Choosing a CPU for a computer
CPU (Center Processing Unit) is the central processing unit responsible for processing control instructions from computer programs and outputs execution results to the corresponding parts. The power and speed of a computer is often judged by the speed of the CPU. Currently there are many types of CPUs with different technologies and processing speeds to meet all user needs.
CPU parameters you need to know
Producer
Currently, there are two major CPU manufacturers that are Intel and AMD, the choice of which manufacturer is mainly due to the user's feelings.
 Intel and AMD CPUs
Intel and AMD CPUs
- Intel CPUs are chosen by many people due to the popularity of the brand, its stability as well as its compatibility.
- AMD CPUs (Advanced Micro Devices) are rated by many as having a "surge" speed but a lot of heat, but the temperature factor has a great influence on the stability of the whole system. If the temperature problem is well solved, then AMD is an interesting choice because it is cheap.
CPU processing speed (Speed)
- CPU processing speed is also known as clock speed. It means the number of CPU clocks that can be executed in a cycle of 1 second or equivalent.
- The clock speed of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), but now the speed of CPUs is gigahertz (GHz), 1GHz = 10 9 Hz .
- Usually, many people judge the power of a computer by the speed of the CPU, but this metric can only be used when comparing processors in the same line (generation) with each other. The true power of the CPU depends on many other factors, please see below.
Multi-Core and Multi-Threading CPU
- The core is a processing unit of the CPU. A multi-core CPU means that it has 2 or more processing units built in, allowing the CPU to perform two or more different tasks at the same time. Newer CPUs have more and more cores (2 cores: Dual Core, 4 cores: Quad Core, 6 cores: Hexa Core,.) and therefore the performance is also higher than the old CPUs.
- Multi-Thread enables a single-core CPU or a multi-core CPU to process multiple data concurrently, reasonably supported by the operating system. The Windows operating system recognizes each thread as its own CPU, but this is only Hyper-threading technology, which helps to create a virtual core, so its performance cannot be equal to the real core of the CPU. .
CPU 4 Core 4 thread means that this CPU has 4 processing units (4 cores, 4 cores) inside and can handle 4 data streams simultaneously. CPU 4 Core 8 Thread means that this CPU has 4 cores inside and each core can process 2 data streams simultaneously, so a total of 8 data streams can be processed at the same time. Thus, it is clear that the 4 Core 8 Thread CPU has much higher processing performance than the 4 Core 4 Thread CPU.
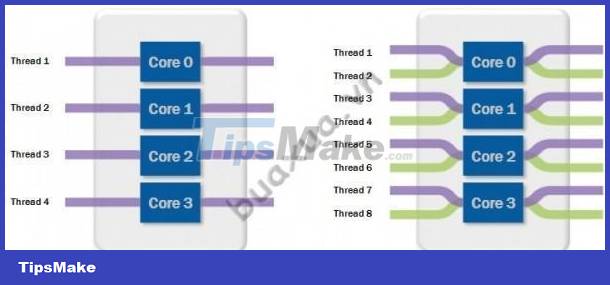 Multi-core multi-threaded CPU
Multi-core multi-threaded CPU
CPU Bus Speed
- The CPU bus speed usually refers to the speed of the Front Bus (FSB), which is the speed of the data transfer pulse between the CPU and the memory control center (Chipset) located on the main circuit board (Mainboard, MotherBoard). Bus speed is in Mhz (Megahertz).
- FSB speed significantly affects the performance of the computer.
CPU internal cache
- Cache memory located inside the CPU has a very high data access speed, so it can meet the processing speed of the CPU. The larger the cache, the more data is received and saved for processing, thereby increasing the CPU's processing speed and of course the higher the CPU's cost.
- For multi-core CPUs, the cache will be divided equally among each core.
- Old, inexpensive CPUs often have very little cache. Newer CPUs today have very large cache memory with many levels L1, L2, L3 (Level 1, Level 2, Level 3).
CPU with integrated graphics processor (GPU, Graphics Processing Unit)
- Some CPUs have a built-in graphics processing unit (GPU). The function of the GPU is to support the rendering of graphics and visual effects instead of the CPU.
- GPUs integrated into the CPU often have less performance than separate graphics devices (VGA Cards), especially in processing 3D graphics, and not all CPUs have integrated GPUs.
- If the CPU is integrated with a graphics processor, you will know more information about the name of the graphics processor chip and its clock speed.
Standard CPU pins (Socket)
- Standard CPU pins are distinguished and named according to the shape and number of CPU pins. Please keep this parameter in mind to select the main board (Mainboard) to match the CPU.
Memory Specifications
- This parameter is rarely published, it indicates what type of memory the CPU supports, what is the maximum capacity, and how many channels are the maximum.
Accessories included with the CPU
- Full CPU will include: Outer box, CPU in tray, plastic bow inside, Logo stickers, brochure, instructions, can be attached with stamps, genuine product certificates.
- Normally the fan and heatsink will be bundled with the CPU, but some CPUs are not included, you have to buy them.
- Some CPUs in the form of discrete (Tray) without box and certificate are sold at a cheaper price.
 CPU kit with fan and heatsink
CPU kit with fan and heatsink
Guarantee
- New CPUs are usually warranted for 36 months (3 years) as long as the warranty stamp is valid and there is no phenomenon of fire, damage to the pins.
