying the full file name and path.
- IPSec is fully integrated with Windows Firewall, allowing connections to be allowed or denied based on security certificates, Kerberos authentication, and . Encryption is also required for connection types.
- A new management interface called Windows Firewall with Advanced Security provides access to many advanced options and allows remote administration.
- You can use separate firewall profiles for different times, such as computers that are joined to the domain, connected to a private network or public network.
Basic configuration
Windows Firewall is enabled by default. When Windows Firewall is turned on, most programs are locked when communicating through the firewall. If you want to unlock a program, you can add it to the Exceptions exceptions list (on the Exceptions tab). For example, you may not be able to send photos in instant messages until you add this instant message program to the exception list. To add a program to this list, simply click the Add program button and select it from the existing list or browse to it by clicking the Browse button.
To enable or disable the Windows firewall, you can follow these steps:
- Open Windows Firewall by clicking the Start button, clicking Control Panel , Security , Windows Firewall .
- Click Turn Windows Firewall On or Off ( see Figure 3 ). If prompted for a password and administrator confirmation, type in the password and provide confirmation.

Figure 3: Windows Firewall options in Control Panel.
- Click On (recommended) or Off (not recommended), then click OK .
If you want the firewall to block everything, including the selected programs on the Exceptions tab, select the Block All Incoming Connections check box. Block All Incoming Connections will block all unsolicited attempts to connect to your computer. Use this setting when you want to get maximum protection for your computer, such as when you connect to a public network in a hotel or airport, or when a computer worm is infecting. infected on the Internet. With this setting, you are not notified when Windows Firewall blocks programs, and programs in the exception list are also ignored.
The Windows Firewall Settings interface has three tabs:
- General: Allows you to enable or disable the firewall, as well as block all incoming connections, even if you have configured an exception.
- Exceptions: Allows you to configure the programs and ports that are allowed to communicate in and out from your Windows Vista computer. Only create a required exception and remove exceptions that you do not need. Never create an exception for a program when you're in the program's unsafe function.
- Advanced: Allows you to select the network interface you want Windows Firewall to protect.
To configure programs as exceptions,
- Open Windows Firewall by going to Start> Control Panel> Security> Windows Firewall .
- Click Allow a program through Windows Firewall . If you have an administrator password prompt and confirmation, type a password and provide confirmation.
- In the Windows Firewall dialog box, select the Exceptions tab, and then click Add Program .
- In the Add A Program dialog box, select the program in the Programs list or click Browse to use the Browse dialog box to find the program.
- By default, any computer, including computers on the Internet, can access this program remotely. To restrict some access, click Change Scope .
- Click OK three times to close all open dialogs.
To open a port in Windows Firewall,
- Open Windows Firewall by clicking Start, Control Panel, Security, Windows Firewall .
- Click Allow a program through Windows Firewall . If you have an administrator password prompt and confirmation, type a password and provide confirmation.
- Click Add port .
- In the Name box, type a name to help you remember what port is used for what purpose.
- In the Port number dialog box, type the port number.
- Click TCP or UDP , depending on the protocol
- By default, any computer, including computers on the Internet, can access this program remotely. To change the scope for the port, click Change scope , then click the option you want to use (The word 'Scope' refers to a set of computers that can use this port).
- Click OK twice to close all open dialogs.
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
Similar to the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security introduced in Windows Vista, Windows Firewall with Advanced Security in Windows Server 2008 is a snap-in Microsoft Management Console (MMC) that allows you to set up and view incoming and outgoing rules. detailed way, integrated with Internet protocol security (IPSec) .
The Windows Firewall with Advanced Security management interface allows you to configure:
- Inbound rules: Windows Firewall blocks incoming traffic unless allowed by a certain rule.
- Outbound rules: Windows Firewall will allow all outgoing traffic unless blocked by a rule.
- Connection security rules: Windows Firewall uses a connection security rule to enforce authentication between two peer computers before they can establish a connection and ensure the information is transferred between two computers. Connection security rules that use IPsec to enforce security requirements.
- Monitoring: Windows Firewall uses a test interface to display information about current firewall rules, connection security rules and related security issues.
Windows Firewall is enabled by default. When Windows Firewall is turned on, most programs are locked to prevent communication through the firewall. If you want to unlock a program, you can add it to the Exceptions list (on the Exceptions tab). For example, you may not be able to send photos in instant messages until you add this instant message program to the exceptions list. To add a program to this list, see the section Allowing a program to pass through a firewall.
- Open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security located in Administrative Tools.
- Click Windows Firewall Properties .
- Under the firewall state, select On (recommended) or Off (not recommended) and click the OK button. See Figure 4.
