Routing and filtering network traffic - Part 1
In this article, I will show you how to configure routers and firewalls as well as NAT, which are required in Microsoft's 70-642 test for Windows Server 2008.
The terms you need to understand:
- Router
- Metric
- Hop
- Static routes
- Dynamic routes
- Router Information Protocol (RIP)
- Split-horizon
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- Firewall
- Stateful firewall
- Windows Firewall
- Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
- Usage profile
- Network address translation (NAT)
The techniques and concepts you need to grasp
- Configure static routes using the Router and Remote Access (RRAS) interface and with the Route.exe command.
- Configure Router Information Protocol (RIP).
- Configure packet filtering, Windows Firewall and Windows Firewall with Advanced Security advanced security
- Configure dial-up routes
- Configure NAT (Network Address Translation)
A router is a device used to manage data flow between network segments, or subnets. When multiple LANs or network segments are connected, routes are created to transmit data from one LAN or segment to another or another segment. A router will direct incoming and outgoing packets based on information that it knows about the status of network interfaces and a list of possible destinations.
By projecting network traffic and routing needs, you can decide whether you want to use a dedicated hardware router, such as Cisco router or a software router such as a router. available in Windows Server 2008. If routing needs are really necessary, then you need to use dedicated hardware routers. As for small networks, software-based routing solutions are also quite feasible. To help with routing, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 supports routing and remote access services - Routing and Remote Access service.
Routing and Router
When you send a packet from one computer to another, the process first determines whether the packet is sent internally to another computer on the same LAN or to the router to route to the destination LAN. . If the packet is sent to a computer on another LAN, it will be sent to the router (or gateway). The router then determines the most feasible route to forward data according to that route. The packet will be sent to the next router and the same process is repeated until it reaches the destination LAN. At the destination LAN, the destination router forwards this packet to the destination computer.
To determine which route is best, routers use complex routing algorithms, which use a range of factors including the speed of the transmission environment, the number of network segments and the possible network segment. conveying traffic at a minimum level. Routers share the status and routing information for each other so they can manage traffic and avoid slow connections. In addition, routers also provide other functions, such as the ability to filter messages and forward them to other locations based on certain criteria. Most routers are multi-protocol routers because they can route data packets using many different protocols.
Metric is a measurement standard, such as hop count (number of routers), used by routing algorithms to determine the optimal path to a destination. A hop is a trip that a packet must go from one router to another or from one router to another and to another router in the network. On large networks, the number of hops a packet needs to reach its destination is called a hop count . When a computer communicates with another computer, the communication process has to access through 4 routers, then it has a hop count of 4. If no coefficients are given, a metric of 4 will be assigned. . If the router has a choice between a route with 4 metrics and a route with 6 metrics, it will select the route with 4 metrics. Obviously, if you want the router to choose a route with 6 metrics, you can override the metric for the route with 4 hop in the routing table with a higher value.
To track the different routes in the network, routers create and maintain routing tables. Routers communicate with each other to maintain their routing tables through a route update. Routing updates can include all or part of the routing table. By analyzing routing updates from all other routers, routers can create a detailed picture of network topology.
Dynamic and static routes
Static routing algorithms are fairly hard algorithms, which are mappings set up by pre-network administrators based on static routing tables to perform routing. These mappings do not change unless the network administrator changes them. Algorithms using static routes are often quite simple in design and work well in environments where network traffic and network design are predictable.
Because static routing systems cannot respond to network changes, they are often not suitable for changing networks frequently or large networks. Most of the predominant routing algorithms are dynamic routing algorithms, which are capable of adjusting to changing network conditions by analyzing incoming routing news. If this information indicates that a network change has occurred, the routing software will recalculate the routes and send new news back to the route. The news will be transmitted throughout the network, based on these news, other routers will re-launch their algorithms and change their routing tables according to the latest data.
Note : Dynamic routing algorithms can be implemented with static routes where appropriate.