Above are the main CPU parameters that are often introduced by stores when selling. Aside from this parameter, the CPU has a lot of other parameters, but it probably doesn't matter to ordinary users.
You can look up detailed information of CPU at website:
* Intel CPU: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/processors.html
* AMD CPU: http:// www.amd.com/en-us/products/processors
Choosing a CPU for a computer
Based on the above parameters, you can know which CPU has higher speed and performance, so you can choose the right CPU for your needs.
Selecting the right CPU for the operating system
- Windows XP only requires a CPU speed of 300MHz or higher. Newer versions of Windows like 7, 8 10 require a CPU clocked at 1GHz or higher.
- If you choose an old CPU, pay attention to the speeds above. As for the new CPUs today, they are all well-suited to operating systems, including the lowest-speed and cheapest CPUs like Intel Celeron or AMD A4.
CPUs from the 7th generation of Intel (Kaby Lake) and AMD (Zen) are only compatible with the Windows 10 operating system.
Selecting the right CPU for application programs
- Ordinary office application programs such as MS Office or Internet access also do not require a CPU with a higher speed than that required by the operating system.
- Common image processing applications Photoshop CC and movie editing Premiere Pro CC require a minimum of an Intel Core 2 or AMD Athlon 64 CPU clocked at 2GHz or higher.
- Watching standard VCD, DVD, SD and HD movies normally you need a CPU with a speed of about 1.5Ghz (Dual core, 2 cores) or 2.6Ghz (single core, 1 core).
- Watching Full HD movies (1080p) you need a CPU with a speed of at least 2.4Ghz (dual core, 2 cores) or 3.5Ghz (single Core, 1 core).
- To watch 4K movies you need a 4th generation CPU from Intel or AMD equivalent.
Choosing the right CPU for games
- Normal games will announce the system requirements needed to play this game, please pay attention to these parameters to select the appropriate CPU.
For applications, games with high graphics effects, 3D, . the manufacturer will tell you which types of graphics devices (Video cards) will meet this game. After choosing the appropriate graphics device, look at its parameters to see what type of CPU is compatible with the graphics device. Compare the CPU requirements of the application and the graphics device and you will know which CPU is right for your needs.
Choosing the right CPU for the cost
- If the cost is low, choose a CPU that meets the minimum requirements of applications, games, .
- If cost is not an issue, then choose a CPU that meets the recommended requirements (Recommended requirements) or the maximum (Maximum requirements) of applications and games.
- You can choose from the latest generation of CPUs, which often have the latest technology, the highest speeds available today, and will continue to meet your needs into the future. close (just close, because the speed of development. too dizzy).
You need to note the comparison between the performance and cost of the CPUs together, this is usually the CPU selection criteria of people in the profession.
Select the CPU to synchronize with other components of the computer
- If you already have the mainboard (Mainboard), please note that the CPU must be compatible with the socket (Slot, Socket) on the mainboard.
- You should not use a CPU with a very low speed while using a high-end graphics device or vice versa. Instead, you should consider balancing the performance of the components together to avoid the case that your computer can't reach its full speed due to the "bottleneck" phenomenon.
CPU and Mainboard must be compatible with each other, the documentation that comes with the Mainboard will indicate which CPUs it supports. Please see the tutorial on how to choose the main board - Mainboard for computers
Performance comparison table between CPU types
You can use the performance comparison parameters between different CPUs to choose a CPU that balances speed and cost.
- Low End CPUs: https://www.cpubenchmark.net/low_end_cpus.html
- Low Mid Range CPUs: https://www.cpubenchmark.net/midlow_range_cpus.html
- High Mid Range CPUs: https://www.cpubenchmark.net/mid_range_cpus.html
- High End CPUs: https://www.cpubenchmark.net/high_end_cpus.html
CPU parameters are evaluated based on the following tests
Basic checks:
- CPU tests Mathematical operations, compression, encryption, SSE, 3DNow! instructions and more
- 2D graphics tests Drawing lines, bitmaps, fonts, text, and GUI elements
- 3D graphics tests Simple to complex DirectX 3D graphics and animations
- Disk tests Reading, writing and seeking within disk files
- Memory tests Allocating and accessing memory speed and efficiency
Extensive configuration tests:
- Advanced Disk
- Advanced CD / DVD
- Advanced 3D graphics
- Advanced Networking (for Ethernet, Internet and Wireless)
- Advanced Memory
- Advanced Visualized Physics
- Advanced DirectCompute
You should read it
- The 12th and 13th generation Core CPUs were so good that AMD almost lost the PC market to Intel
- Intel brought its strongest chip, a Core i9 processor, to a laptop
- What is Intel's new Core i9 CPU line?
- Intel updates the CPU price list for PCs with X 12 series of chips
- Is Core i5 laptop price Core i3 worth buying?
- Information about the new generation Intel Core i3 / i5 / i7 mobile processors
 Choosing memory for your computer
Choosing memory for your computer Choosing a case and a power supply for a computer
Choosing a case and a power supply for a computer How to assemble an optical drive for a computer
How to assemble an optical drive for a computer How to assemble a hard drive for a computer
How to assemble a hard drive for a computer How to assemble the Mainboard into the computer case
How to assemble the Mainboard into the computer case How to assemble memory into the mainboard of a computer
How to assemble memory into the mainboard of a computer