The supernova exploded twice in the universe, surprising astronomers
Newly discovered astronomers in the universe once had a supernova exploded twice, leaving certain extremes that astounded astronomers.
According to them, this mysterious supernova is actually a type of supernova named superluminous .
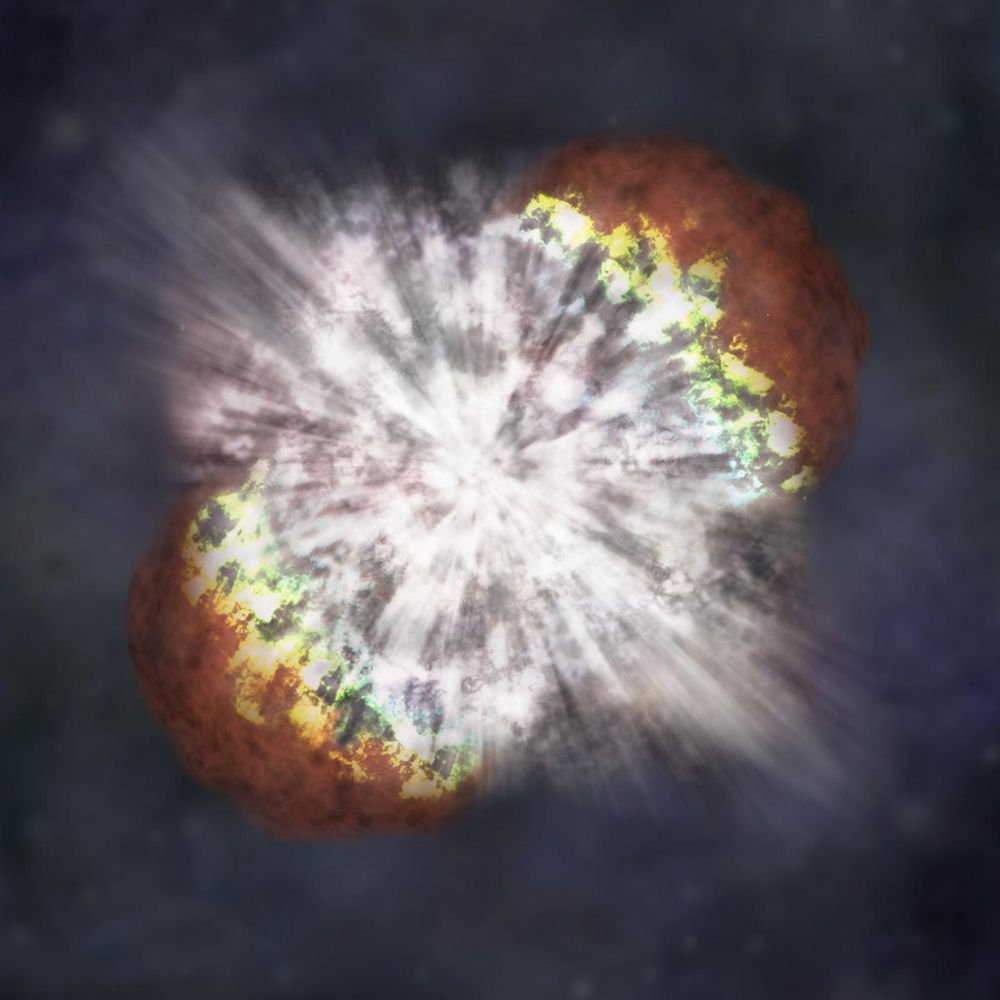

Photo source: Space.
Scientists say that the chance of supernova exploding twice accounts for an extremely low ratio of 1/1000 in the universe. Even these strange supernova explosions glow 100 times more than other supernovae explode.
" We are not yet able to determine the main cause of superluminous explosion twice so oddly," said Matthew Smith, an Southampton astronomer at the UK .
According to the study, every time a superluminous meteor explodes will last for several days, emitting a powerful magnet magnetism, releasing energy, the plasma magnetic field burns the materials around it. Causing a series of stars in the galaxy around that area is obscured by dust and smoke.
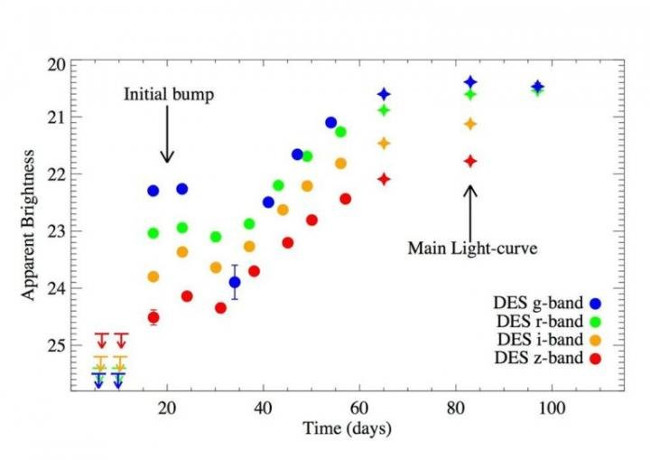
Photo source: Space.
You should read it
- ★ The mysterious flaw developing in supernova Tycho is astonishing to the scientific world
- ★ The world's most expensive telescope captures stunning views of the famous supernova remnant
- ★ Fastest star in the Milky Way, speed 8,226,967 km/h
- ★ The largest-ever explosion in the universe created a giant hot-air sphere that could hold 15 Milky Way galaxies
- ★ 14 interesting facts about the universe amaze you