Distance-Vector and Link-State algorithms
Routers use routing protocols based on distance-vector vectors to periodically advertise or advertise routes in their routing tables, but they will only send it to their neighboring routers. . Route information exchanged between distance-vector-based routers is not synchronized and unanswered. Distance-vector routing protocols are simple and easy to understand and easy to configure. The downside to these routers is that many routes to a particular network can bring up multiple entries in the routing table, which leads to a large routing table. In addition, if you have a large routing table, your network traffic will increase as it periodically advertises the routing table to other routers, even after the network has converged. Finally, the distance-vector protocol convergence of large networks can take a long time, up to several minutes.
Link-state algorithms are known as the shortest path finding algorithms. Instead of using broadcast mode, link-state routers send updated information directly (or by using multicast traffic) to all routers within the network. However, each router sends only a portion of the routing table that describes the status of its own links. Basically, link-state algorithms only send small news. Because they converge faster, link-state algorithms are less routing loops than distance-vector algorithms. In addition, link-state algorithms do not exchange routing information when interactive networks converge. They have small routing tables because only one optimal route is saved for each network ID.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
The popular routing protocol, RIP (Routing Information Protocol), is a distance-vector protocol designed for exchanging routing information within a small to medium sized network. The biggest advantage of RIP is that it is very simple in configuration and deployment.
RIP uses a routing metric by hop count (number of routers) to measure the distance between source and destination networks. Each hop in a path from source to destination is assigned a hop-count value, typically equal to 1. When a router receives a route update that contains a new destination network entry or has been changed, that router will Add 1 to the metric value indicated in the upgrade and enter the network in the routing table. The sender's IP address will be used as the next hop.
Since RIP only uses hop count to determine the best path to an interactive network, if RIP finds multiple links to the same remote network with the same hop-count , it will automatically perform a weighting. by ' round-robin ' download. RIP can perform load balancing for up to 6 links.
However, there is a problem with using hops when two links to a remote network have different bandwidths. For example, if you have a 56KB switching link and a T1 1,544Mbps link, an ineffective phenomenon will occur when sending equal data across both paths. To overcome this drawback, you must design a network with equal bandwidth links or use a routing protocol that can include bandwidth factors in the manifest.
RIP prevents endless loops in routing by enforcing a limit on the number of allowed hops in a path from source to destination. The maximum number of hops in a path is 15. If a router receives a routing upgrade containing a new entry or has been changed, and if the metric increment by 1 makes the metric equal to 16, the network target considered impossible. Obviously, this makes RIP impossible to scale in large or very large networks. Note: The endless counting problem is the reason why the maximum hop count of RIP for an IP network is set to 15. The maximum hop count values will make time converge long. more then the endless counting phenomenon appears.
Initially, the routing table for each router consists only of networks that are physically connected to it. A RIP router periodically (30s) sends messages containing its routing table entries so that other routers can update their routing tables. RIP version 1 uses IP address broadcast packets for its announcements, version 2 uses multicast or broadcast packets. All RIP messages are sent on UDP port 520.
RIP routers can also communicate routing information through triggered updates, which are triggered when the network topology changes. Unlike scheduled announcements, activated updates will be sent immediately instead of waiting for the next periodic notification. For example, when a router detects a link or router error, it will upgrade its own routing table and send updated routes. Routers that receive this enabled upgrade will change its routing table and disseminate this change to other routers.
You can configure each RIP router with a list of routers (by IP address) to accept RIP notifications. By configuring a list of RIP peer routers, RIP statements from unauthorized RIP routers will be discarded. In addition, to prevent RIP traffic from being received by any node except neighboring RIP routers, you can set up several routers to use one-way RIP messages to neighboring RIP routers.
Because RIP is a distance-vector protocol, so when interactive networks expand in size, periodic notifications by RIP routers can cause traffic overload. One drawback of RIP is its high convergence time. When the network topology changes, it takes several minutes before the RIP routers reconfigure themselves to the new network topology. When the network reconfigures itself, routing loops can cause data loss. To overcome this problem, RIP adds split-horizon .
To overcome some of the shortcomings of RIP, RIP Version 2 (RIP II) was born. RIP v2 provides the following features:
- You can use a password for authentication by specifying a key used to verify routing information for the router. Password authentication is defined in RFC 1723, but there are newer authentication mechanisms, such as Message Digest 5 (MD5).