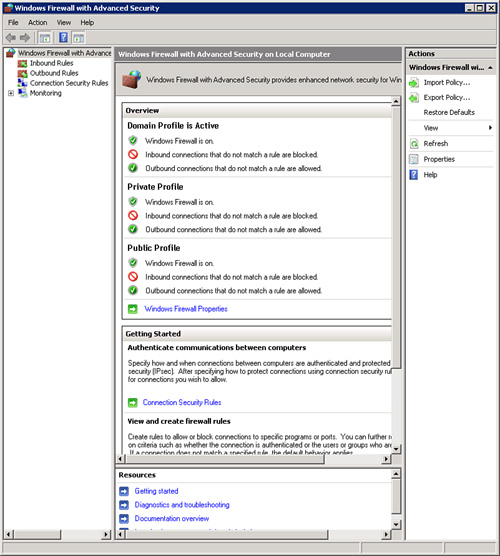
Figure 4: Properties of Windows Firewall
Create incoming and outgoing rules
You can create inbound rules to control access to your computer from the network. These rules can prevent:
- Unwanted software is copied to your computer
- Unauthorized or involuntary access to data on your computer
- Unwanted configuration of your computer from remote locations.
To configure advanced properties for a rule with Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, follow the steps below:
- Right-click the name of the inbound rule and click Properties .
- From the Properties dialog box for the incoming rule, configure the settings on the following tabs:
- General: Rule name, the program to which the rule applies, the rule's action (allow connections, only allow secure or locked connections).
- Programs and Services: The program or service that the rule applies.
- Users and Computers: If the rule's action is to allow only secure connections, then the computer account will be authenticated to create secure connections.
- Protocols and Ports: Rule IP protocol, source and destination TCP or UDP ports and ICMP or ICMPv6 settings.
- Scope: The destination addresses and sources of the rule.
- Advanced: The profile or type of the rule interface applies.
You can also use Windows Firewall with Advanced Security to create outbound rules to control access to network resources from your computer. Outbound rules can prevent:
- Utilities on your computer access network resources without your knowledge.
- Utilities on your computer download software without your knowledge.
- Users on your computer download software without your knowledge.
Specify Firewall Profile
A firewall profile is a way of group settings, such as firewall rules and connection security rules used for computers, depending on where the computer is connected. On computers running this version of Windows, there are three profiles of Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. Only one profile is used at a time.
The profiles provided here are:
- Domain: Used when a computer is connected to a network where the computer's domain account resides.
- Private: Used when a computer is connected to a network where the computer's domain account does not reside, such as a home network. Private settings need to be more restrictive than domain profile settings.
- Public: Used when a computer connects to a domain via a public network, such as airport and cafe networks. The public profile settings need to be the most restrictive because the computer is connected to the public network and will not have the same security protection as in the corporate environment.
Use the netsh command to configure Windows Firewall
To see the current firewall configuration, including the opened ports, you can use the following command:
netsh firewall show state
Note : If the firewall state shows that the Operational mode is set to Enable, this means that Windows Firewall is enabled but no ports are opened.
To open ports at the firewall for DNS (port 53), you can use the following command:
netsh firewall add portopening ALL 53 DNS-server
To view the firewall configuration, use the command:
netsh firewall show config
To enter the netsh advfirewall context, at the command prompt, type:
netsh
When you enter the netsh context, prompt will display> netsh. At the> netsh command prompt, enter the advfirewall context type:
advfirewall
When in the advfirewall context, you can type commands in that context.
These commands include:
- Export : Export the current firewall policy to a file.
- Help : Displays a list of available commands.
- Import : Import a policy from a file.
- Reset : Restore Windows Firewall with Advanced Security to the default policy.
- Set : Support command below:
- set file: Copy the console output to a file.
- set machine: Set the current computer to operate.
- show: Displays properties for individual profiles. For example, show allprofiles, show domainprofile, show privateprofile and show publicprofile.
In addition to the commands available for the advfirewall context, advfirewall also supports several sub-contexts. To enter a sub-context, type the name of the sub-context at the netsh advfirewall> prompt. The available sub-contexts are:
- consec : Allows you to view and configure computer security connection rules.
- Firewall : Allows you to view and configure firewall rules.
- Monitor : Allows you to view and set up test configuration.
Manage Windows Firewall with Advanced Security through Group Policy
To focus on configuring a large number of computers on an organization network using Active Directory directory services, you can deploy settings for Windows Firewall with Advanced Security through GP (Group Policy). Group Policy provides access to the entire set of Windows Firewall with Advanced Security features, including profile settings, rules, and computer connection security rules.