7 Windows Recovery Options to Make System Recovery Easy
While Windows computers are more reliable than ever, you should still make sure you have your built-in recovery options enabled and understood. Then you'll be prepared if your PC fails to boot due to corrupted system files, malware, or hardware failure. Here's an overview of what they offer, from least to most.
1. Restore from a system restore point
System Restore is a Windows restore feature that allows you to restore your computer to a previous point in time. Whether you made a critical change that caused your system to malfunction or a bad Windows update left your computer unusable, System Restore can undo the changes and get your system back online.
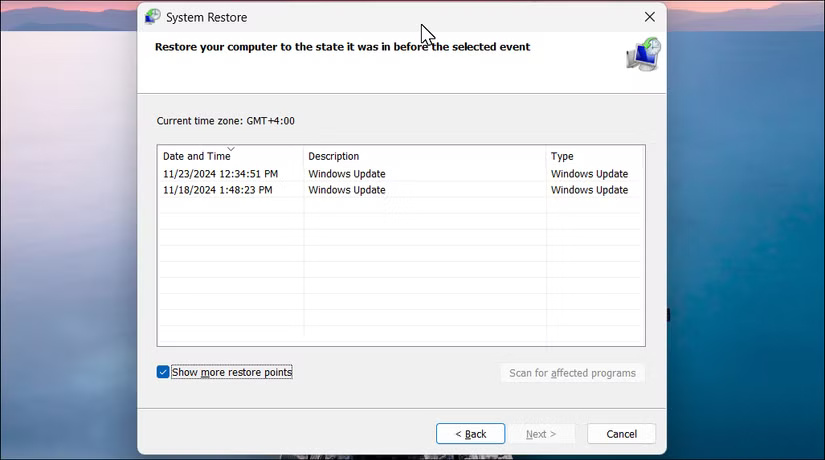
To use restore points, you must first enable system protection for your installation drive. When enabled, Windows automatically creates restore points when you install new applications, drivers, or Windows updates. You can also create restore points manually or configure your system to create restore points daily.
If you haven't configured system protection, follow the instructions to set it up and create a restore point on Windows.
2. Use the Startup Repair function
Startup Repair is a Windows recovery feature that can scan for and fix known problems that prevent your computer from starting. These problems include missing or corrupted system files, incorrect boot sectors or Master Boot Record, driver and application conflicts, and malware infections.
To use Startup Repair, first boot into the Windows Recovery Environment. Once you're in the Windows Recovery Environment, navigate to Advanced options . Then, go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup repair > Restart . Windows will restart and attempt to automatically repair your computer.

3. Go back to the previous version of Windows
If your computer isn't working properly after a recent update, you can use the Go Back option to revert to a previous build of Windows. This is a handy feature for early adopters who install the latest Windows updates as they become available, which can sometimes cause problems.

By default, the Go Back option is available for 10 days after installing an update. However, if you frequently need to roll back updates, you can extend the Windows restore period to 60 days using a simple registry tweak.
4. Fix Problems Using Windows Update
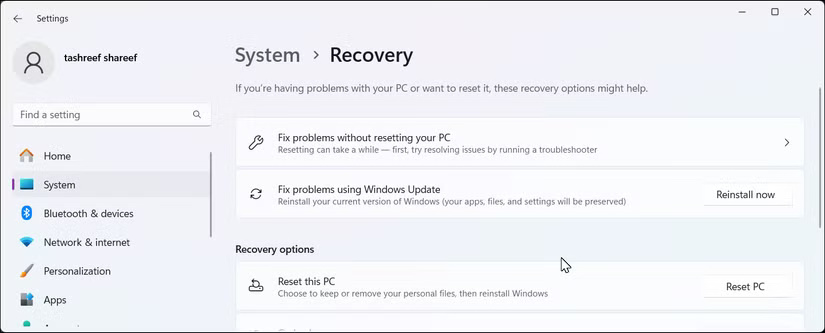
Fix Problems Using Windows Update is the latest recovery option for Windows and the easiest way to reinstall Windows 11. This option lets you fix system component corruption by reinstalling your current version of Windows — while keeping your apps, documents, and settings intact.
To access this tool, go to Settings > System > Recovery . Here, look for Fix Problems Using Windows Update and click Reinstall now . Read the description to make sure you understand what will happen, then click OK to start the process. Once the reinstallation is complete, restart your computer to complete the repair process.
5. Reset PC
An easy way to reset your Windows computer to its factory settings is to use the Reset this PC option in the Settings app. As the name suggests, this option will reinstall Windows to restore your computer to its factory settings, removing any apps that didn't come with the system. However, you have the option to keep your personal files and settings in the process.
But when is a reset appropriate? You might use a reset if your computer isn't working properly, to troubleshoot performance issues, or if you just want to start over without reinstalling. Since this is the most invasive option, you shouldn't use it unless the above options don't fix the problem.
6. Create a PC recovery drive
The above options cover most problems, but if Windows has a serious problem, you obviously won't be able to access it from within the operating system. This is where a recovery drive comes in handy. This is a backup option that includes a copy of your Windows environment, including the troubleshooting tools and system files needed to reinstall Windows if necessary.
From there, you can choose the advanced repair options we discussed earlier, such as Startup Repair, rolling back to a previous build, and performing a system restore. If all else fails, you can perform a reset to reinstall Windows.
7. Use the media to reinstall Windows 11
If all other recovery methods fail, you can reinstall Windows using USB installation media. A clean installation will erase all of your data from the installation drive, including your apps, settings, and personal files.
To clean install Windows 11, you need a bootable USB. You can then boot from the newly created installation media and continue with the installation.
While Windows offers many solutions for recovering from crashes, malware attacks, and hardware failures, it's important to properly back up your PC to protect your data. These backup strategies include creating full system image backups and cloning your hard drive on Windows, which you can restore even after catastrophic hardware failure.
You should read it
- ★ This is how to delete Recovery partition and Recovery partition 450 MB on Windows 10
- ★ 3 ways to hide recovery partition (Recovery) on Windows 10 / 8.1 / 7
- ★ How to create a Windows 10 recovery USB when it fails?
- ★ Windows File Recovery: Microsoft's free data recovery application
- ★ How to create a Windows 10 recovery USB when it fails