- RIP v2 includes a subnet mask in routing information and supports variable-length subnets. Variable-length subnet masks can be linked to destinations, allowing an increase in the number of hosts or subnets possible in the network.
- The routing table can contain information about the router's IP address needed to reach the destination. This helps prevent data packets from being forwarded through extended routers on the system.
- Multicast packets only broadcast to RIP v2 routers and are used to reduce the load on hosts that do not listen to RIP v2 packages. The multicast IP address for RIP v2 packages is 224.0.0.9. Note: Silent RIP buttons must also listen to multicast traffic sent to address 224.0.0.9. If you are using Silent RIP, verify that your Silent RIP nodes can listen for multicast RIP v2 notifications before deploying multicast RIP v2.
Note :
RIPv2 supports multicast for upgrading routing tables. RIPv1 does not support this feature. RIPv1 router cannot communicate with RIPv2 routers that use multicast to update.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
For small and medium networks, distributing data throughout the network and maintaining routing tables at each router does not become a serious problem. However, for large networks, there are hundreds of routers, the routing table can be quite large (several megabytes), the computation of routes requires a lot of time because some routers may have problems or not.
Some protocols, such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) , allow regions (groups of adjacent networks) to be grouped together into an autonomous system (AS). Areas that make up these autonomous regions often correspond to an administrative domain, such as a room, building, or geographic location. An AS can be a network or can be a group of networks, owned and managed by a network administrator or a group of network administrators in general.
OSPF is a link-state routing protocol used in medium and large sized networks to calculate routing table entries by building a shortest path tree. OSPF is designed for large interactive networks (especially those networks with more than 15 router hop). The downside of OSPF is that it is quite complicated to set up and requires specific planning.
Note:
The OSPF protocol component in Routing and Remote Access has been removed from Windows Server 2008.
Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS)
With RRAS , a computer running Windows Server 2008 operating system can act as a network router, routing IP packets between networks. This router service allows LANs and WANs to be easily interconnected. Routing techniques are built into the operating system, providing small and large businesses with a safe and cost-effective way of cross-connecting their networks.
You can install the Routing and Remote Access service by using the Add Roles Wizard. To install Routing and Remote Access service, follow the steps below:
- In the Server Manager main window, under Roles Summary, click Add roles . Or if you use the Initial Configuration Tasks window, under Customize This Server, click Add roles .
- In the Add Roles Wizard, click Next .
- In the list of server roles, select Network Policy and Access Services. Click Next twice.
- In the role service list, select Routing and Remote Access Services to select all service roles. You can also choose separate server roles. Click Next .
- Proceed through the steps in the Add Roles Wizard to complete the installation process.
After completing the installation process, the Routing and Remote Access service is installed in a disabled state. To enable Routing and Remote Access service, follow these steps:
- Open Routing and Remote Access .
- By default, the internal computer is listed as a server.
- To add another server, in the console tree, right-click Server Status , and then click Add Server .
- In the Add Server dialog box, click the appropriate option, then click OK .
- In the console tree, right-click the server you want to activate, then click Configure and Enable Routing and Remote Access . Click Next .
- Click the Custom Configuration button and click Next .
- To enable LAN routing , select LAN routing and click Next .
- Click the Finish button
To enable LAN and WAN routing after the Routing and Remote Access service has been activated:
- Open Routing and Remote Access.
- Right-click the server name you want to enable routing, and then click Properties .
- On the General tab, select the appropriate IPv4 Router and IPv6 Router check boxes, and select Local Area Network (LAN) Routing Only or LAN and Demand-Dial Routing .
- Click OK .
Create static routes
In some cases, you need to add a static route to your Windows Server 2008 router. This must have both advantages and disadvantages. Creating a static route is completely simple; however, the routes you configure are not shared between routers. Static routes specify the network address and subnet mask to inform the router about how to reach a destination. The router uses that information to determine which gateway will forward the data so that the packet can reach its destination host.
Static routes can be configured in one of two ways:
- Use the route command.
- Use RRAS management interface.
Use the Route command
The route command is used to view and change the network routing table for an IP network. The route print command will display the list of current routes that the host knows (see Figure 1).
