Break and continue commands in Python
In Python , the break and continue statements can change the "flow" of a normal loop.
These loops repeat a code block until the condition checks False, but sometimes we want to terminate the current loop or even the entire loop without checking the conditional expression. That's when we need the help of break and continue commands.
Break command in Python
The break statement ends the loop containing it and passes the control to the next command after that loop's code block. If the break statement is in a nested loop (loop inside another loop), break will terminate the innermost loop.
Syntax of break order:
break Break order diagram:
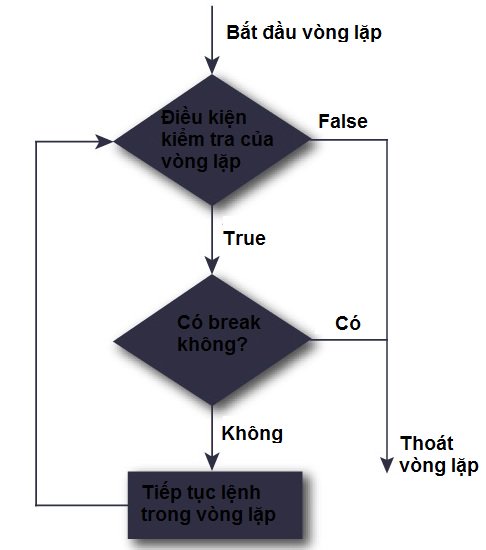
If using break in the for Python loop, it will look like this:
for var in sequence:
#khối code bên trong vòng lặp for
if dieu_kien:
break
#code khác bên trong vòng lặp for
#code bên ngoài vòng lặp for
When break is executed, "#code inside the for loop" will be ignored and redirected to "#code outside the for loop".
If you use the break in the while loop, Python will look like this:
while dieu_kien_kiem_tra:
#code bên trong vòng lặp while
if dieu_kien:
break
#code khác bên trong vòng lặp while
#code bên ngoài vòng lặp while
When break is executed, "#code inside while loop" will be ignored and redirected to "#code outside the while loop".
Example of a break Python command
Example 1:
#Sử dụng break trong for
for val in "string":
if val == "i":
break
print(val)
print("Kết thúc!")
In the above code, we loop the string "string", and check the condition, if the letter "i" will execute the break command, if another letter "i" prints to the screen. Running the above code we get the result that the previous letters "i" have been printed. Then the loop ends, as shown below:
str Kết thúc! Example 2:
bien = 10 while bien > 0 : print ( 'Giá trị biến hiện tại là: ' , bien) bien = bien - 1 if bien == 5 : break print ( "OK!") The above code checks and prints the variable in descending value from 10, until the variable is equal to 5, the loop ends.
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 10
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 9
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 8
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 7
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 6
OK!
The continue command in Python
The continue command is used to ignore the rest of the code inside the loop, applied to the current iteration. That means the loop does not terminate, it will continue with the next iteration.
Structure of continue:
continue Diagram of the continue command in Python:

The continue statement in the for loop will look like this:
for var in sequence:
#khối code bên trong vòng lặp for
if dieu_kien:
continue
#code khác bên trong vòng lặp for
#code bên ngoài vòng lặp for
When the continue is executed, "#code inside the for loop" is ignored and returned to "# Block of code inside for for loop"
The continue statement in the while loop will look like this:
while dieu_kien_kiem_tra:
#code bên trong vòng lặp while
if dieu_kien:
tiếp tục
#code khác bên trong vòng lặp while
#code bên ngoài vòng lặp while
When the continue executing " #code khác bên trong vòng lặp while" will be ignored and returned to " #code bên trong vòng lặp while"
For example, the continnue command in Python
Example 3:
# Sử dụng continue trong for
for val in "string":
if val == "i":
continue
print(val)
print("Kết thúc!")
This code is identical to the above, only replace the break command with continue. Here, when looping the string "string" to the letter "i" will ignore the print variable print (val) and return to the command if val == "i" :, we get the result:
strng Kết thúc! Example 4:
bien = 10
while bien > 0 :
bien = bien - 1
if bien == 5 :
continue
print ( 'Giá trị biến hiện tại là: ' , bien)
print ( "OK!")
If bien = 5 then skip and repeat the next iteration, resulting in:
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 9
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 8
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 7
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 6
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 4
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 3
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 2
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 1
Giá trị biến hiện tại là: 0
OK!
In the next section we will learn about pass commands and iterative techniques in Python, so you can watch!
Exercises: More than 100 Python exercises have solutions (sample code)
Next article: Pass command in python
Previous article: while loop in Python