If, if ... else, if ... elif ... else commands in Python
In the previous section we learned about some Python data types and how to use it, and also know a bit about While in Python commands. In this section, you will learn more about the most common command in Python if.
If you have learned other programming languages, you already know the use of this command, but in Python programming language it has some interesting features. Let's find out.
Decision making is necessary when we want to execute a code only when it satisfies certain conditions. The if . elif . else command is used in Python to serve this purpose. Here we will learn about if statements in Python , each item has an example and a specific explanation for you to understand.
Main content:
- If command structure in Python
- If . else statement
- If . elif . else command in Python
- The if statement is nested in Python
If command structure in Python
if điều kiện
khối lệnh
Here, the program evaluates the condition and will execute the command when the condition is True. If the condition False, the command will not be executed.
In Python, the command block of the if statement is indented inside. If's block starts with an indent interval and the first indented line will be interpreted as an if statement end.
If command diagram in Python

Example 1:
# Nếu là số dương ta sẽ in một thông điệp thích hợp num = 3
if num > 0 :
print ( num , "là số dương." )
print ( "Thông điệp này luôn được in." )
num = - 1
if num > 0 :
print ( num , "là số dương." )
print ( "Thông điệp này cũng luôn được in." )
Output of the program above:
3 l à s ố d ươ ng .
Th ô ng đ i ệ pn à y lu ô n đượ c in .
Th ô ng đ i ệ pn à yc ũ ng lu ô n đượ c in .
In the above example, num> 0 is a condition, if's block is executed when the condition is satisfied. When num equals 3, check the condition, true, if the block of if is executed. When num equals -1, does not satisfy the condition, if's block is ignored and the last print () is executed.
A bit more careful, you will see that the print () statement is not indented, which indicates that print () is outside the if block, so it will be executed, regardless of the condition.
If . else statement
If . else command structure
if điều kiện:
Khối lệnh của if
else:
Khối lệnh của else
If . else command checks the condition and executes if if the condition is true. If the condition is false, the else block of the statement will be executed. Indentation is used to separate command blocks.
If . else command diagram
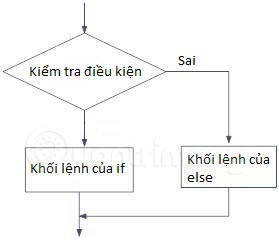
Example 2:
# Kiem tra xem so am hay duong
# Va hien thi thong bao phu hop
num = 3
if num >= 0:
print("So duong hoac bang 0")
else:
print("So am")
num1=-1
if num1 >= 0:
print("So duong hoac bang 0")
else:
print("So am")
In Listing 2, we examine two variables, num and num1. When num equals 3, satisfies condition num> = 0, if's block is executed. num1 = -1 does not satisfy condition num1> = 0 so else's block is executed and ignores if's block.
The result of the above command will print the two line screen: the above line is the result of checking the variable num and the lower line is the variable num1.
So duong hoac bang 0
So am
If . elif . else command in Python
Structure of if . elif . else command
if điều kiện:
Khối lệnh của if
elif test expression:
Khối lệnh của elif
else:
Khối lệnh của else
elif is else if abbreviation, it allows us to check many conditions.
If the condition is false, it will check the condition of the next elif block and so on.
If all conditions are wrong, it will execute else's block.
Only one block in if . elif . else is executed according to the condition.
There may be no or more elif, the else part is optional.
Diagram of if . elif . else command

Example 3:
x = int(input("Nhap mot so: "))
if x < 0:
x = 0
print('So am')
elif x == 0:
print('So 0')
elif x == 1:
print('So 1')
else:
print('So duong') Output result:

If x is a negative number, print the screen: "So am".
If x = 0, it will print: "So 0".
If x = 1, it will print: "So 1".
If all three conditions are wrong, print: "So duong".
The if . elif . elif . command replaces the switch or case statement in other programming languages.
The if statement is nested in Python
You can write the if . elif . else statement in an if . elif . else block, and make the if statement nested. There is no limit to the number of commands that are inserted into another command. Indentation is the only way to identify cage levels, so it can be confusing and confusing. You should limit use if possible.
Example 4:
# Trong code này, nhập vào một số
# Kiểm tra xem số âm hay dương
# hay bằng không và hiển thị
# thông báo thích hợp
# Sử dụng hàm if lồng nhau
num = float(input("Nhập một số: "))
if num >= 0:
if num == 0:
print("Số Không")
else:
print("Số dương")
else:
print("Số âm")
Result 1:
Nhập một số: 10
Số dương
Result 2:
Nhập một số: -5
Số âm
Result 3:
Nhập một số: 0
Số Không
Now that you know the basic elements when using the if statement in Python. The next section we will learn about for for loop. Have you remembered to it.
Next article: For in Python loop
Previous lesson: Introducing about strings, numbers, and lists in Python