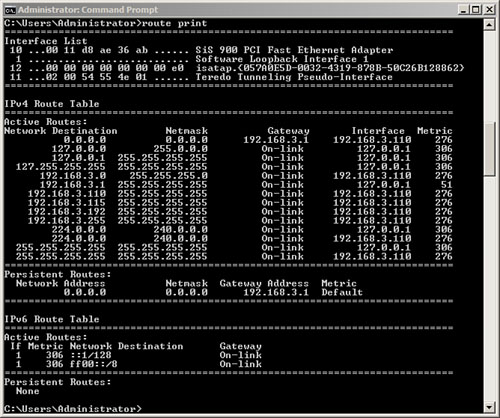
Figure 1: Results of the Route Print command
Routes added to the routing table will not be valid unless the -p switch is specified. Unstable lines only last until the computer is restarted or until the interface loses response. The interface can be positively lost when the plug-and-play interface is removed (such as laptops and hot-plugged computers), when the cord is removed from the media card (if the adapter supports identifying media errors). ), or when the interface is disconnected from the adapter in the Network and Dial-up Connections folder.
How to use the route command:
ROUTE [-f] [-p] [command [destination]] [MASK netmask] [gateway]
-> [METRIC metric]
- -f— Delete the routing table for all gateway entries. If this command is used in conjunction with one of the other commands, the routing tables will be deleted before this command is run.
- -p — When used with the add command, create a persistent route during system startup processes. By default, routes are not maintained when the system restarts. When used with the print command, displays a list of registered persistent routes. Ignoring all other commands, this command always affects persistent routes.
- Destination — Specifies the network or host that the packets are being sent.
- MASK netmask - Specifies the subnet mask to associate with this route entry. If the netmask value is not specified, it will receive the default value of 255.255.255.255.
- gateway — Specify the gateway or router.
- METRIC metric — Assigns an integer metric (from 1 to 9,999) used in calculating the most expensive, most reliable and fastest routes.
The commands that can be used in the previous syntax are PRINT, ADD, DELETE and CHANGE:
- PRINT — Display a route
- ADD — Add a route
- DELETE — Delete a route
- CHANGE — Change an existing route
Note:
Durable routes are stored in the Registry location below:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParametersPersistentRoutes
For example, to create a static route, you can type
route ADD 132.133.200.0 MASK 255.255.255.0 63.197.142.1 METRIC 2
After this command is executed, any packet sent to the network address 132.133.200.0 or the host whose IP address is in the range 132.133.200.1 to 132.133.200.254 will be forwarded to the router with the local host address 63.197.142.1. If multiple entries specify these destination addresses, this route will have a 2 hop metric.
Use Routing and Remote Access
To add a static route to a Windows Server 2008 computer, you need to use the Routing and Remote Access program in Administrative Tools or use the appropriate MMC snap-in. Next, right-click Static Routes under IPv4 or IPv6 and select New Static Route for IP Networks (see Figure 2).
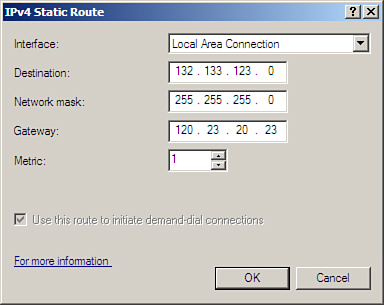
Figure 2: Use the Routing and Remote Access interface to create a static route
With a static IP route, in Interface, Destination, Network Mask, Gateway, and Metric, enter the interface, destination, mask, gateway and metric. If this is a demand-dial interface, Gateway will not be provided. You can then check the box Use This Route to Initiate Demand-Dial Connections to initiate the demand-dial connection to communicate with the route.
With static IP addresses, the destination will provide a space for you to enter the destination of the route. The destination can be a host address, subnet address, network address or destination of a certain default route (0.0.0.0). Subnet mask provides space for you to enter network mask of static route. The network mask number is used in conjunction with the destination to distinguish when the route is used.
Mask 255.255.255.255 means that only one corresponds exactly to the number of destinations that can be used for this route. Mask with 0.0.0.0 means that any destination can be used for the route. The gateway provides a space for you to enter the forwarding IP address for the route. For LAN interfaces, the gateway address must be configured and must be an accessible IP address for the network segment of the selected interface. For demand-dial interfaces, the gateway address is not configured or used. The metric provides a space to type the hop number of the route to reach the destination. Metric is often used to indicate the number of routers (hop) to the destination. When deciding between multiple routes to the same destination, the route with the lowest metric will be selected as the best route.
Demand-Dial routing
Two types of Demand-Dial connections can be created for routing:
- On-demand connection
- Persistent connection ( Persistent )
For demand-dial connections, a connection to the remote router is set up only when needed. The connection is established to route information and is terminated when the link is no longer used. The advantage of this connection is cost savings because of not using dedicated links.
With durable connections, the link does not need to be terminated. Even when it is not in use, it remains open. Connections between network routers can be one-way or two-way links, which means that a connection can be initiated by just one router or both routers. With one-way connections, a router is designated as a answering router and the other router is designated as the calling router, the calling router is responsible for initiating connections.
Dinh One-Way Demand-Dial route
Demand-dial connections can be created inside the Routing and Remote Access snap-in. How you configure the connection depends on whether you are configuring a one-way connection or two-way connection. To create a demand-dial interface on the calling router, you can follow these steps:
- Right-click Network Interfaces within the RRAS console and click New Demand-Dial Interface . This will launch the Demand-Dial Interface Wizard. Click Next .
- Type a name for the interface and click Next .
- Select the connection type, click Next . Select the device to be used to create the connection. Click Next .
- Type the phone number of the remote server to which you will dial. Click Next .
- From the Protocols and Security window, select the necessary options:
- Route IP Packets on This Interface
- Add a User Account So a Remote User Can Dial In
- Send a Plain-Text Password If That's The Only Way to Connect
- Dùng Scripting để kết nối kết nối với Router Remote
- Configure a static route to the remote network, click Next .
- From the Dial Out Credentials window, specify the username and password that dial-out router will use to connect to the remote router. Click Next .
- Click Finish .
Lưu ý : Trước khi tạo một giao diện demand-dial mới, bạn cần bảo đảm rằng router đã được kích hoạt cho LAN và việc định tuyến demand-dial thay cho chỉ việc định tuyến LAN. Bạn có thể kích hoạt tùy chọn này bằng cách kích phải vào máy chủ RRAS và chọn Properties. Từ tab General, chọn LAN and Demand-Dial Routing.
Router trả lời cũng cần được cấu hình cho kết nối one-way demand-dial. Bạn cũng cần phải tạo một tài khoản người dùng trên router trả lời với các điều khoản dial-in và các điều khoản chính sách thích hợp. Tài khoản người dùng sẽ được sử dụng để thẩm định các kết nối từ các router gọi. Một tuyến tính sau đó sẽ được cấu hình trên tài khoản người dùng. Thêm vào đó cũng cần bảo đảm rằng khi tạo tài khoản người dùng, tùy chọn Password Never Expires phải được chọn và tùy chọn User Must Change Password at Next Logon thì không.
Lưu ý :
Khi cấu hình router gọi, bạn cần bảo đảm rằng các tiêu chuẩn dial-out phải tương ứng với tên tài khoản người dùng được cấu hình trên router trả lời.
Định tuyến Two-Way Demand-Dial
Việc tạo kết nối two-way demand-dial cũng tương tự như việc cấu hình kết nối one-way, tuy nhiên có một số điểm khác. Giao diện demand-dial được tạo trên mỗi máy chủ RRAS bởi quá trình đã phác thảo trước để tạo kết nối one-way demand-dial. Bạn phải gán tên cho giao diện và chỉ định số điện thoại để quay số, thiết bị được sử dụng, giao thức và các thiết lập bảo mật, các tiêu chuẩn dial-out. Bên cạnh đó bạn cũng phải cấu hình tài khoản người dùng, với các điều khoản truy cập từ xa tương ứng, trên mỗi máy chủ RRAS. Cần lưu ý rằng tên tài khoản người dùng phải giống hệt tên được gán cho giao diện demand-dial của router gọi. Cuối cùng, bạn phải cấu hình một tuyến tĩnh bằng giao diện demand-dial.
Note:
Cần nhớ thời điểm khi bạn cấu hình two-way demand dial thì các tên tài khoản người dùng trên router trả lời phải giống với tên giao diện demand-dial trên các router gọi.
Cấu hình việc định tuyến Demand-Dial
Khi một kết nối demand-dial được tạo, bạn có thể cấu hình nó sâu hơn bằng cách sử dụng cửa sổ Properties cho kết nối. Từ tab Options, cấu hình kiểu kết nối: demand-dial hoặc bền. Cũng có thể thiết lập chính sách quay số bằng cách chỉ định số lần mà router gọi nên quay lại nếu không có trả lời và bằng cách chỉ định thời gian giữa những lần quay số lại.
Tab Security cho phép bạn cấu hình các tùy chọn bảo mật cho kết nối dial-out. Cấu hình này gồm có: các mật khẩu không được an toàn có được phép hay không? Kết nối có yêu cầu mã hóa dữ liệu và có kịch bản sẽ được chạy sau quay số không.
Bạn có thể tạo một vài cấu hình khác đối với giao diện demand-dial. Việc lọc Demand-dial cho phép bạn kiểm soát kiểu lưu lượng IP có thể khởi tạo kết nối. Bạn có thể cho phép hoặc từ chối kết nối dựa trên kiểu lưu lượng IP. Cho ví dụ, bạn có thể chỉ muốn lưu lượng web và FTP khởi tạo kết nối Demand-dial chẳng hạn. Giờ Dial-out chỉ định số lần trong ngày một kết nối có thể được khởi tạo. Điều này cho phép một quản trị viên có thể kiểm soát được thời điểm kết nối demand-dial được sử dụng.
Quản lý RIP
Sau khi các giao diện demand-dial hay LAN được tạo, việc cấu hình các giao diện giao thức định tuyến thích hợp là bước cuối cùng trong quá trình cấu hình máy chủ RRAS với tư cách là một router mạng. Bạn phải thêm vào giao thức định tuyến bằng cách kích phải vào nút General và chọn New Routing Protocol. Cửa sổ xuất hiện sẽ liệt kê các giao thức bạn có thể chọn. Chọn RIPv2 và kích OK.
Sau khi giao thức định tuyến được thêm vào, bạn phải thêm vào các giao diện. Để thực hiện điều đó, kích phải vào giao thức định tuyến tương ứng và chọn New Interface. Sau khi bạn chọn một giao diện và kích OK, cửa sổ Properties cho giao diện sẽ xuất hiện, cho phép bạn cấu hình nó.
Mỗi giao diện RIP đều có một cửa sổ thuộc tính riêng, từ cửa sổ này bạn có thể cấu hình một số tùy chọn. Bên trong giao diện điều khiển RRAS, mở phần IP Routing, RIP; sau đó kích phải vào một trong các giao diện có sẵn và kích Properties.
Tab General cho phép bạn cấu hình chế độ hoạt động. Bạn có thể chọn Autostatic Update Mode hoặc Periodic Update Mode. Với nâng cấp autostatic, các thông báo RIP sẽ được gửi đi khi các router khác yêu cầu nâng cấp. Bất kỳ router nào đã biết trong khi nâng cấp autostatic sẽ được đánh dấu là router tĩnh và được duy trì lại trong bảng định tuyến cho tới khi quản trị viên xóa chúng. Trong chế độ nâng cấp định kỳ (periodic), các thông báo sẽ được gửi đi một cách định kỳ. (Khoảng thời gian tuyên bố định kỳ sẽ xác định tần suất như thế nào). Các tuyến này sẽ được xóa tự động khi router ngừng hoặc khởi động lại. Giao thức gói dữ liệu gửi đến và gửi đi cho phép bạn cấu hình kiểu các gói, chẳng hạn như RIPv1 hoặc RIPv2, router gửi và chấp nhận.
Các tùy chọn Activate Authentication và Password cho phép ban duy trì một mức bảo mật bổ sung. Nếu sự thẩm định được kích hoạt, tất cả các gói dữ liệu gửi đến và gửi đi phải gồm mật khẩu được chỉ định trong trường mật khẩu. Khi sử dụng cơ chế thẩm định, hãy bảo đảm rằng tất cả các router lân cận phải được cấu hình bằng một mật khẩu giống nhau.
Từ tab Security, một quản trị viên có thể cấu hình bộ lọc tuyến RIP. Router có thể được cấu hình để gửi và chấp nhận tất cả các tuyến, gửi và chấp nhận chỉ các tuyến từ một dải nào đó, hoặc chấp nhận và gửi tất cả các tuyến ngoại trừ các tuyến được chỉ định.
Tab Neighbors được sử dụng để cấu hình cách router tương tác với các router RIP khác như thế nào. Tab Advanced có một vài tùy chọn cấu hình:
- Periodic Announcement Interval: Điều khiển khoảng thời gian tạo ra các thông báo nâng cấp.
- Time Before Route Expires: Xác định một router được duy trì bao lâu trong bảng định tuyến trước khi hết hạn.
- Time Before Route Is Removed: Xác định một router đã hết hạn được duy trì lại bao lâu trong bảng định tuyến trước khi bị xóa đi.
- Enable Split Horizon Processing: Bảo đảm rằng các vòng lặp định tuyến không xuất hiện trước khi router biết từ một router không quảng bá lại đến mạng đó.
- Enable Triggered Updates: Điều khiển xem những thay đổi trong bảng định tuyến có được gửi ra ngay lập tức hay không.
- Send Clean-Up Updates when Stopped: Điều khiển xem router có gửi một thông báo khi nó bị stop để thông báo cho các router khác rằng các tuyến mà nó phụ trách không tồn tại.
- Process Host Routes in Received Announcements: Điều khiển xem các tuyến chính đã nhận trong các thông báo RIP được chấp nhận hay từ chối .
- Include Host Routes in Send Announcements: Điều khiển xem các tuyến chính có được gộp vào trong thông báo RIP hay không.
- Process Default Routes in Received Announcements: Điều khiển xem các tuyến mặc định đã nhận trong thông báo RIP được chấp nhận hay từ chối.
- Process Default Routes in Send Announcements: Điều khiển xem các tuyến mặc định có được nhóm vòa các thông báo RIP hay không.
- Disable Subnet Summarization: Tùy chọn này có sẵn chỉ cho RIPv2. Nó điều khiển xem các mạng con có được thông báo đến các router trên các mạng con khác hay không.
Note:
Khi một vòng lặp định tuyến xuất hiện, các gói dữ liệu sẽ được đẩy tới và lui giữa các router. Khi quá trình split-horizon được kích hoạt, các tuyến không được thông báo quay trở lại đến router mà chúng nhận tin từ đó. Cho ví dụ, nếu router B nhận các tuyến được thông báo từ router A thì router B sẽ không thông báo các tuyến này cho router A nữa. Khi quá trình Split Horizon with Poison Reverse được kích hoạt, các tuyến được thông báo trở lại router mà chúng nhận tin từ đó với một số hop count vô tận.
Bộ lọc dữ liệu
Việc lọc gói cho phép các quản trị viên có thể chỉ định kiểu lưu lượng gửi đến và gửi đi được phép đi qua router Windows Server 2008. Khi cấu hình các bộ lọc dữ liệu, bạn có thể cho phép tất cả lưu lượng ngoại trừ lưu lượng bị chặn bởi bộ lọc. Hoặc bạn có thể từ chối tất cả lưu lượng ngoại trừ lưu lượng được cho phép bởi bọ lọc.
Để bổ sung thêm bộ lọc dữ liệu, bạn thực hiện theo các bước dưới đây:
- Open Routing and Remote Access .
- Trong cây truy cập, kích General bên dưới Routing and Remote Access/Server Name/[IPv4 hoặc IPv6].
- Trong panel chi tiết, kích phải vào giao diện mà trên đó bạn muốn thêm vào một bộ lọc, sau đó kích Properties .
- Trên tab General , kích Inbound Filters hoặc Outbound Filters .
- Trong hộp thoại Inbound Filters hoặc Outbound Filters, kích New .
- Trong hộp thoại Add IP Filter, đánh các thiết lập cho bộ lọc, sau đó kích OK .
- Trong Filter action, chọn Filter action thích hợp và kích OK .